Katalla, Alaska
| Katalla | |
|---|---|
| Ghost town | |
|
The steamers Altona and Thlinket unloading rail supplies in Katalla, 1907. | |
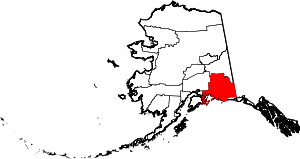
 Katalla Location within the state of Alaska | |
| Coordinates: 60°11′42″N 144°31′16″W / 60.19500°N 144.52111°WCoordinates: 60°11′42″N 144°31′16″W / 60.19500°N 144.52111°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Alaska |
| Census area | Valdez-Cordova |
| Government | |
| • State senator | Gary Stevens (R) |
| • State rep. | Louise Stutes (R) |
| Time zone | Alaska (AKST) (UTC-9) |
| • Summer (DST) | AKDT (UTC-8) |
Katalla (pronounced KA-tell-ah) is a ghost town in the Valdez-Cordova Census Area in the U.S. state of Alaska, 76 km (47 mi) southeast of Cordova. The name of this town was sometimes spelled Catalla. It is now abandoned.
Geography
Katalla is located within the Chugach National Forest near Controller Bay and the Bering River at.[1]
History

Katalla was at the center of the now-abandoned Katalla oil field. This was the first discovery of commercial quantities of oil in Alaska (1902). The town reportedly had a population of 5,000 in 1907-1908.
This was the result of the announcement that the Copper River and Northwestern Railway (CR&NW) was going to use the town's location as its access to the Pacific Ocean and the Bering River coal fields. Violent storms in the fall of 1907 destroyed the jetty being built and it was decided to move the railroad's terminus to nearby Cordova.[4]
The famous "ship of gold" SS Portland, ran aground and sank at Katalla in November 1910, during one of these autumn storms. The town's population continued to depend on the small oil field for income until December 25, 1933 when fire damaged its refinery and operations ceased. The town's post office closed in 1943 and the town site was abandoned.
The oil and gas extraction rights for the Katalla area were granted to the Chugach Alaska Corporation by the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act. Before that, however, at least some of the rights to the field were owned by the California-Mexican-Alaska Holding Company, which dissolved and sold its assets to the Alaska Coal, Oil & By-Products Company in 1929.[5]
A Korean coal mining consortium resurrected potential interest in Katalla after they did coal exploration in the Bering River coal fields in the early 1980s. Interest waned as the coal reserves did not appear economically viable, and a haul route to Katalla would by necessity have to cross areas subject to slope instability and periodical glacial dam outbursts from Bering Lake.
References
- ↑ "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. 2011-02-12. Retrieved 2011-04-23.
- ↑ Harrison, Edward Sanford, ed. (May 1911). "TOM WHITE, Discoverer of the Katalla Oil Fields (photo with caption)". Alaska-Yukon Magazine. XI (4): 19.
- ↑ Brown, Tricia. "Katalla: Alaska's First Oil Well". LitSite Alaska. University of Alaska Anchorage. Retrieved September 10, 2016.
- ↑ Elizabeth A. Tower (1990). Ghosts of Kennecott, The Story of Stephen Birch. p. 42.
- ↑ University of Alaska Anchorage Consortium Library, Archives and Special Collections. "California-Mexican-Alaska Holding Company letter to stockholders". consortiumlibrary.org. Retrieved 2016-05-10.
Further reading
- Jessup, David Eric. "The Rise and Fall of Katalla: 'The Coming Metropolis of Alaska'," Alaska History, Vol. 20, No. 1, Spring 2005.