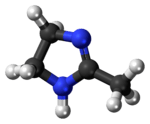
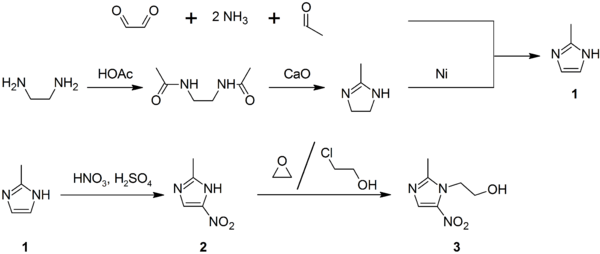Lysidine (chemical)
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Methyl-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole | |
| Identifiers | |
| 534-26-9 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 10341 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.816 |
| EC Number | 208-596-6 |
| PubChem | 10798 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H8N2 | |
| Molar mass | 84.12 g/mol |
| Melting point | 87 °C (189 °F; 360 K) (decomposes) |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases | R36/37/38 |
| S-phrases | S26 S37/39 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Lysidine is a derivative of 2-imidazoline derivative. It is a colorless solid with basic properties and soluble in organic solvents. It is used as a precursor to other compounds of pharmaceutical interest.
Synthesis and reactions
It is prepared by condensing ethylenediamine with acetic acid to give the diamide, which undergoes CaO-induced cyclization. Alternatively, it arises from the condensation of glyoxal, acetaldehyde, and ammonia.
Lysidine is an intermediate in the synthesis of the drug metronidazole. In the presence of Raney nickel, it undergoes dehydrogenation to 2-methylimidazole, which can then be further elaborated.[2]
References
- ↑ Lysidine at Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ Kraft, M. Ya.; Kochergin, P. M.; Tsyganova, A. M.; Shlikhunova, V. S. (1989). "Synthesis of metronidazole from ethylenediamine". Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal. 23 (10): 861. doi:10.1007/BF00764821.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/15/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.