Elegant parrot
| Elegant parrot | |
|---|---|
 | |
| At Walsrode Bird Park, Germany | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Psittaciformes |
| Superfamily: | Psittacoidea |
| Family: | Psittaculidae |
| Subfamily: | Psittaculinae |
| Tribe: | Pezoporini |
| Genus: | Neophema |
| Species: | N. elegans |
| Binomial name | |
| Neophema elegans (Gould, 1837) | |
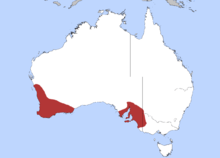 | |
| Distribution of the elegant parrot | |
The elegant parrot (Neophema elegans) is a species of parrot in the family Psittaculidae. It is endemic to Australia.
Taxonomy
The elegant parrot was originally named by the renowned ornithologist and artist John Gould in 1837, its specific name Latin for "elegant". It is one of six species of grass parrot in the genus Neophema, and within it a member of the subgenus Neonanodes. Its common name is elegant parrot, but has also been called elegant parakeet, elegant grass parakeet, and grass parrot in the past.[2]
Description
The elegant parrot is 23 cm (9.1 in) long and predominantly golden olive in colour with a dark blue frontal band line above with lighter blue. while abdomen and vent are yellow. The female is a duller shade of olive all over and has a narrower blue frontal band. The wings are predominantly olive with outer flight feathers dark blue. The yellow edged tail has shades of olive and blue. The bill and legs are grey and the eyes dark brown. Juveniles are duller and lack the frontal bands.[2]

Distribution and habitat
The elegant parrot is found in two disjunct regions, one across southwestern Australia from Moora in the north to Merredin and Esperance in the east, and in southeastern South Australia (including Kangaroo Island) north to Marree, and east into western Victoria.[2]
Breeding
Breeding season is anywhere from July to November or after rainfall, with one or occasionally two broods raised depending on rainfall. A hollow higher than 15 m (49 ft) above the ground in a tree, usually a eucalypt along a watercourse or stringybark forest, is utilised for nesting, and a clutch of four to six round white eggs measuring 21 x 18 mm is laid there.[3]
References
- ↑ BirdLife International (2012). "Neophema elegans". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.2. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- 1 2 3 Lendon, Alan H. (1973). Australian Parrots in Field and Aviary (2nd ed.). Sydney: Angus and Robertson. pp. 277–81. ISBN 0-207-12424-8.
- ↑ Beruldsen, G (2003). Australian Birds: Their Nests and Eggs. Kenmore Hills, Qld: self. p. 251. ISBN 0-646-42798-9.
