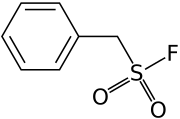
PMSF
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride | |
| Identifiers | |
| 329-98-6 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:8102 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL190503 |
| ChemSpider | 4620 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.774 |
| KEGG | C06747 |
| MeSH | Phenylmethylsulfonyl+fluoride |
| PubChem | 4784 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H7FO2S | |
| Molar mass | 174.194 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
In biochemistry, phenylmethane sulfonyl fluoride or phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) is a serine protease inhibitor commonly used in the preparation of cell lysates. PMSF does not inhibit all serine proteases. It is rapidly degraded in water and stock solutions are usually made up in anhydrous ethanol, isopropanol, corn oil, or DMSO. Proteolytic inhibition occurs when a concentration between 0.1 - 1 mM PMSF is used. The half-life is short in aqueous solutions (110 min at pH 7, 55 min at pH 7.5, and 35 min at pH 8, all at 25 °C).[1]
PMSF binds specifically to the active site serine residue in a serine protease. It does not bind to any other serine residues in the protein. This is a result of the hyperactivity of that serine residue caused by the specific environmental conditions in the enzyme's active site. Because PMSF binds covalently to the enzyme, the complex can be viewed by X-ray crystallography; it can therefore be used as a chemical label to identify an essential active site serine in an enzyme.
- Enzyme(active)Ser-O-H + F-SO2CH2C6H5 → EnzymeSer-O-SO2CH2C6H5 + HF
- Serine protease + PMSF → Irreversible enzyme-PMS complex + HF
The median lethal dose is less than 500 mg/kg. PMSF is a cytotoxic chemical which should be handled only inside a fume hood.
PMSF is commonly used in protein solublization in order to deactivate proteases from digesting proteins of interest after cell lysis.
References
- ↑ GT James (1978). "Inactivation of the protease inhibitor phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride in buffers". Analytical Biochemistry. 86 (2): 574–9. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(78)90784-4. PMID 26289.
External links
- The MEROPS online database for peptidases and their inhibitors: PMSF