Loop subdivision surface
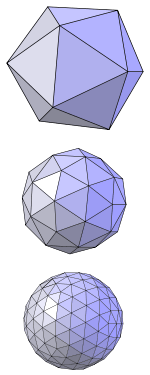
Loop Subdivision of an icosahedron (top) after one and after two refinement steps
In computer graphics, Loop subdivision surface is an approximating subdivision scheme developed by Charles Loop in 1987 for triangular meshes.
Loop subdivision surfaces are defined recursively, dividing each triangle into four smaller ones. The method is based on a quartic box spline, which generate C2 continuous limit surfaces everywhere except at extraordinary vertices where they are C1 continuous.
Geologists have also applied Loop Subdivision Surfaces to erosion on mountain faces, specifically in the Appalachians.
External links
- Charles Loop: Smooth Subdivision Surfaces Based on Triangles, M.S. Mathematics thesis, University of Utah, 1987 (pdf).
- Homepage of Charles Loop.
- Jos Stam: Evaluation of Loop Subdivision Surfaces, Computer Graphics Proceedings ACM SIGGRAPH 1998, (pdf, downloadable eigenstructures).
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 2/7/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.