Kairine
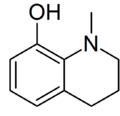 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| 5080-60-4 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 15544231 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H13NO | |
| Molar mass | 163.22 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Kairine is a derivative of tetrahydroquinoline which was first described by Wilhelm Fischer in 1883. Its name comes from the Greek kairos, meaning "the right time".[1] It is an antipyretic, formerly used against typhoid fever, but now largely obsolete due to severe side effects. Both kairine and its N-ethyl homolog show similar antipyretic activity.[2][3][4][5]
See also
References
- ↑ W.E.Flood (1963). The Origins of Chemical Names. Oldbourne Book Co Ltd. p. 126.
- ↑ Fischer, Wilhelm (1883). "On Kairine and Kairoline". New Remedies. 12 (2): 41.
- ↑ Fruitnight, J. Henry (1886). "Kairine and Antipyrine". Medical Record. 29 (23): 646–648.
- ↑ Bockmuhl M, Dorzbach E. Antipyretics of the tetrahydroquinoline series. Med. u. Chem. (1942) 4: 179-212.
- ↑ Slater, Leo Barney (2009). War and Disease: Biomedical Research on Malaria in the Twentieth Century. Rutgers University Press. p. 26. ISBN 978-0-8135-4438-0.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/18/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.