Mastcam-Z
Mastcam-Z is a multispectral, stereoscopic imaging instrument selected by NASA for the upcoming Mars 2020 rover mission. The Principal Investigator is Dr Jim Bell of Arizona State University.[1] The instrument will be built by Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, California.
Science Roles
There are three major objectives for the Mastcam-Z planned by the science team.
- Characterize the overall landscape geomorphology, processes, and the nature of the geologic record (mineralogy, texture, structure, and stratigraphy) at the rover field site.
- Assess current atmospheric and astronomical conditions, events, and surface- atmosphere interactions and processes is to assess current atmospheric and astronomical conditions, events, and surface-atmosphere interactions and processes.
- Provide operational support and scientific context for rover navigation, contact science, sample selection, extraction, and caching, and the other selected Mars-2020 investigations.[2]
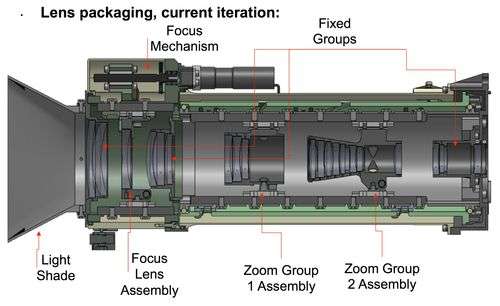
Design and Capabilities
Malin Space Science Systems will build Mastcam-Z and provide uplink planning services.[3] It will consist of two zoom cameras mounted on the remote sensing mast of the Mars 2020 rover. The design draws heavily on that of the Mastcam camera used on the Mars Curiosity Rover with some upgrades. It uses the same size, detectors, electronics interface, firmware, and operations protocols. It has improvement in lens assembly which gives it 3.6:1 zoom capability, whereas the zoom feature was removed from the final design in Curiosity (originally planned to have 15:1 zoom). Each of the zoom cameras have broadband red/green/blue (RGB) imaging and narrow-band visible/near-infrared (VNIR) color imaging. The sensor consists of a ON Semiconductor KAI-2020CM CCD with an array size of 1600 x 1200 pixels. It will be able to image with fields of view (FOV) from ~ 5° to ~ 15°.[4][5]
Education and Public Outreach
The Mastcam-Z science and engineering group teamed up with the Planetary Society of Pasadena, California, to provide public education and outreach. All raw Mastcam-Z images will be published to the web within minutes of downlink to Earth. The Planetary Society will maintain a website dedicated to instrument background, Mars science information for teachers and students, as well as Mars 2020 mission status updates.[6]
References
- ↑ "NASA chooses ASU to design, operate camera system for Mars 2020 mission". ASU News. Retrieved 25 August 2015.
- ↑ "Mastcam-Z". Jet Propulsion Lab. Retrieved 25 August 2015.
- ↑ "NASA Selects MSSS to Provide Science Camera for Mars 2020 Rover Mission". Malin Space Science Systems. Retrieved 25 August 2015.
- ↑ "Mastcam-Z". Jet Propulsion Lab. Retrieved 25 August 2015.
- ↑ Bell, J.F. "Mastcam-Z: A Geologic, Stereoscopic, and Multispectral Investigation on the NASA Mars-2020 Rover" (PDF). Retrieved 25 August 2015.
- ↑ "Planetary Society Selected as Mars 2020 Camera Partner". Planetary Society. Retrieved 1 September 2015.