London Overground
 | |||
|
A London Overground class 378 train at Canonbury | |||
| Overview | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Owner | Transport for London (TfL) | ||
| Locale | Greater London; Hertfordshire, UK | ||
| Transit type | Suburban rail & Commuter rail | ||
| Number of lines | 9 | ||
| Number of stations | 112 (10 operated) | ||
| Annual ridership | 160 million [1] | ||
| Website |
www | ||
| Operation | |||
| Began operation | 11 November 2007 | ||
| Operator(s) | Arriva Rail London 13 November 2016-2023[2] | ||
| Reporting marks | LO (National Rail) | ||
| Technical | |||
| System length | 167 km (103.8 mi)[3] | ||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8½ in) Standard | ||
| Electrification |
25 kV AC overhead lines 750 V DC third rail | ||
| |||
The London Overground (also known as the Overground) is a suburban rail network in the United Kingdom. Established in 2007,[4] it serves a large part of Greater London and parts of Hertfordshire, with 112 stations on several routes. The network forms part of the National Rail network, but under the franchise control and branding of Transport for London (TfL). Operation has been franchised to Arriva Rail London since 13 November 2016.
The Overground has been assigned the colour orange as a mode specific colour by Transport for London. This colour is used in the Overground version of the TfL roundel, for the representation of Overground routes on the tube map, in train interiors and elsewhere.[5]
History
Background
Rail services in Great Britain are mostly run under franchises operated by private train operating companies, marketed together as National Rail.
The concept of developing a network of orbital services around London goes back to the independently produced Ringrail proposals in the early 1970s.[6] Some of these were evaluated in the London Rail Study of 1974 (The Barren Report) and Barren suggested consideration of a North London Network of orbital services, based on a later suggestion by the Ringrail Group, which involved using many existing rail routes, rather than new construction suggested in earlier drafts of the Ringrail Plan.
The proposal from Barren was for several overlapping services mainly using the North London Line, generally at 20-minute intervals. The suggested routes followed the original North London Line service from Broad Street to Richmond, and new services from Barking to Clapham Junction, and a third service from Ealing Broadway to North Woolwich. However, the continuing antipathy to the railways from the third Wilson government, along with the lack of interest in minor local train services by British Railways' management, meant that few of these initiatives were carried forward.
In 1979, the then GLC decided to sponsor an improved service from Camden Road, on the North London Line, to North Woolwich, opening up a previously freight-only line between Dalston and Stratford and linking it to an improved Stratford – North Woolwich service. This was given the marketing name 'Cross Town Link-Line', and operated with basic 2-car diesel units.
The next initiative came from the GLC in 1984, when the Thatcher Government supported the Broadgate development that would entail the demolition of Broad Street Station. The closure process was convoluted because of problems in making alternative arrangements for the North London Line, and the remaining services operating from Watford to the City. These would eventually run to and from Liverpool Street via a new section of track, the Graham Road Curve.
Nevertheless, the new Richmond to North Woolwich service quickly settled down, but the then British Rail made a serious management error replacing the existing 3-car Class 501 electric trains (built 1957[7]) with slightly newer but shorter 2-car Class 416 electric trains (built 1959[8]), that quickly became overcrowded. In 1988, by reorganising and reducing services on the Great Northern routes from Moorgate, about 18 relatively modern Class 313 dual-voltage electric trains were transferred to operate the North London and Watford services, from both Euston and Liverpool Street.
Several voluntary sector groups, the Railway Development Society (RDS), later Railfuture, Transport 2000's then London groups, and the Capital Transport Campaign, launched a series of leaflets and briefings promoting a concept called Outer Circle. This used a name once associated with a semicircular service that operated from Broad Street to Mansion House, but ceased during World War 1.
The pamphlets and briefings, first issued in 1997, initially suggested a route from Clapham Junction to the Greenwich Peninsula, intended to improve access from south London to the Millennium Dome. However, this was thwarted by architect Richard Rogers who considered a railway route on an elevated viaduct could cause 'community severance' and so the Victorian brick viaduct was demolished. Nothing further happened to develop this network until after the new GLA was set up in 2000. But the lobbying discreetly continued with a series of short briefings published by one RDS member based in North London. Mayoral and GLA candidates were approached to discuss the viability of the Outer Circle concept. The principle was widely supported and was adopted into the first Mayor's Transport Plan, published in 2001.
Meanwhile, a pilot scheme was launched in 2003 to bring several National Rail local services, mainly in South London and operated by multiple companies, under the ON – Overground Network brand. TfL introduced consistent information displays, station signage and maps on the selected routes in South London. Although this pilot was primarily an exercise in branding, some service improvements were introduced, and it was the first instance of the newly created TfL having a visible influence over National Rail services. The pilot scheme was later dropped.
In January 2004 the Department for Transport announced a review of the rail industry in Great Britain.[9] As part of that review, proposals were put forward by TfL for a "London Regional Rail Authority" to give TfL regulatory powers over rail services in and around Greater London.[10]
A result of this consultation was agreement by the then Secretary of State for Transport, Alistair Darling, to transfer part of the Silverlink Metro Group of services rail franchise to TfL control. [11]
Silverlink had two areas of operation: Silverlink County regional services from Euston to Northampton, St Albans Abbey, Bletchley and Bedford; and Silverlink Metro within the London urban area. When the franchise was split up in 2007, County services were taken over by the London Midland franchise,[12] and the Metro services came under TfL control. TfL decided to let this franchise as a management contract, with TfL taking the revenue risk.
Initial announcements
On 20 February 2006, the Department for Transport announced that TfL would take over management of services then provided by Silverlink Metro.[13] Tenders were invited to operate the service under the provisional name of the North London Railway. On 5 September 2006, London Overground branding was announced, and it was confirmed that the extended East London Line would be included.
Launch

On 11 November 2007, TfL took over the franchise for North London Railway routes, formerly Silverlink Metro.
The official launch ceremony was on 12 November 2007 at Hampstead Heath station by the Mayor of London, Ken Livingstone, with a later media event on the bay platform at Willesden Junction.
The launch was accompanied by a marketing campaign entitled "London's new train set", with posters and leaflets carrying an image of model railway packaging containing new Overground trains, tracks and staff.[15]
At the launch, TfL undertook to revamp the routes by improving service frequencies, staffing all stations, improving station facilities, introducing new rolling stock and allowing Oyster pay as you go throughout the network from the outset.[16]
All stations were "deep-cleaned"[17] following the TfL takeover, and Silverlink branding removed. Station signage was replaced with Overground-branded signs using TfL's corporate New Johnston typeface.[16][17]
On 15 April 2009 the North London Line platforms at Stratford moved to new high-level platforms 1 & 2 from low-level platforms 1 & 2, the latter being needed for the DLR's Stratford International service. Platforms 1 & 2 comprise an island platform with step-free access to platform 12 and subway links to platforms 3–11.[18]
On 27 September 2009, Imperial Wharf station opened on the West London Line, between West Brompton and Clapham Junction.
East London Line extension
On 27 April 2010, the East London Line became part of the London Overground network when the Phase 1 extension was completed.[19] The former London Underground line was extended northwards, mostly along the former Broad Street viaduct of the North London Line, to the re-opened Dalston Junction, and southwards to Crystal Palace and West Croydon.
Operations began with a limited preview service between Dalston Junction and New Cross/New Cross Gate,[20] with full operation between Dalston Junction and West Croydon/Crystal Palace on 23 May.[21] On 28 February 2011, the line between Dalston Junction and Highbury & Islington was opened. In attendance were the Mayor of London, Boris Johnson, and London Underground's Managing Director, Mike Brown. TfL said in November 2010 that ridership was ahead of forecast at 92,000 a day, and that patronage at Surrey Quays had "gone through the roof".[22]
The incorporation of the East London Line into the Overground network has added substantial sections of line in tunnel, including the historic Thames Tunnel, the oldest tunnel under a navigable river in the world. A peculiarity is that at Whitechapel the London Overground runs below the London Underground (though there are other parts of the network where this occurs, e.g.: the Watford Junction to Euston route between Kenton and South Kenton – shared with the Bakerloo line – passes under the Metropolitan line between Northwick Park and Preston Road).
South London Line extension
The next addition opened on 9 December 2012, from Surrey Quays to Clapham Junction via the South London Line, calling at Queens Road Peckham, Peckham Rye, Denmark Hill, Clapham High Street and Wandsworth Road. The extension uses an alignment between Surrey Quays and just north of Queen's Road Peckham that had been disused since 1911, new track was laid following some major civil engineering works. Passive provision has also been made for a new station at New Bermondsey, to be constructed when funding becomes fully available. This was put on hold in 2009, although a suitable station 'foundation structure' has been built to facilitate completion in the future.
Funding for the railway rebuilding project was secured in February 2009,[23] including £64 million from the DfT and £15 million from TfL, with construction beginning in May 2011.
The route passes over both Loughborough Junction and Brixton stations without stopping, and this lack of interchange stations was criticised by local politicians during the planning phase of the project.[24][25] No stations are planned at these locations as the line is on high railway arches, making the cost of any station construction prohibitive.[26]
North-east and East London
On 31 May 2015 the Liverpool Street to Enfield Town, Cheshunt (via Seven Sisters) and Chingford services, as well as the Romford to Upminster service, were transferred from Abellio Greater Anglia to Transport for London to become part of the London Overground network.[27][28]
Network

Introduction
The initial network, service levels and timetables were a continuation of Silverlink Metro services, a set of routes primarily built and electrified by the North London and London & North Western railway companies in the 19th and early 20th centuries. As the Overground name implies, the majority of the network is above ground, and it mostly consists of railway lines that connect areas outside Central London, with a considerable portion of the network in Zone 2. The network also uses Euston in central London, the southern terminus of the Watford DC Line.
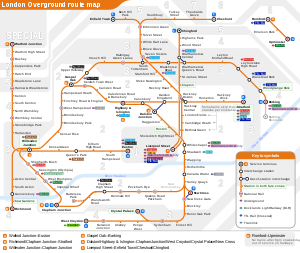
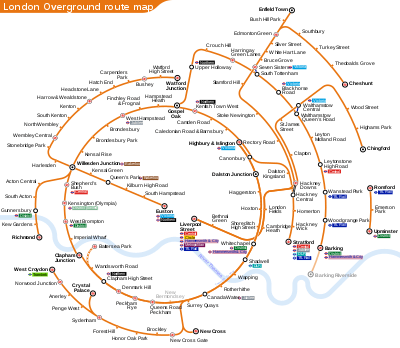
The network interchanges with the Bakerloo, Central, District, Hammersmith & City, Jubilee, Northern, Circle, Metropolitan and Victoria tube lines, and also with the Docklands Light Railway, Tramlink and TfL Rail networks. The Overground lines appear on Tube maps issued by TfL,[29] and a separate map of the system is available.[30]
Much of London Overground passes through less affluent areas, and is seen as contributing to their regeneration.[31] The North London and Gospel Oak to Barking lines were previously considered by the Transport Committee of the London Assembly to be neglected and not developed to their full potential.[32]
Services
As of May 2015, typical service frequencies in trains per hour are:[33]
| Routes | Frequency (per hour) | Depot(s) | Fleet |
|---|---|---|---|
| East & South London | 4 Highbury & Islington – West Croydon 4 Highbury & Islington – Crystal Palace 4 Dalston Junction – New Cross 4 Dalston Junction – Clapham Junction |
New Cross Gate TMD | Class 378 Electrostar |
| North & West London | 4 Richmond – Stratford 2 Clapham Junction – Stratford 2 Clapham Junction – Willesden Junction (Stratford at peaks) |
Willesden TMD | |
| Watford Local | 3 London Euston – Watford Junction | ||
| Gospel Oak – Barking | 4 Gospel Oak – Barking | Class 172 Turbostar | |
| London Liverpool Street - Enfield Town/Cheshunt |
4 (peak), 2 (off-peak) London Liverpool Street – Enfield Town 2 London Liverpool Street – Cheshunt |
Ilford TMD Chingford sidings Gidea Park Sidings |
Class 315, Class 317 |
| London Liverpool Street - Chingford |
4 London Liverpool Street – Chingford | ||
| Romford – Upminster | 2 Romford – Upminster |
Sunday service is similar on all routes except for Highbury & Islington - West Croydon, which starts/terminates at Dalston Junction, and Dalston Junction - Clapham Junction, which is extended to/from Highbury & Islington.
Stations
The Overground serves the following stations:
| Lea Valley Lines | Romford to Upminster Line | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Out of the 112 stations on the London Overground network, 10 of them (seven being on the East London Line) are underground or sub surface.
Operations
LOROL has its head office and control centre in Swiss Cottage. Rolling stock is maintained at depots at Willesden Junction and New Cross (newly built for the extended East London line). There are also sidings at Silwood Triangle (just north of New Cross depot), built in 2013–14.[34] Satellite locations for stabling trains include Stratford, London Euston and sidings (mainly used by London Midland), and Barking Depot in East London (a central depot for the National Express Group franchise c2c). Train crews are based at stations including Euston, Willesden Junction, Watford Junction, New Cross, Stratford and Gospel Oak. Until recently London Overground operated with a Conductor or Guard on its North London, West London and Gospel Oak services. With the other 60% of Overground services already operated by only a driver, it was decided in 2013 to convert these remaining two person operated trains to driver only.[35]
Operator
The Overground is operated by a private company, Arriva Rail London. Following a model similar to that used for the Docklands Light Railway, TfL invited tenders for operation of the Overground. Unlike National Rail operators under the franchise control of the Department for Transport, TfL would set fares, procure rolling stock and decide service levels. The operator would take an element of revenue risk: TfL takes 90% of the revenue and 10% is retained by the operator, responsible for revenue collection.
The first operator, London Overground Rail Operations Limited (LOROL), a 50:50 joint venture between the MTR Corporation of Hong Kong and Laing Rail was chosen by TfL on 19 June 2007.[36] The contract was signed on 2 July 2007 for seven years with the option of a two-year extension.[37] In preparation for the launch of the Overground, MTR Laing renamed itself London Overground Rail Operations. In February 2013, it was awarded a concession extension until 14 November 2016.
In April 2015, Transport for London placed a notice in the Official Journal of the European Union, inviting expressions of interest in operating the next concession.[38] In March 2016, TfL announced that Arriva Rail London had won the right to operate the London Overground concession, starting from 13 November 2016.[39]
Ticketing
Ticketing is a mix of paper, Oyster card electronic smart card and contactless payment cards for "pay-as-you-go" travel. As with all National Rail and TfL services in London, passengers can use a Travelcard (daily, seven-day, monthly or annual); as on other National Rail services in London, paper single, return and cheap day return tickets priced under the zonal fare scheme are also available.
As part of an effort to improve safety and protect revenue, TfL has announced that it will introduce ticket barriers at a number of stations. The stations that did not have barriers when TfL took over have been fitted with standalone Oyster card readers similar to those at ungated Underground and DLR stations. The validators at Blackhorse Road which were needed to enter/exit the Oyster card system when changing to and from the Victoria line were replaced with route validators, coloured pink to signify this. Route validators are used to show that a traveller using Oyster PAYG changed lines at that station, showing which of the possible routes was used. Typically, this avoids paying for zone 1 when the passenger did not travel into it.
Ticket stock is common National Rail stock as Overground services remain part of the National Rail network, but sometimes with a large TfL roundel in the centre and the repeated legend "Rail Settlement Plan" or on newer visions "National Rail" on a light green background. This ticket stock, coded "TFL" on the reverse, was introduced in November 2007.[40]
Ticket pricing
Oyster PAYG is charged on the same zone-based rules as for the Underground and the Docklands Light Railway. Stations outside Greater London (except Watford Junction) are included in the new Travelcard Zones 7-9. On 2 January 2008 Acton Central was rezoned from zone 2 to 3, Hampstead Heath from 3 to 2 and Willesden Junction from 3 to 2 and 3.[41]
Paper tickets are charged on the same zone-based rules as for Underground and DLR paper tickets, which were expanded to take in the extra zones covered. Watford Junction has its own fare scale. Paper tickets are significantly more expensive than using Oyster PAYG.
Performance
Although a TfL service, the Overground is part of the National Rail network, unlike the Underground. The most recent figures released by Network Rail (NR), for period 7 (2013/2014), showed that it had achieved 96.6% of the Public Performance Measure (PPM) target for punctuality and reliability set by the ORR – down 0.9 percentage points on the period last year. The moving annual average (MAA) of the PPM for the 12 months to 12 October 2013 was 96.5%.[42] TfL, in conjunction with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, has investigated the use of data from the Oyster smartcard ticketing system to measure the performance of the Overground explicitly from the passenger perspective.[43]
In the autumn 2011 National Passenger Survey, conducted by Passenger Focus, London Overground received an overall satisfaction rating of 92%, a 7% improvement on the previous survey.[44] However, a survey in February 2014 by the consumer group Which? found that customer satisfaction of London Overground was at 6th place (out of 20 train operators) with a satisfaction percentage of 58%.[45]
Branding
_south_entrance_April2010.jpg)
Public presentation is visually associated with TfL design standards, using similar graphic design elements to those used on the Underground, drawing on the design heritage of Frank Pick. These design standards have been applied to London Overground stations, signage, rolling stock and publicity. London Overground also uses the TfL corporate typeface, New Johnston, on its signage, publicity, stationery and on its fleet of trains. In common with other TfL services, the Overground is denoted by its own colour, a vivid orange (Pantone 158C). The use of an orange colour was inherited from the former East London line prior to its transfer from Underground to Overground.[5][29][46]
London Overground lines are shown on the tube map using its modal colour of orange, and no attempt is made to distinguish between the different Overground lines by colour coding. Like the Docklands Light Railway, the Overground is represented as a double line rather than a solid single line, to distinguish it from the colour-coded Underground lines. The London Overground also uses a variant of the TfL roundel. TfL denotes its different transport modes such as London Underground or London Buses with variants of the roundel device using a range of colours, and the London Overground version consists of an orange ring with a blue bar. The roundel has its origins in a 1933 design by the London Passenger Transport Board and has spawned many variations.[29][47][48]
Unlike other National Rail stations, London Overground stations which are not served by another National Rail operator now omit the red National Rail "double arrow" logo from signage outside the stations, using only the Overground roundel instead.[49] A few refurbished or new stations on the reopened East London line display the station name in large orange three-dimensional uppercase letters.
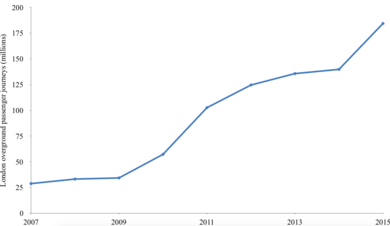
Passenger numbers
Passenger numbers have grown very quickly since the start of London Overground in 2007. Large jumps occurred in 2010/11 and 2011/12 due to the opening of the extensions of the East London line and South London line. The transfer of some suburban services from London Liverpool Street in May 2015 from the Greater Anglia franchise to London Overground also distorted numbers, contributing to a very large growth between 2014/15 and 2015/16.[28]
| |
|
% Change |
|---|---|---|
| 2007–2008 | 28.8 | N/A |
| 2008–2009 | 33.2 | |
| 2009–2010 | 34.3 | |
| 2010–2011 | 57.2 | |
| 2011–2012 | 102.6 | |
| 2012–2013 | 124.6 | |
| 2013-2014 | 135.7 | |
| 2014-2015 | 139.8 | |
| 2015-2016 | 184.4 |
Rolling stock

Since the Overground took over from Silverlink, TfL has pursued a programme of rolling-stock replacement in order to remove from service the ageing second-generation EMUs and Class 150 DMUs it inherited from Silverlink. In 2009, Class 378 Capitalstars built by Bombardier Transportation were introduced on the electrified lines to replace the Class 313 and Class 508 units used previously, while the Class 150s were replaced by new Class 172 Turbostar units on the non-electrified Gospel Oak to Barking Line. By October 2010 the new rolling stock had completely replaced the units previously operated by Silverlink.[52][53][54] The Class 313 EMUs and Class 150 DMUs units have been cascaded to other train operating companies such as Southern, First Capital Connect and First Great Western. The Class 508 units were stored at Eastleigh Works but were subsequently scrapped in 2013 after being deemed unfit.
The Class 378 trains were officially unveiled at Willesden Junction on 13 July 2009. They include a number of tube-style features, including longitudinal seating and increased standing room to provide a high-capacity metro service. They also benefit from walk-through carriage interiors and air conditioning.[55][56] The North London Line has a base fleet of 24 four-car units, Class 378/2. However, these were delivered as three-car units (378/0), with the extended trains being introduced from September 2010, following platform extension works and delivery of the first 20 four-car units (378/1) for the East London Line.[57] A further 13 dual-voltage units were delivered to expand services, taking the total fleet to 57 four-car units. These trains are to be extended to five-car sets towards the end of 2014, starting with the East London Line sets.
The trains are leased from newly formed rolling stock operating company (ROSCO) QW Rail Leasing until 2027. TfL planned initially to buy the new fleet outright, but in February 2008 announced that it would lease the trains in order to free up the £250 million capital cost of purchase, combined with reducing the risk of making a loss through any future sell-on of the fleet.[58]
Eight two-car Class 172/0 units, to be leased from Angel Trains, were ordered on behalf of TfL in November 2007,[59][60] and entered service in 2010.[61] These were originally restricted to a top speed of 40 miles per hour (64 km/h) as opposed to their intended design speed of 100 mph (160 km/h),[62] as it was thought there was a fault with the exhaust system requiring modifications to the original design and the already procured units. However, it transpired that the exhaust emission testing had been flawed and that there were no major problems with the units or the original design. Electrification of the Gospel Oak to Barking line was advocated by TfL, local boroughs and passenger groups, but had not been included as part of Network Rail's Route Utilisation Strategy.[32] Electrification has now been approved, but there is serious concern that this will not be finished until 2017.
Before its closure to become part of the Overground, services on the East London line were operated with London Underground A60 and A62 Stock.
Current fleet
| Class | Image | Type | Top speed | Number | Train Numbers | Carriages | Seat layout | Routes operated | Built | Years operated | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mph | km/h | ||||||||||
| Class 172/0 Turbostar |  |
DMU | 100 | 160 | 8 | 172001–172008 | 2 | 2+2 | Gospel Oak to Barking Line | 2010 | 2010–present |
| Class 315 | EMU | 75 | 121 | 17 | 315801–315817 | 4 | 2+3 | Lea Valley Lines Romford to Upminster Line |
1980–1981 | May 2015–present | |
| Class 317/7 |  |
EMU | 100 | 161 | 8 | 317708, 317709, 317710, 317714, 317719, 317723, 317729, 317732 |
4 | 2+2 | 1981–1982 | May 2015–present | |
| Class 317/8 | EMU | 100 | 161 | 6 | 317887–317892 | 4 | 2+3 | 1981–1982 | May 2015–present | ||
| Class 378/1 Capitalstar |  |
EMU | 75 | 120 | 20 | 378135–378154 | 5 | Longitudinal | East London South London |
2008–2011 | 2009–present |
| Class 378/2 Capitalstar |  |
EMU | 75 | 120 | 37 | 378201–378234 378255–378257 |
5 | Longitudinal | North London West London Watford East London South London |
2008–2011 | 2009–present |
| | |||||||||||
Past fleet
| Class | Image | Type | Top speed | Number | Carriages | Routes operated | Built | Years operated | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mph | km/h | |||||||||
| Class 150/1 Sprinter |  |
DMU | 75 | 120 | 6 | 2 | Gospel Oak-Barking | 1984–1987 | 2007–2010 | Replaced by Class 172 Transferred to First Great Western |
| Class 313/1 |  |
EMU | 75 | 120 | 23 | 3 | North London Watford DC West London |
1976–1977 (Refurbishment 1997–2001 by Silverlink) |
2007–2010 | Replaced by Class 378 Transferred to First Capital Connect (Great Northern), Network Rail and Southern |
| Class 508/3 |  |
EMU | 75 | 120 | 3 | 3 | Watford DC Line | 1979–1980 (Refurbished 2003 by Silverlink) |
2007–2010 | Replaced by Class 378 Stored at Eastleigh Works until scrapping in 2013. |
Future fleet
In 2012, TfL announced its intention to procure a fleet of new, longer DMUs, as the Class 172s were unable to handle the passenger demand, causing overcrowding throughout the day. TfL issued a tender for manufacturers to supply eight three- or four-car trains.[63] However, this proposal was subsequently shelved when the Government announced that the Gospel Oak to Barking line would be electrified, with proposals instead to purchase a fleet of new EMUs.
TfL invited expressions of interest for a total of 39 four-car EMUs in April 2014, with 30 required for the Cheshunt and Chingford routes, 8 for the Gospel Oak to Barking, and 1 for the Romford to Upminster.[64] Since then the planned procurement has been increased to 45 four-car EMUs, with the additional 6 units intended for the Watford DC Line. The intention is that the five-car Class 378 trains used on the Watford route will be cascaded back to the North London and East London Lines to allow for strengthened services. In June 2015, TfL announced that Bombardier had been awarded the contract to build the new trains.[65]
To increase capacity, Class 378 trains are being lengthened from four coaches to five (the first lengthened train entered service on the East London Line in November 2014, and started to be introduced on the North London Line in April 2015). Some station platforms will need to be lengthened to accommodate the longer trains. TfL's Business Plan provides for the introduction of five-car services on the East London line first, followed on the rest of the electrified Overground network by the end of 2015.[66]
In July 2015 TfL announced that it had placed a £260m order for 45 4-car Bombardier Aventra EMUs, with an option for 24 more, (to be known as Class 710) similar to those that will be used by Crossrail, for use on the West Anglia Routes and the Watford DC, GOBLIN and Romford to Upminster lines, from 2018.[67]
Livery

All Electrostar and Turbostar stock in service now carries Overground livery. It is similar to Underground livery, and consists of white coaches, a longitudinal thick blue stripe and a thin orange stripe along the bottom, London Overground roundels at midpoints along the coaches, black window-surrounds and orange doors. The ends of each unit are painted yellow to comply with National Rail standards.[68] The seat upholstery features a moquette by fabric designers Wallace Sewell.[69]
As railway lines have been transferred to London Overground operation, services are sometimes operated using rolling stock inherited from the previous train operating company, and for a temporary period these trains have been branded with transitional livery until they are replaced with newer rolling stock. When the first London Overground services began, they were operated using Silverlink rolling stock which retained Silverlink's purple and lime green livery with yellow doors. The Silverlink logos were removed and Overground banners were added. This rolling stock was eventually completely replaced with new, Overground-branded trains.
Similarly, since the takeover of the Lea Valley Lines, Overground services are being run with trains inherited from Abellio Greater Anglia which are mostly in a plain white livery with red doors. Rather than replace this rolling stock, the trains are to be repainted with full Overground livery and the interiors refurbished with Wallace Sewell upholstery and TfL standard signage and route maps.[70]
Planned developments

24-hour services
London Overground will run 24-hour trains on Friday and Saturday nights between Highbury & Islington and New Cross Gate from 2017.[71]
Gospel Oak to Barking Line
Electrification
It was announced in June 2013 that £115 million of funding for electrification was being made available as part of upgrades to rail infrastructure included in the government's 2013 spending round.[72] At the same time Transport for London announced that they had obtained a £90 million commitment from the Chancellor of the Exchequer and the Secretary of State for Transport.[73]
In September 2015, Network Rail awarded the £56.9m contract to electrify the line to J. Murphy & Sons.[74] There will be part closures (on weekends and from South Tottenham to Barking) from June to late September 2016, followed by a full closure from October to February 2017. There will be further evening and weekend works until late June 2017, and finally around four months of further work to add the wires so that electric Class 710 trains can run from early 2018.[75] The line will be electrified using the NR Series 2 OLE range.[76]
Extension to Barking Riverside
It was announced as part of the 2014 United Kingdom budget that the Gospel Oak to Barking Line of London Overground would be extended to Barking Riverside.[77] £263 million will be spent to extend the line to the brownfield 10,800-home Barking Riverside housing development, which Barking and Dagenham Council does not believe to be viable without improved transport connections. The developers of the site, Barking Riverside Limited, will provide £172m towards the project with the remainder coming from Transport for London.[78] Construction will start in 2017 and be completed by 2021.[78]
Proposed developments
Watford DC Line move to Bakerloo

In 2007 TfL proposed re-extending the Bakerloo line to Watford Junction.[79] It was suggested that most or all of the line from Queen's Park to Watford Junction would be used exclusively by the London Underground, and London Overground services would be withdrawn.
As part of this change, Overground services would have been diverted at Primrose Hill Junction via Primrose Hill (closed to passengers since 1992) to Camden Road, providing a new service between Queen's Park and Stratford.[80] Had this change taken place, Kilburn High Road and South Hampstead would no longer have had direct services to Euston station, hindering access to central London.
Croxley Link
Funding has since been confirmed for the Croxley Rail Link, diverting the Watford branch of the Metropolitan line to Watford Junction via Watford High Street, where it will share tracks with the Overground.[81]
Old Oak Common interchange

A long-term plan exists to create an interchange with High Speed 2 at the proposed Old Oak Common station. Planning documents issued by the Department for Transport suggest that the new station, on a site just south of Willesden Junction, could open by 2025 and offer connections with the Overground on both the North London and West London Lines.
The station would also be served by Crossrail, Great Western Main Line services and Heathrow Express, and the proposals indicate the possibility of interchange with the Bakerloo and Central lines.[82] The plans are supported by the London Borough of Hammersmith and Fulham.[83]
In June 2013, the Mayor of London and the London Boroughs of Brent, Ealing and Hammersmith & Fulham released 'vision' consultation documents[84] about the Old Oak Common area.
The vision mentions various connections to the London Overground system, linking Old Oak to the North London Line, West London Line, and to two new London Overground branches, to Hounslow, and – via the Dudding Hill Line – to Thameslink stations on the Midland Main Line.
Thamesmead extension
In addition to the plan to extend the Gospel Oak to Barking Line to Barking Riverside, there are also proposals to extend it further under the river to a station in Thamesmead, and then on Abbey Wood to connect with the future Crossrail line.[85]
Future acquisitions
Following the completion of the first phase of the London Overground network in December 2012, TfL has expressed its intention to take over the operation of other suburban lines in the London area. As with the original London Overground system, this would involve devolving National Rail services from the DfT's franchising system to a TfL-managed concession.
On 21 January 2016 it was announced consideration was being given to the possibility of gradually transferring the suburban services operated by Southeastern, South West Trains and Govia Thameslink Railway (Great Northern, Thameslink and Southern) to TfL to create a London Suburban Metro.[86]
Past attempts on acquiring routes
In 2012–13 TfL and the Greater London Authority publicised a proposal for further expansion, identifying a number of services in North-East and South-East London as suitable candidates.[87][88][89] Part of this proposal was fulfilled in May 2015 with the transfer of the Lea Valley and Romford-Upminster Lines out of Liverpool Street to the London Overground network, but TfL's aim of acquiring Southeastern metro services currently remains at the proposal stage. Under this scheme, TfL would take over rail services out of London Victoria, Charing Cross and Cannon Street to Dartford, Sevenoaks, Orpington and Hayes, but this was rejected following spending cuts imposed by the 2013 United Kingdom budget.[90] The possibility of TfL acquiring routes out of London Bridge has also been discussed.[89]
In October 2015 the prospect of London Overground expansion was raised again when the London Assembly Transport Committee published a report which advocated the devolution of a number of commuter rail services and the creation of a "South London Metro". In particular, the report identified four rail franchises due for renewal which could be taken over by TfL:[91][92]
- the South Western franchise from London Waterloo to South West London suburbs
- the Thameslink, Southern and Great Northern franchise (Great Northern and Southern metro services) out of Moorgate to North London and out of London Bridge/Victoria to South London suburbs
- the Integrated Kent franchise (Southeastern metro services) out of Victoria/Charing Cross/Cannon Street/London Bridge to South East London suburbs
Kent County Council had initially expressed opposition to the Dartford route plans on account of limited capacity for Kent express trains being lost to expanded TfL services,[93] but after negotiations with the London Assembly, reached an agreement to support the proposals.[94]
Greenford Branch
The Department for Transport have proposed that Transport for London should take over the Greenford to West Ealing Line in West London. This would bring Greenford, South Greenford, Castle Bar Park, Drayton Green and West Ealing into the Overground network. Trains on this branch would no longer run directly to Paddington, but would terminate at West Ealing in order to free up line capacity for the forthcoming Crossrail services, and West Ealing station would be reconstructed to allow Greenford branch trains to terminate there. If this proposal were to go ahead, it would happen when the Greater Western franchise ends in 2019.[95]
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to London Overground. |
- London Underground
- Overground Network
- Orbirail
- Crossrail
- Docklands Light Railway
- Tramlink
- London Buses
- East London Transit
- Cycling in London
References
- ↑ LOROL: Factsheet Accessed 17 June 2016
- ↑ "Arriva named as new operator for London Overground". Transport for London. 18 March 2016. Retrieved 8 November 2016.
- ↑ "LOROL takes over West Anglia routes" (PDF). LOROL. Retrieved 27 July 2016.
- ↑ "Introducing London Overground – a new era for London Rail" (Press release). Transport for London. 5 September 2006. Retrieved 10 June 2011.
- 1 2 "TfL Colour standards" (PDF) (4 ed.). Transport for London. Archived (PDF) from the original on 5 July 2016. Retrieved 5 July 2016.
- ↑ A new RingRail for London : the key to an integrated public transport system. G L Crowther, 1973.
- ↑ Haresnape, Brian; Swain, Alec (1989). British Rail Fleet Survey 10: Third Rail DC Electric Multiple-Units. Shepperton: Ian Allan. p. 40. ISBN 0-7110-1760-3.
- ↑ Haresnape & Swain 1989, p. 34
- ↑ "The Future of Rail – White Paper CM 6233". Department for Transport. 15 July 2004. Archived from the original on 17 May 2008. Retrieved 25 August 2008.
- ↑ "Bob Kiley outlines proposals for London Regional Rail Authority" (Press release). Transport for London. 23 March 2004. Retrieved 26 June 2011.
- ↑ "London Rail Authority". AlwaysTouchOut.com. 7 September 2006. Retrieved 25 August 2008.
- ↑ "New trains and more services for the Midlands" (Press release). Department for Transport. 21 June 2007.
- ↑ Darling, Alistair (14 February 2006). "Silverlink Metro". Hansard. Retrieved 25 August 2008.
- ↑ "London Overground network map" (PDF). Transport for London. 2007. Retrieved 21 August 2008.
- ↑ "London's new train set". Transport for London. January 2008. Archived from the original (leaflet) on 29 October 2010. Retrieved 11 November 2007.
- 1 2 "Creating London Overground" (PDF). Transport for London. 2007. Archived from the original (leaflet) on 9 April 2008. Retrieved 11 November 2007.
- 1 2 "All Change". The Londoner. Greater London Authority. November 2007. Archived from the original on 14 December 2007. Retrieved 4 November 2007.
- ↑ London Overground: Stratford Platform Changes (Information leaflet, TfL January 2009)
- ↑ "East London line officially opens". BBC News. London. 27 April 2010. Retrieved 2 April 2010.
- ↑ "New era of rail travel as London Overground's east London route opens to the public" (Press release). Transport for London. 27 April 2010. Retrieved 26 June 2011.
- ↑ "Full service begins on newly extended East London Line". BBC News. 23 May 2010. Retrieved 27 May 2010.
- ↑ Abbott, James (December 2010). "Overground champion bows out". Modern Railways. London. p. 48.
- ↑ "Final section of Capital's orbital railway gets the go-ahead" (Press release). Transport for London. 12 February 2009. Retrieved 26 June 2011.
- ↑ "Junction joy South". South London Press. Streatham. 24 April 2004. Archived from the original on 9 May 2004. Retrieved 3 November 2009.
- ↑ Martin Linton MP (4 August 2006). "Parliamentary Debate: London Orbital Rail Network". Hansard. Retrieved 3 November 2007.
- ↑ "East London Line Extensions – Loughborough Junction". AlwaysTouchOut. 9 November 2006. Retrieved 3 November 2007.
- ↑ London Overground operator appointed to run additional services for TfL Travel & Tour World 4 June 2013
- 1 2 Topham, Gwyn (29 May 2015). "Clean, reliable and integrated: all change for neglected rail services in London". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on 30 May 2015. Retrieved 31 May 2015.
- 1 2 3 "Tube Map" (PDF). Transport for London. December 2013. Retrieved 24 March 2014.
- ↑ "London Overground" (PDF). Transport for London. December 2013. Retrieved 24 March 2014.
- ↑ "Response to Network Rail's Draft Cross London Route Utilisation Strategy" (PDF). Transport for London. February 2006. Retrieved 10 January 2007.
- 1 2 "London's Forgotten Railway: The Transport Committee's Review of the North London Railway". Greater London Authority. March 2006. Retrieved 9 December 2012.
- ↑ London Overground timetables. Transport for London. Retrieved 31 May 2015.
- ↑ http://www.ianvisits.co.uk/blog/2013/12/02/a-look-around-the-london-overground-upgrade-project/
- ↑
- ↑ "Milestone reached in transformation of London's overland rail network as operator is announced" (Press release). Greater London Authority. 19 June 2007. Retrieved 9 December 2012.
- ↑ "MTR Laing beats Go-Ahead unit Govia to win North London rail franchise". London South East. Thomson Financial. 19 June 2007.
- ↑ TfL starts search for next operator to run Overground Transport for London 9 April 2015
- ↑ "Arriva wins London Overground concession". Railway Gazette. 18 March 2016. Retrieved 18 March 2016.
- ↑ "National Rail News". Journal of the Transport Ticket Society. Kemsing: Transport Ticket Society (527): 450. December 2007. ISSN 0144-347X.
- ↑ "Your guide to fares and tickets (2 January 2008 until further notice)" (PDF). Transport for London. November 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 April 2008. Retrieved 10 July 2008.
- ↑ "Rail performance results period 7". Network Rail.
- ↑ Frumin, Michael (2008). "Oyster-Based Performance Metrics for the London Overground".
- ↑ "National Passenger Survey Autumn 2011 Main Report" (PDF). Passenger Focus. 26 January 2012. Retrieved 9 December 2012.
- ↑ "Best and worst UK train companies". Which?. 17 February 2014. Retrieved 21 February 2014.
- ↑ "Design standards". Transport for London. Archived from the original on 23 April 2015. Retrieved 25 October 2015.
- ↑ "Lonodn Overground Basic Elements Standard – Issue 2" (PDF). Transport for London. January 2009. p. 8. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 May 2015. Retrieved 25 October 2015.
- ↑ "Designing Modern Britain – London Transport". London: Design Museum. Retrieved 25 August 2008.
- ↑ "London Overground Signs Standard – Issue 3" (PDF). Transport for London. 3 August 2009. p. 18. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 May 2015. Retrieved 25 October 2015.
- 1 2 "TfL annual report 2015-16" (PDF).
- 1 2 "TfL annual report 2011/12" (PDF).
- ↑ Miles, Tony (December 2010). "LOROL Class 150s all with FGW". Modern Railways. London. p. 90.
- ↑ "Focus on 313s". Inter City Railway Society. Retrieved 17 March 2013.
- ↑ "BR withdrawn dc electric train sets". Railfaneurope.net. Retrieved 17 March 2013.
- ↑ "In Pictures: Mayor Unveils New London Overground Train". The Londonist. 13 July 2009. Retrieved 14 July 2009.
- ↑ "London Overground introduces Class 378 train fleet". Transport Briefing. 13 July 2009. Retrieved 14 July 2009.
- ↑ "trains extended London Overground's electric train fleet" (Press release). Transport for London. 15 September 2010. Retrieved 9 December 2012.
- ↑ "Transport for London signs new train leasing contract" (Press release). Transport for London. 20 February 2008. Retrieved 26 June 2011.
- ↑ "Class 172 Turbostar". The Railway Centre.
- ↑ "The Underground Roundel moves Overground". Today's Railways (UK) (70). Sheffield. September 2007. pp. 24–30.
- ↑ Modern Railways (741). London. July 2010. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Miles, Tony (August 2010). "Class 172 ready for introduction". Modern Railways (743). London. p. 75.
- ↑ "TfL seeks new Barking line trains as two-car '172s' struggle". Rail (697). Peterborough. 30 May 2012.
- ↑ "More EMUs for London Overground". Railway Gazette. 9 April 2014. Retrieved 9 April 2014.
- ↑ "Bombardier wins London Overground EMU contract". Railway Gazette. 19 June 2015. Retrieved 19 June 2015.
- ↑ Turvill, Bill (March 2013). "London Overground goes for five cars". Modern Railways. Tunbridge Wells. p. 88.
- ↑ Rail Magazine, Issue 778, Page 14
- ↑ "London Overground Train Graphics Standard – Issue 2" (PDF). Transport for London. January 2009. p. 89. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 May 2015. Retrieved 25 October 2015.
- ↑ "London Transport Museum – our moquette range". London Transport Museum. Archived from the original on 17 July 2011. Retrieved 10 July 2011.
- ↑ "It Looks Like 315817 Is The Prototype Overground Class 315 Train". The Anonymous Widower.
- ↑ "Travel boost for Londoners as Chancellor and Mayor confirm expansion of night time services & new WiFi for the Tube" (Press release). Department for Transport. 20 February 2015. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- ↑ HM Treasury (June 2013). "Investing in Britain's future" (PDF). The Stationery Office. p. 26. Retrieved 26 June 2012.
- ↑ "Mayor secures 'unprecedented' transport settlement for London to support long-term economic growth". Greater London Authority. 26 June 2013. Retrieved 17 July 2013.
- ↑ http://www.railtechnologymagazine.com/Rail-News/j-murphy-sons-to-carry-out-electrification-of-gospel-oak-barking-route
- ↑ "TfL tries to reduce line-closure time for GOBLIN electrification". 2 February 2016.
- ↑ "CP5 Enhancements Delivery Plan June 2015" (PDF). Network Rail. June 2015. Retrieved 21 January 2016.
- ↑ Freddy Mayhew. "Budget 2014: Commitment to Overground extension to Barking Riverside announced alongside funding for new homes". Barking and Dagenham Post. Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- 1 2 "London Overground Barking Riverside extension approved".
- ↑ "Scenario Testing for the Further Alterations to the London Plan" (PDF). Greater London Authority. March 2006. p. 16. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 September 2007. Retrieved 19 June 2007.
- ↑ "East London Line Extensions". alwaystouchout.com. 9 November 2006. Retrieved 4 February 2011.
- ↑ Binnie, Adam (13 December 2011). "Croxley Rail Link plan approved by Government". Watford Observer.
- ↑ "Update on High Speed 2" (PDF). Transport for London. Retrieved 9 December 2012.
- ↑ "Old Oak Common: The Transport and Regeneration Case for a HS2 Interchange" (PDF). London Borough of Hammersmith & Fulham. December 2009. Retrieved 28 May 2010.
- ↑ Vision for Old Oak Consultation
- ↑ "Call to bring London Overground to Thamesmead – south east London's largest town with no trains". This is London Local. 22 September 2014.
- ↑ https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/493754/dft-tfl-rail-prospectus.pdf
- ↑ "The Mayor's Rail Vision" (PDF). Greater London Authority. February 2012. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 September 2013. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ↑ "Expanding TfL's rail network". TfL. Archived from the original on 22 January 2014. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- 1 2 Waterson, James (29 November 2012). "TfL hopes to push Overground onto key suburban rail routes". City A.M. London. Retrieved 23 December 2012.
- ↑ "London's major transport projects spared axe but City Hall faces big cuts". London Evening Standard. 26 June 2013. Retrieved 26 June 2013.
- ↑ "Devolving Rail Services to London: Towards a South London Metro" (PDF). London Assembly Transport Committee. October 2015. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 October 2015. Retrieved 24 October 2015.
- ↑ Bull, John. "Devocalypse Now: Taking Control of South London's Railways". London Reconnections. Retrieved 24 October 2015.
- ↑ "TfL's takeover proposal for Kent trains 'unacceptable'". BBC News. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ↑ "TfL could take over some Kent rail lines". BBC News. 15 June 2015. Retrieved 26 June 2015.
- ↑ "The Price of Oranges: DfT ask TfL to take on Greenford and Upminster". London Reconnections. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
Further reading
- Wayne Asher. 2015. A Very Political Railway – the rescue of the North London Line. ISBN 978-1-85414-378-5
- John Glover. 2013. London's Overground. ISBN 978-0-7110-3524-9
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to London Overground. |
| Look up Underground, aboveground, underground, or overground in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- "London Overground". Transport for London. Retrieved 24 March 2014.
- "Live travel news". Transport for London. Retrieved 11 July 2008.
- "London Overground". JourneyCheck. Retrieved 11 July 2008.
- "Home Page". London Overground Rail Operations Ltd. Retrieved 11 July 2008.
- "Tube Map". Transport for London. Retrieved 11 July 2008.
- "Tube Map 2010" (PDF). Transport for London. Retrieved 19 May 2011.
- "London Overground". alwaystouchout.com.
| Preceded by London Underground East London line operator before 2007 |
Operator of London Overground 2007 – present (East London Line from 2010) |
Incumbent |
| Preceded by Silverlink North London Railways franchise before 2007 |