Lituanica SAT-2
| Operator | Vilnius University, NanoAvionics |
|---|---|
| Website |
n-avionics |
| Mission duration | 3-15 months (planned) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | Q3 2016 (planned) |
| Rocket | Dnepr |
| Launch site | Yasny Cosmodrome |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Low Earth |
LituanicaSAT-2 is the second 3U Lithuanian satellite to be launched on a Dnepr rocket with a satellite number LT01 on the QB50-DS flight.[1] This mission is led by Vilnius University in cooperation with NanoAvionics and is a part of the international "QB50" mission. LituanicaSAT-2 is an in-orbit technology demonstration mission during which the propulsion system prototype for small satellites will be tested. The satellite will be deployed in sun- synchronous orbit at an altitude of 475 km.[2]
"QB50" mission
LituanicaSAT-2 is a part of a network of 50 nano-satellites called “QB50” (EU 7FP project) led by Von Karman Institute, Belgium.[3] The science objective of the mission is to carry out long term measurements of key parameters and constituents in yet largely unexplored lower thermosphere and ionosphere.[1] The "QB50" mission is intended to demonstrate the possibility of launching a network of 50 CubeSats built by Universities Teams all over the world as a primary payload on a low-cost launch vehicle to perform first-class science.[4] Another purposes of the QB50 project is to achieve a sustained and affordable access to space for small scale research space missions and planetary exploration.[4]
The scientific purpose of LituanicaSAT-2 mission as a part of "QB50" is to provide long-term multipoint, in-situ measurements. The contribution of the LituanicaSAT-2 is to accomplish the molecular Oxygen measurements Flux-Φ-Probe Experiment (FIPEX).[2]
LituanicaSAT-2 mission objectives
- In-orbit demonstration of propulsion system prototype developed by NanoAvionics according to contract with Vilnius University.[1] The experiment is to demonstrate the orbital maneuvering and drag compensation capabilities of a 3U CubeSat using an integral green monopropellant micro-thruster. The idea behind this experiment is to increase TRL of small satellite micro propulsion which will be developed as commercial product.[3]
- Test of the data uplink and downlink capability between CubeSats and remotely piloted aircraft systems (RPAS). The purpose of the experiment is to determine technical challenges associated with RPAS and CubeSat radio communication and prove the feasibility of such networks.[3]
LituanicaSAT-2 technical overview

LituanicaSAT-2 is consisting of three main modules: a science unit with the FIPEX (Flux-Φ-Probe Experiment) sensor for "QB50", a functional unit with NanoAvionics Command and Service module plus power unit and an experimental unit with the “green” propulsion system.[1]
LituanicaSAT-2 is commanded by NanoAvionics SatBus 3C1 which is a main system bus unit based on high-performance, low power consumption STM ARM Cortex 32 bit architecture that integrates 3 in 1 functionality on a single board.[2]
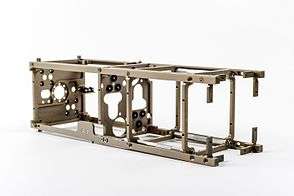
The propulsion sub-system is designed to provide 0.3N thrust and up to 200 m/s of delta V. The fuel used is a contemporary green monopropellant fuel blend based on ADN. It gives 252s of Isp, has a density of 1.24 g/cm3 with a chamber temperature of 1600 °C. Key fuel selection factors were non-toxicity, stability and benign handling properties at the same time giving very similar or even better performance as a worldwide proven hydrazine monopropellants. Current TRL is at level 5/6.[3]
The power generation of LituanicaSAT-2 is provided by 4 fixed and 4 deployable mono crystalline silicon solar panels custom designed and manufactured by NanoAvionics. The panels are able to reach an efficiency of 20%.[2]
LituanicaSAT-2 structure is custom designed by NanoAvionics and manufactured locally. The structure is made of 7075 aluminium alloy with hard anodized surfaces.[2] Some of LituanicaSAT-2 parts were 3D-printed using special materials approved for aerospace industry.[5]
See also
External links
References
- 1 2 3 4 "LituanicaSAT 2 (QB50 LT01)". space.skyrocket.de. Retrieved 2016-09-04.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "LituanicaSAT-2 | NanoAvionics". n-avionics.com. Retrieved 2016-09-04.
- 1 2 3 4 "LituanicaSAT-2 – University Space Engineering Consortium". unisec-europe.eu. Retrieved 2016-09-04.
- 1 2 "THE PROJECT". www.qb50.eu. Retrieved 2016-09-04.
- ↑ "LituanicaSAT-2 Parts". dukubu.lt. Retrieved 2016-09-04.