Perinone
 | |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| 4424-06-0 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 70517 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.022.363 |
| EC Number | 224-597-4 |
| PubChem | 78141 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C26H12N4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 412.41 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Orange solid |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
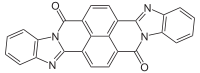
Perinone is a class of organic compounds. The parent compound has two isomers, each of which are useful pigments.
It is prepared from naphthalenetetracarboxylic dianhydride by condensation with o-phenylenediamine. The two Isomers of perinone[1] are useful pigments. The trans isomer is called Pigment Orange 43 ("PO43") and the cis isomer is called Pigment Red 194 ("PR194").[2] Like some structurally related compounds perinone is also an organic semiconductor.[3]
References
- ↑ Jin Mizuguchi Crystal Structure and Electronic Characterization of trans-and cis-Perinone Pigments J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, vol. 108, pp. 8926–8930. doi:10.1021/jp031351d
- ↑ K. Hunger. W. Herbst "Pigments, Organic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2012. doi:10.1002/14356007.a20_371
- ↑ W. James Feast et al.: Poly(4-vinyltriphenylamine): synthesis and application as a hole transport layer in light-emitting diodes. In: Polymer Bulletin 42, 1999, S. 167–174.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/26/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.