Jungfrau railway
| Jungfrau railway | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overview | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Locale | Bern/Valais, Switzerland | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line length | 9.3 km (5.8 mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Track gauge | 1 Metre (3 ft 3 3⁄8 in) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum radius | 100 m | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrification | 3-phase, 1,125 V, 50 Hz | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Highest elevation | 3,454 m (11,332 ft) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maximum incline | 25 % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rack system | Strub | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
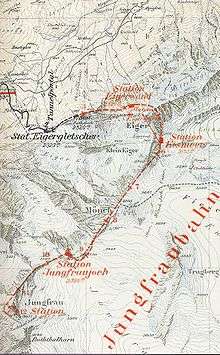
The Jungfrau railway (German: Jungfraubahn, JB) is a metre gauge (3 ft 3 3⁄8 in gauge) rack railway which runs 9 kilometres (5.6 mi) from Kleine Scheidegg to the highest railway station in Europe at Jungfraujoch (3,454 m), between the Bernese Oberland and Valais in Switzerland. The railway runs almost entirely within the Jungfrau Tunnel, built into the Eiger and Mönch mountains and containing two stations in the middle of the tunnel, where passengers can disembark to observe the neighbouring mountains through windows built into the mountainside. The initial open-air section culminates at Eigergletscher (2,320 m), which makes it the second highest open-air railway in Switzerland.[1] The line is electrified at 3-phase 1,125 volts 50 Hertz, and is one of four lines in the world using three-phase electric power.
At Kleine Scheidegg the JB connects with the Wengernalpbahn (WAB), which has two routes down the mountain, running respectively to the villages of Lauterbrunnen and Grindelwald. From both villages, branches of the Berner Oberland Bahn (BOB) connect to the Swiss Federal Railways at Interlaken.[2]
The line is owned by the Jungfraubahn Holding AG, a holding company that also owns the Wengernalpbahn and Lauterbrunnen–Mürren mountain railway railways. Through that holding company it is part of the Allianz - Jungfrau Top of Europe marketing alliance, which also includes the separately owned Berner Oberland Bahn and Schynige Platte railways.[3][4]
History
- 1860 (approximately) - there were many different plans for a mountain railway on the Jungfrau, which failed due to financial problems.
- 1894 the industrialist Adolf Guyer-Zeller received a concession for a rack railway, which began from the Kleine Scheidegg railway station of the Wengernalpbahn (WAB), with a long tunnel through the Eiger and Mönch up to the summit of the Jungfrau.
.jpg)

- 1896 construction began. The construction work proceeded briskly.
- 1898 the Jungfraubahn opened as far as the Eigergletscher railway station, at the foot of the Eiger.
- 1899 Six workers are killed in an explosion. There is a four-month strike by workers. Adolf Guyer-Zeller dies in Zürich on 3 April. The section from Eigergletscher station to Rotstock station opens on 2 August
- 1903 The section from Rotstock station to Eigerwand station opens on 28 June.
- 1905 The section from Eigerwand station to Eismeer station opens on 25 July
- 1908 There is an explosion at Eigerwand station.
- 1912 21 February, sixteen years after work commenced, the tunneling crew finally breaks through the glacier in Jungfraujoch. Jungfraujoch station was inaugurated on 1 August.
- 1924 The "The house above the clouds" at Jungfraujoch is opened on 14 September.
- 1931 The research station at the Jungfraujoch is opened.
- 1937 The Sphinx Observatory is opened. A snowblower is purchased and this results in year-round operation.
- 1942 Relocation of the company offices from Zürich to Interlaken.
- 1950 The dome is installed on the Sphinx Observatory.
- 1951 The adhesion section between Eismeer station and Jungfraujoch station is converted to rack operation.
- 1955 A second depot at Kleine Scheidegg is constructed. The post office inaugurates its relay station on the Jungfraujoch.
- 1972 The panoramic windows are installed at Eigerwand and Eismeer. The Jungfraujoch mountain house and tourist house are destroyed by fire on 21 October.
- 1975 A new tourist house is opened.
- 1987 A new mountain house is opened on 1 August.
- 1991 A new station hall is opened at the Jungfraujoch.
- 1993 The small Kleine Scheidegg depot is extended.
- 1996 The covered observation deck at the Sphinx Observatory is opened.
- 1997 For the first time the annual visitor numbers exceed 500,000.
- 2000 On 1 June a daily record number of 8,148 visitors is achieved.
Stations
- Kleine Scheidegg, 2,061 m (6,762 ft)
- Eigergletscher, 2,320 m (7,612 ft)
- Eigerwand, 2,864 m (9,396 ft)
- Eismeer, 3,158 m (10,361 ft)
- Jungfraujoch, 3,454 m (11,332 ft)
2008 proposals
In early 2008, Jungfraubahn Holding AG announced it is exploring the futuristic idea of an efficient fast form of access to the Jungfraujoch as an addition to the rack railway. A feasibility study has been commissioned. The additional access would be the world's longest tunnel-lift system. The study is to show if and how such a tunnel-lift system - for example as a fast lift or funicular - from the Lauterbrunnen Valley to the Jungfraujoch could be realised without disturbing the unique landscape of the UNESCO World Heritage site.
The attractiveness of the cogwheel railway should thus be enhanced, as guests could use the fast lift for the uphill or downhill journey. Through a marked reduction in travelling time, the trip to the Jungfraujoch could also become a half-day excursion.
Rolling stock
Since most of the railway is inside a tunnel, it was designed to run with electricity from conception. The latest rolling stock consists of twin-unit motorcoaches carrying up to 230 people per train which operate at 12.5 km/h on the steepest parts of the ascent. The motors function at two speeds which allows the units to operate at double this speed on the less steep part of the ascent (above Eismeer station).
The motors will operate in a regenerative mode which allows the trains to generate electricity during the descent, which is fed back into the power distribution system. Approximately 50% of the energy required for an ascent is recovered during the descent. It is this generation that regulates the descent speed.
Snow clearing equipment is essential on the open section of line between Kleine Scheidegg railway station and Eigergletscher railway station. Originally snow ploughs were used but more recently snow blowing equipment has been brought into service.
The railway also operates some dedicated freight vehicles to supply the visitor facilities at Jungfraujoch, including a tank to transport additional water.
Main characteristics
| Altitude of top station above Sea Level | 3454 m |
|---|---|
| Difference in height | 1393 m |
| Operational length | 9.3 km |
| Gauge | 1,000 mm (3 ft 3 3⁄8 in) |
| Rack rail type | Strub |
| Operational Speed | 12.5 km/h (25 km/h on shallower gradients such as above Eismeer) |
| Steepest gradient | 25% |
| Smallest curve radius | 100 m |
| Tunnels | 3: longest 7122 m, shortest 110 m. 80% of length of the entire railway. |
| Power system | 3-phase 50 Hz 1125Volt |
Gallery
 Train between Kleine Scheidegg and Eigergletscher
Train between Kleine Scheidegg and Eigergletscher The Schreckhorn dominates the view from the window at the Eismeer station. One of two stations in the tunnel on the way to the Jungfraujoch
The Schreckhorn dominates the view from the window at the Eismeer station. One of two stations in the tunnel on the way to the Jungfraujoch- A snowblower at Kleine Scheidegg railway station
 The Jungfraubahn runs using a 1125 Volt, 3-phase alternating current system which requires the trains to collect power from twin overhead wires, using two pantographs, as seen here (the third phase is earthed to the track).
The Jungfraubahn runs using a 1125 Volt, 3-phase alternating current system which requires the trains to collect power from twin overhead wires, using two pantographs, as seen here (the third phase is earthed to the track). The strub rack system underneath a railcar (Rowan locomotive He 2/2 no. 6)
The strub rack system underneath a railcar (Rowan locomotive He 2/2 no. 6) A cogwheel from a Jungfrau Railway railcar strub rack system
A cogwheel from a Jungfrau Railway railcar strub rack system
See also
References
- ↑ After the Gornergrat railway (3,090 m)
- ↑ Eisenbahnatlas Schweiz. Verlag Schweers + Wall GmbH. 2012. p. 82. ISBN 978-3-89494-130-7.
- ↑ "Jungfrau Railway Holding AG". Jungfraubahn. Retrieved 2013-02-12.
- ↑ "Jungfraubahn Holding AG + Berner Oberland-Bahnen AG". Jungfraubahn. Retrieved 2013-02-12.
- ↑ Between Heaven and Earth. History and technology - science and research on the Jungfraujoch - Top of Europe, Jungfraubahnen.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Jungfraubahn. |
- Jungfrau Railways website (English)
- Video of a day trip to Jungfraubahn
- "Alpine Climbing by Railroad" Popular Mechanics, December 1911, pp. 830–831.
