Knuckle thread
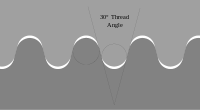
Knuckle threads are an unusual highly rounded thread form. The large space between the rounded crests and roots provides space for debris to be shifted to not interfere with the thread, making this form resistant to debris and thread damage.[1]
Standards
Knuckle threads with a flat 30 degree flank thread angle are standardized in DIN 405 for inch pitches and diameters ranging from 8mm to 200mm.[2] A more recent standard DIN 20400 uses metric thread pitch and lists diameters from 10mm to 300mm.[3] As DIN is a German organization, many instances of the DIN thread charts[4] write numbers with a comma as the decimal point. For a thread pitch p, the crest and root rounding radius is slightly less than p/4, and approximately the middle third of each thread flank is flat.
The American Petroleum Institute (API) specification 5B[5] lists a "round thread" for tubing, often referred to as "8 round" or "8rd" for 8 threads per inch. The only other pitch listed is 10 threads per inch. The thread angle at the flank is 60 degrees, and the crest and root rounding radius is approximately p/6 for threads of pitch p. Both the thread angle and rounding radius are more like ordinary ISO threads than DIN. For 0.125 inch thread pitch (8 threads per inch), the API round thread root radius is 0.017 inch, and the crest radius is 0.020 inch. API threads taper at 3/4 inch of diameter per foot of length.
Many knuckle threads follow neither the DIN nor API standards, and are custom designed and fabricated for the particular application.
Applications
This thread form's good debris tolerance is the source of its use in oilfields, where it provides a leak-free connection in field use. Many European automobiles use a knuckle thread for their "tow eye," an external threaded recess where a steel towing lug can be fitted. For example, some Porsche cars use DIN 405 Rd 20 x 1/8", and some BMW use a thread similar to DIN 405 Rd 16 x 1/8".

Other applications use a knuckle thread's rounded edges to reduce the stress on softer materials at a point of connection. Some linear actuators use a knuckle thread to reduce the wear of the steel leadscrew against a plastic sliding nut. Firefighting respirator standard EN 148-1 "Respiratory protective devices - Threads for facepieces" lists a knuckle thread to connect metal and rubber parts.
The rounded crest and root of knuckle threads resembles the Edison screw used on light bulbs, although bulbs have a much shallower thread angle than most knuckle threads. The root profile of knuckle threads resembles a ball screw thread, although the flank and crest of ball screw threads is often truncated.
References
- ↑ Bornemann Gewindetechnik GmbH. "Knuckle threads". Retrieved 2014-01-13.
- ↑ Prandl, Michael. "Knuckle Thread DIN 405". Retrieved 2014-01-13.
- ↑ Prandl, Michael. "Knuckle Thread DIN 20400". Retrieved 2014-01-13.
- ↑ Maryland Metrics Corporation. "Thread Data Charts". Retrieved 2014-01-13.
- ↑ American Petroleum Institute. "API Specifications". Retrieved 2014-01-13.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Knuckle threads. |