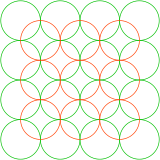
Overlapping circles grid
| square circle grid | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1+ | 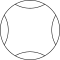 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 4 |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 9 |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Centered square lattice forms | |||||
| 5 |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 13 |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |
| triangular circle grid | |||||
| 1+ |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
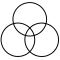
| 3 |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
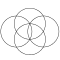
| 4 |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
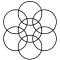
| 7 |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
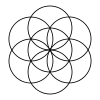
| 19 |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |
An overlapping circles grid is a geometric pattern of repeating, overlapping circles of equal radii in two-dimensional space. The two most common designs are based on circles centered on triangular and square lattice pattern of points.
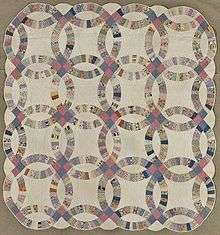
Patterns of seven overlapping circles appear in historical artefacts from the 8th century BC onwards. They are found on a Cypro-Archaic I cup of the 8th-7th century BC in Cyprus; at the Temple of Osiris at Abydos in Ancient Egypt; and on Roman mosaics, for example at Herod's palace in the 1st century BC. The patterns are used extensively to construct girih decorations including 6- and 12-pointed stars in Islamic art. Patterns based on a square grid of overlapping circles are found in quilt design, in Ancient Egypt as noted in the 1856 book The Grammar of Ornament, and in the Hindu temple at Prambanan in Java.
Triangular grid of overlapping circles
 |
| This pattern can be extended indefinitely, seen here with hexagonal rings of 1, 7, 19, 37, 61, 91 circles... |
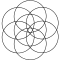
The triangular lattice form, with circle radii equal to their separation is called a seven overlapping circles grid.[1] It contains 6 circles intersecting at a point, with a 7th circle centered on that intersection.
Overlapping circles with similar geometrical constructions have been used infrequently in various of the decorative arts since ancient times. The pattern has found a wide range of usage in popular culture, in fashion, jewelry, tattoos and decorative products.
Historical occurrences
Five patterns of 19 overlapping circles can be seen on one of the granite columns at the Temple of Osiris in Abydos, Egypt,[2] and a further five such circles adorn a column opposite the building. They are drawn in red ochre and some are very faint and difficult to distinguish.[3] David Furlong[4] states that these engravings can date no earlier than 535 BCE and probably date to the 2nd and 4th century CE. His research is based on photographic evidence of Greek text, yet to be fully deciphered. The text is seen alongside the designs and the position close to the top of columns, which are greater than 4 meters in height. Furlong suggests the Osirion was half filled with sand prior to the circles being drawn and therefore likely to have been well after the end of the Ptolemaic dynasty.[3] The drawings are not mentioned in the extensive listings of graffiti at the temple compiled by Margaret Murray in 1904.[5] Similar patterns were sometimes used in England as apotropaic marks to keep witches from entering buildings.[6]
1, 7, and 19-circle hexagonal variant
In the examples below the pattern has a hexagonal outline, and is further circumscribed.
-

1-circle with completed arcs as a Slavic solar symbol
-

7-circle: Mosaic floor from a bathhouse in Herod's palace, 1st century BCE
-
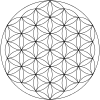
19-circle symbol with completed arcs inside larger circle
-

19-circle: Two symbols drawn in red ochre Temple of Osiris at Abydos, Egypt
-
19-circle: A window at the southern apsis of the church of Preveli Monastery (Moni Preveli), Crete.
Similar patterns
In the examples below the pattern does not have a hexagonal outline.
-

Drawing by Leonardo da Vinci (Codex Atlanticus, fol. 307v)
-

Cup with mythological scenes, a sphinx frieze and the representation of a king vanquishing his enemies. Cypro-Archaic I (8th–7th centuries BC). From Idalion, Cyprus.
-

Ball held by the male Imperial Guardian Lion at the Gate of Supreme Harmony, Forbidden City, Beijing, China, showing the geometrical pattern on its surface.
-

Floor decoration from the northern Iraq palace of King Ashurbanipal, visible in the Museum of Louvre, dated 645BC.
Islamic decoration

In Islamic art, the pattern is one of several arrangements of circles (others being used for fourfold or fivefold designs) used to construct grids for Islamic geometric patterns. It is used to design patterns with 6- and 12-pointed stars as well as hexagons in the style called girih. The resulting patterns however characteristically conceal the construction grid, presenting instead a design of interlaced strapwork.[7]
Modern usage
.jpg)
Martha Bartfeld, author of geometric art tutorial books, described her independent discovery of the design in 1968. Her original definition said, "This design consists of circles having a 1-[inch] radius, with each point of intersection serving as a new center. The design can be expanded ad infinitum depending upon the number of times the odd-numbered points are marked off." Her subsequent books refer to the design as the Flower of Life, attributed to New Age author Drunvalo Melchizedek.[8]
Stephen Wolfram's book A New Kind of Science also refers to this pattern as the flower of life from Melchizedek's name for it.[9] Eric W. Weisstein's book CRC Concise Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Second Edition, also references the pattern and Melchizedek's name.[10]
The pattern and modern name have propagated into wide range of usage in popular culture, in fashion, jewelry, tattoos and decorative products.
The pattern in quilting has been called diamond wedding ring or triangle wedding ring to contrast it from the square pattern.
Besides an occasional use in fashion,[11] it is also used in the decorative arts. For example, the album Sempiternal (2013) by Bring Me the Horizon uses the 61 overlapping circles grid as the main feature of its album cover,[12] whereas the album A Head Full of Dreams (2015) by Coldplay features the 19 overlapping circles grid as the central part of its album cover. Teaser posters illustrating the cover art to A Head Full of Dreams were widely displayed on the London Underground in the last week of October 2015.[13]
Construction
The pattern figure can be drawn by pen and compass, by creating multiple series of interlinking circles of the same diameter touching the previous circle's center. The second circle is centered at any point on the first circle. All following circles are centered on the intersection of two other circles.

Progressions
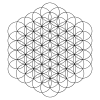
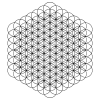
The pattern can be extended outwards in concentric hexagonal rings of circles, as shown. The first row shows rings of circles. The second row shows a three-dimensional interpretation of a set of n×n×n cube of spheres viewed from a diagonal axis. The third row shows the pattern completed with partial circle arcs within a set of completed circles.
Expanding sets have 1, 7, 19, 37, 61, 91, 127, etc. circles, and continuing ever larger hexagonal rings of circles. The number of circles is n3-(n-1)3 = 3n2-3n+1 = 3n(n-1)+1.
These overlapping circles can also be seen as a projection of an n-unit cube of spheres in 3-dimensional space, viewed on the diagonal axis. There are more spheres than circles because some are overlapping in 2 dimensions.
| 1-circle |
7-circle (8-1) |
19-circle (27-8) |
37-circle (64-27) |
61-circle (125-64) |
91-circle (216-125) |
127-circle... (343-216) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 1-sphere (1×1×1) |
8-sphere (2×2×2) |
27-sphere (3×3×3) |
64-sphere (4×4×4) |
125-sphere (5×5×5) |
216-sphere (6×6×6) |
343-sphere (7×7×7) |
 |
 |
 |
||||
| +12 arcs | +24 arcs | +36 arcs | +48 arcs | +60 arcs | +72 arcs | +84 arcs |
 |
 |
 |
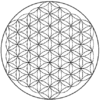 |
 |
 |
Other variations
Another triangular lattice form is common, with circle separation as the square root of 3 times their radii. Two offset copies of this circle pattern makes a rhombic tiling pattern, while three copies make the original.
Richard Kershner showed in 1939 that no arrangement of circles can cover the plane more efficienctly than this hexagonal lattice arrangement.[14]
-

19 circle example
-

Example on Ayyubid Raqqa ware stoneware glazed jar. Syria, 12th/13th century
-
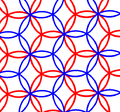
Two offset copies of the minimal covering circle pattern (left) make a rhombic tiling pattern, like this red, blue version.
-

Three offset copies of the minimal covering circle pattern (left most image) make the 7-circle pattern, like this red, green, blue version.
Related concepts

The center lens of the 2-circle figure is called a Vesica piscis, from Euclid. Two circles are also called Villarceau circles as a plane intersection of a torus. The areas inside one circle and outside the other circle is called a lune.
The 3-circle figure resembles a depiction of borromean rings and is used in 3-set theory Venn diagrams. Its interior makes a unicursal path called a triquetra. The center of the 3-circle figure is called a reuleaux triangle.
 Vesica piscis |
 Borromean rings |
 Venn diagram |
 Triquetra |
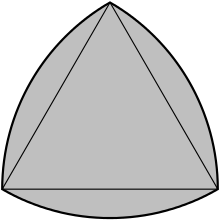 Reuleaux triangle |
The 7-circle pattern has also been called an Islamic seven-circles pattern for its use in Islamic art.
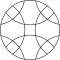
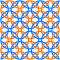
Square grid of overlapping circles
| ||
|
The square lattice form can be seen with circles that line up horizontally and vertically, while intersecting on their diagonals. The pattern appears slightly different when rotated on its diagonal, also called a centered square lattice form because it can be seen as two square lattices with each centered on the gaps of the other.
It is called a Kawung motif in Indonesian batik, and is found on the walls of the 8th century Hindu temple Prambanan in Java.
It is called a Apsamikkum from ancient Mesopotamian mathematics.[15]
-

The square grid can be seen in a face-centered cubic lattice, with 12 spheres in contact around every sphere
-

The related five overlapping circles grid is constructed by from two sets of overlapping circles half-offset.[1]
See also
- Uniform tiling symmetry mutations - pattern mutations in 3D space
- Knot theory
References
- ↑ Islamic Art and Geometric Design: Activities for Learning
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W. "Flower of life". MathWorld.
- 1 2 Stewart, Malcolm (2008). "The "Flower of Life" and the Osirion – Facts are more interesting than Fantasy". Egyptian Tour (David Furlong). Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ↑ Furlong, David. "The Osirion and the Flower of Life". Retrieved 2015-11-08.
- ↑ Murray, Margaret Alice (1904). The Osireion at Abydos London. p. 35. Retrieved November 4, 2015.
- ↑ Kennedy, Maev (31 October 2016). "Witches' marks: public asked to seek ancient scratchings in buildings". The Guardian. Retrieved 31 October 2016.
- ↑ Broug, Eric (2008). Islamic Geometric Patterns. Thames and Hudson. pp. 22–23 and passim. ISBN 978-0-500-28721-7.
- ↑ Bartfeld, Martha (2005). How to Create Sacred Geometry Mandalas. Santa Fe, NM: Mandalart Creations. p. 35. ISBN 9780966228526. OCLC 70293628.
- ↑ Wolfram, Stephen (May 14, 2002), A New Kind of Science, Wolfram Media, Inc., pp. 43 and 873–874, ISBN 1-57955-008-8
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W. (2002), CRC Concise Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Second Edition, CRC Press, p. 1079, ISBN 1420035223
- ↑ E.g. Zaman, Sana (14 May 2013). "Zaeem Jamal Launches New Collection on Board a Private Yacht in Dubai Marina". Haute Living. Retrieved 9 November 2015.
- ↑ Cooper, Ed (25 February 2013). "Bring Me The Horizon: This album needs to be the one that lasts forever". The Independent. Retrieved 8 November 2015.
- ↑ Denham, Jess (6 November 2015). "Coldplay new album: Beyonce and Noel Gallagher to feature on A Head Full of Dreams". The Independent. Retrieved 8 November 2015.
- ↑ Sphere Packings, Lattices and Groups, John Conway, Neil J. A. Sloane, Chapter 2, section 1.1, Covering space with overlapping circle. pp. 31-32. Figure 2.1 Covering the plane with circles (b) The more efficient or thinner covering in a hexagonal lattice.
- ↑ Mesopotamian Mathematics 2100-1600 BC: Technical Constants in Bureaucracy and Education (Oxford Editions of Cuneiform Texts), Eleanor Robson, Clarendon Press, 1999, ISBN 978-0198152460 at books.google.com
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Flower of Life. |