Ornatenton Formation
| Ornatenton Formation Stratigraphic range: Middle Jurassic | |
|---|---|
| Type | Geological formation |
| Sub-units | Macrocephalae Subformation, Ornatenton Subformation, Glaukonitsandmergel Subformation |
| Underlies | Kandern Formation, Impressamergel Formation |
| Overlies | Variansmergel Formation |
| Thickness | up to 50 meters |
| Location | |
| Country | Germany |
The Ornatenton Formation is a Jurassic marine formation in Germany that is middle Callovian in age. The formation represents a shallow marine environment.[1][2][3]
History and naming
The Ornatenton Formation was named by Gert Bloos, Gerd Dietl and Günter Schweigert in 2005. This southern German Jurassic layer had already been previously referred to as the 'Ornatenton' by Friedrich August von Quenstedt in 1857. The formation was named after the ammonite Ammonitus ornatus, today known as Kosmoceras ornatum. A type locality has not yet been determined.
Definition and distribution area
The Ornatenton Formation is composed mainly of mudstone with some iron-oolith benches, glauconitic sandstones, and a horizon of carbonate concretions. It stretches from the Eastern Alps to the Rhine valley, and the facies area stretches into Switzerland where it is known as the ‘argovian’ facies. In southern Germany, the formation is underlain by the Variansmergel Formation and regionally overlapped by the Kandern or Impressamergel Formation, while in the Wutach area it is replaced by the Wutach Formation. Further east, in the French Alps, it dovetails with the Sengenthal Formation. Its thickness varies from a few meters in the Swabian Jura up to about 50 meters in the Plettenberg area.
Time frame and subdivision
The Ornatenton Formation is divided into three subformations: the Macrocephalae Subformation, the Ornatenton Subformation, and the Glaukonitsandmergel Subformation. Some of the sediments of the Ornatenton Formation are dated to the upper Bathonian, but most were deposited during the Callovian. The formation locally reaches into the lower Oxfordian.
Paleofauna
The remains of dinosaurs and marine reptiles are known from the Ornatenton Formation alongside a rich invertebrate fauna including the oyster Gryphaea dilatata along with the ammonites Clydoniceras discus, Bullatimorphies bullatus, Macrocephalites gracilis, Reineckeia anceps, Erymnoceras coronatum, Peltoceras athleta, Quenstedtoceras lamberti, Quenstedtoceras mariae, and Cardioceras cordatum.[1][4][5]
| Vertebrates reported from the Ornatenton Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
|
W. albati |
Partial skeleton belonging to a single individual.[1] |
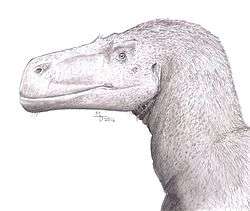
A large megalosaurid theropod. |
| |||
|
L. sp. |
Vertebral centra and teeth.[1] |
|||||
|
M. sp. |
A skull and lower jaws.[1] |
|||||
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Rauhut, Oliver W.M., Hübner, Tom R., and Lanser, Klaus-Peter, 2016, "A new megalosaurid theropod dinosaur from the late Middle Jurassic (Callovian) of north-western Germany: Implications for theropod evolution and faunal turnover in the Jurassic", Palaeontologia Electronica 19.2.26A: 1-65
- ↑ Mönnig, E. 1993, "Die Ornatenton-Formation in NW Deutschland." Newsletter in Stratigraphy, 28(2/3):131-150. (In German)
- ↑ Riegraf, W. 1994, "Der Ornatenton in Deutschland und seine Äquivalente", pp. 7-72. In Martill, D.M. and Hudson, J.D. (eds.), Fossilien aus Ornatenton und Oxford Clay. Goldschneck-Verlag, Korb. (In German)
- ↑ Lange, W. 1973, "Ammoniten und Ostreen (Biostratigraphie, Ökologie, Zoogeographie) des Calloviums - Oxfordium Grenzbereichs im Wiehengebirge." Münstersche Forschungen Geologie und Paläontologie, 27:1-209. (In German)
- ↑ Klassen, H. 1984. Geologie des Osnabrücker Berglandes XVI. Naturwissenschaftliches Museum, Osnabrück. (In German)