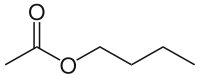
Butyl acetate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Butyl acetate | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Butyl ethanoate | |
| Other names
n-Butyl acetate Acetic acid n-butyl ester Butile | |
| Identifiers | |
| 123-86-4 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Abbreviations | BuAcO |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:31328 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL284391 |
| ChemSpider | 29012 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.236 |
| EC Number | 204-658-1 |
| KEGG | C12304 |
| PubChem | 31272 |
| RTECS number | AF7350000 |
| UNII | 464P5N1905 |
| UN number | 1123 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H12O2 | |
| Molar mass | 116.16 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Fruity |
| Density | 0.8825 g/cm3 (20 °C)[1] |
| Melting point | −78 °C (−108 °F; 195 K) [1] |
| Boiling point | 126.1 °C (259.0 °F; 399.2 K) at 760 mmHg[1] |
| 0.68 g/100 mL (20 °C)[1] | |
| Solubility | Miscible in EtOH Soluble in acetone, CHCl3[1] |
| log P | 1.82[1] |
| Vapor pressure | 0.1 kPa (−19 °C) 1.66 kPa (24 °C)[1] 44.5 kPa (100 °C)[2] |
| Henry's law constant (kH) |
0.281 L·atm/mol |
| Thermal conductivity | 0.143 W/m·K (0 °C) 0.136 W/m·K (25 °C) 0.13 W/m·K (50 °C) 0.116 W/m·K (100 °C)[1] |
| Refractive index (nD) |
1.3941 (20 °C)[1] |
| Viscosity | 1.002 cP (0 °C) 0.685 cP (25 °C) 0.5 cP (50 °C) 0.305 cP (100 °C)[1] |
| Structure | |
| 1.87 D (24 °C)[1] | |
| Thermochemistry | |
| 225.11 J/mol·K[2] | |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH |
−609.6 kJ/mol[2] |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH |
3467 kJ/mol[2] |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Flammable |
| GHS pictograms |   [3] [3] |
| GHS signal word | Warning |
| H226, H336[3] | |
| P261[3] | |
| R-phrases | R10, R66, R67 |
| S-phrases | S25 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 22 °C (72 °F; 295 K)[4] |
| 370 °C (698 °F; 643 K)[4] | |
| 150 ppm[1] (TWA), 200 ppm[1] (STEL) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) |
10768 mg/kg (rats, oral)[4] |
| LC50 (median concentration) |
160 ppm (rat, 4 hr) 2000 ppm (rat, 4 hr) 391 ppm (rat, 4 hr) 1242 ppm (mouse, 2 hr)[5] |
| LCLo (lowest published) |
14,079 ppm (cat, 72 min) 13,872 ppm (guinea pig, 4 hr)[5] |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
| PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 150 ppm (710 mg/m3)[4] |
| REL (Recommended) |
TWA 150 ppm (710 mg/m3) ST 200 ppm (950 mg/m3)[6] |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) |
1700 ppm[6] |
| Related compounds | |
| Related acetates |
Ethyl acetate Propyl acetate Amyl acetate |
| Related compounds |
Butanol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
n-Butyl acetate, also known as butyl ethanoate, is an ester which is a colorless flammable liquid at room temperature. Butyl acetate is found in many types of fruit, where along with other chemicals it imparts characteristic flavors and has a sweet smell of banana or apple. It is used as a synthetic fruit flavoring in foods such as candy, ice cream, cheeses, and baked goods. Butyl acetate is often used as a high-boiling solvent of moderate polarity.
The other three isomers of butyl acetate are: isobutyl acetate, tert-butyl acetate, and sec-butyl acetate.
Production
Butyl acetates are commonly manufactured by the Fischer esterification of butanol (or its isomer to make an isomer of butyl acetate) and acetic acid with the presence of catalytic sulfuric acid under reflux conditions with the following reaction:[7]
Occurrence in nature
Apples, especially of the Red Delicious variety, are flavored in part by this chemical. The alarm pheromones emitted by the Koschevnikov gland of honey bees contain butyl acetate.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Lide, David R., ed. (2009). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (90th ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4200-9084-0.
- 1 2 3 4 Acetic acid, butyl ester in Linstrom, P.J.; Mallard, W.G. (eds.) NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69. National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg MD. http://webbook.nist.gov (retrieved 2014-06-28)
- 1 2 3 Sigma-Aldrich Co., Butyl acetate. Retrieved on 2014-06-28.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "MSDS of n-Butyl acetate". https://www.fishersci.ca. Fisher Scientific. Retrieved 2014-06-28. External link in
|website=(help) - 1 2 "n-Butyl acetate". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- 1 2 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0072". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ Acetic acid. (2003). In Ullman's encyclopedia of industrial chemistry (6th ed., Vol. 1, pp. 170-171). Weinheim, Germany: Wiley-VCH.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Butyl acetate. |
- Ethylene and other chemicals in fruit
- Material Safety Data Sheet
- CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards

