Iohexol
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intrathecal, intravascular, oral, intracavital, rectal |
| ATC code | V08AB02 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | Low |
| Metabolism | Nil |
| Biological half-life | Variable |
| Excretion | Renal, unchanged |
| Identifiers | |
| |
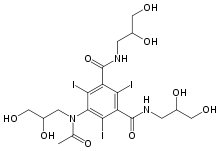
| Synonyms | 5-[N-(2,3-Dihydroxypropyl)acetamido]-2,4,6-triiodo-N,N'-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)isophthalamide |
| CAS Number |
66108-95-0 |
| PubChem (CID) | 3730 |
| DrugBank |
DB01362 |
| ChemSpider |
3599 |
| UNII |
4419T9MX03 |
| KEGG |
D01817 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:31709 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1200455 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.060.130 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H26I3N3O9 |
| Molar mass | 821.138 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Iohexol is a contrast agent, sold under the trade names Omnipaque and Exypaque; this compound is also sold as a density gradient medium under the names Accudenz, Histodenz and Nycodenz.[1][2] It is available in various concentrations, from 140 to 350 milligrams of iodine per milliliter. Omnipaque 350 is commonly used as a contrast agent during coronary angiography.
The osmolality of iohexol ranges from 322 mOsm/kg—approximately 1.1 times that of blood plasma—to 844 mOsm/kg, almost three times that of blood.[3] Despite this difference, iohexol is still considered a low-osmolality contrast agent; the osmolality of older agents, such as diatrizoate, may be more than twice as high.[4]
References
- ↑ "HistoDenz (D2158)", product information sheet, Sigma-Aldrich. Accessed on line Nov. 19, 2015.
- ↑ "Nycodenz®: A universal density gradient medium", Axis-Shield Density Gradient Media. Accessed on line Nov. 19, 2015.
- ↑ GE Healthcare (May 2006). "Omnipaque (Iohexol) injection. Product label". DailyMed. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 2007-03-28.
- ↑ Amersham Health (April 2006). "Hypaque (Diatrizoate Meglumine and Diatrizoate Sodium) injection, solution. Product label". DailyMed. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 2007-03-29.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 4/2/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.