Niemeyer–Dolan technique
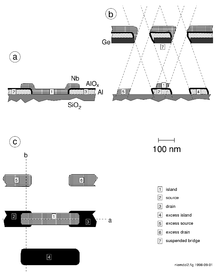
The Niemeyer–Dolan technique, also called the Dolan technique or the shadow evaporation technique, is a thin-film lithographic method to create nanometer-sized overlapping structures.
This technique uses an evaporation mask that is suspended above the substrate (see figure). The evaporation mask can be formed from two layers of resist. Depending on the evaporation angle, the shadow image of the mask is projected onto different positions on the substrate. By carefully choosing the angle for each material to be deposited, adjacent openings in the mask can be projected on the same spot, creating an overlay of two thin films with a well-defined geometry.[1][2][3]
Usage
The Niemeyer–Dolan technique is used to create thin-film electronic nanostructures such as quantum dots and tunnel junctions.
References
- ↑ J. Niemeyer, PTB-Mitt. 84, 251 (1974)
- ↑ J. Niemeyer and V. Kose, Appl. Phys. Lett. 29, 380 (1976), doi:10.1063/1.89094
- ↑ G.J. Dolan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 31, 337 (1977), doi:10.1063/1.89690