Personal RF safety monitors
Electromagnetic field densitometers measure the exposure to electromagnetic radiation in certain ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. This article concentrates on densitometers used in the telecommunication industry, which measure exposure to radio spectrum radiation. Other densitometers, like extremely low frequency densitometers which measure exposure to radiation from electric power lines, also exist. The major difference between a "Densitometer" and a "Dosimeter" is that a Dosimeter can measure the absorbed dose, which does not exist for RF Monitors. Monitors are also separated by "RF Monitors" that simply measure fields and "RF Personal Monitors" that are designed to function while mounted on the human body.
Introduction
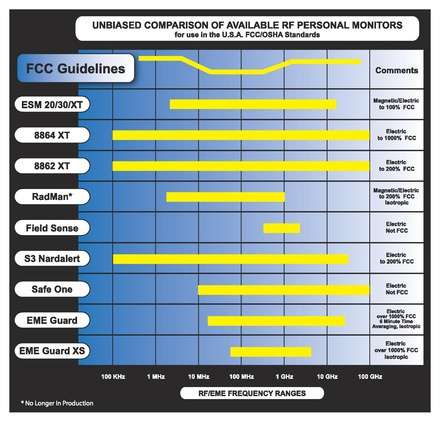
Electromagnetic field densitometers, as used in the cellular phone industry, are referred to as "personal RF safety monitors" or personal protection monitors (PPM).[1] They form part of the personal protective equipment worn by a person working in areas exposed to radio spectrum radiation. A personal RF safety monitor is typically worn either on the torso region of the body or handheld and is required by the occupational safety and health acts of many telecommunication companies.
Most of the scientifically proven RF safety monitors are designed to measure the RF exposure as a percentage of the two most common international RF safety guidelines: International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP) guidelines[2] and the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC).[3] The ICNIRP guidelines are also endorsed by the WHO.[4] RF Personal Safety monitors were originally designed for RF Engineers working in environments where they could be exposed to high levels of RF energy or be working close to a RF source, for example working at the top of a telecommunication tower, or working on the rooftop of a building with transmitting antennas present. Most international RF safety programs include the training and use of RF Personal safety monitors and the IEEE C95.7 specifies what an RF Personal Monitor is.[5]
In some cases the RF safety monitor comes in a version or mode for the general public.[6] These meters can then be used to determine areas where the public might be exposed to high levels of RF energy or it might be used to indicate the RF level at areas where the general public has access.
Specification
The specifications of a RF monitor determines the work environment it can be used for. Wideband RF monitors can be used at a broader variety of base station site types than for example a narrowband, cellular RF monitor which is designed only to be used in the mobile telephone- and data networks. Below find a table with the different basic specifications of some RF monitors:
| Specification | EME Guard XS [7] | Narda Radman Mobile [8] | SafeOne [9] | fieldSENSE [10] | EME Guard [11] | Nardalert S3 [12] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency Range | 80 MHz – 6 GHz | E-Field 50 MHz - 6 GHz
H-Field 50 MHz – 1 GHz |
10-10000 MHz | E-Field 380 MHz- 2.7 GHz | 27 MHz- 40 GHz | 100 kHz- 50 GHz |
| Directivity | Isotropic (Tri-axial) | Isotropic (Tri-axial) | Isotropic (Tri-axial) | Vertically Polarized | Isotropic (Tri-axial) | Radial and Dual-polarized |
| Reference standard | ICNIRP
FCC Safety Code 6 User-definable 2004/40/EC |
ICNIRP
FCC Safety Code 6 |
ICNIRP
FCC IEEE NCRP Safety Code 6 |
ICNIRP
FCC IEEE NCRP |
ICNIRP
FCC Safety Code 6 User-definable |
FCC
IEEE C95.1 Safety Code 6 (2015) ICNIRP |
| Exposure level indicators | 1 X LED => 1%
2 X LED => 5% 3 X LED => 20% 4 X LED => 100% 5 X LED => 225% 6 X LED => 500% 7 X LED => 2000% (Broadcast 100 MHz: Visual & Audio Alarms Activated 5 to 350 V/m User-definable at factory) |
1 X LED => 12.5%
2 X LED => 25% 3 X LED => 50% (Buzzer alarm) 4 X LED => 100% (Buzzer alarm) |
1 X LED => 5%
2 X LED => 15% 3 X LED => 40% 4 X LED => 63% (1 Hz buzzer alarm) 5 X LED => 100% (1 Hz buzzer alarm) 6 X LED => 160% (2 Hz buzzer alarm) 7 X LED => 250% (4 Hz buzzer alarm) |
1 X LED => 25%
2 X LED => 50% 3 X LED => 75% 4 X LED => 100% (Vibrator and buzzer alarm user-definable) |
User Variable (if Authorized)
Defaults are 50 and 200% Audio, Visual and/or Vibrate | |
| Data logger | No | No | No | No | Yes | Optional |
| Battery life | >100 hours | 200 hours | 2,000 hours | 250 hours | >100 hours | > 40 Hours (Rechargeable via USB) |
| Dimensions | 132.5 x 48.5 x 28.7 mm | 157 X 36 X 26 mm | 58 x 105 x 23 mm | 132 X 41 X 23 mm | 172 X 60 X 35 mm | 120 x 83 x 32 mm |
| Weight | 120g | 130g | 88g | 91g | 320g | 230g |
| Operating temperature | -10⁰C to +50⁰C | -10⁰C to + 55⁰C | -10⁰C to +40⁰C | -10⁰C to +50⁰C | -10⁰C to +50⁰C | -10⁰C to +50⁰C |
| Calibration interval | 24 Months | 36 Months | 24 Months | 24 Months | 24 Months | 48 Months |
| Approx. price USD | $550 | $700 | $700 | $500 | $1800 | $1700 |
Operating instructions
Each specific personal RF safety monitor has its own operating instructions. And most of the monitors have different operating modes. For instance, the Narda Radman has a mode in which it can be body worn by the operator, but it also has a probe mode where the operator can scan certain areas to find accurate exclusion zones.[13] The fieldSENSE on the other hand has a monitor and measure mode.[14] The measure mode is similar to the Radman’s probe mode, but the monitor mode is used by mounting the fieldSENSE onto an inactive antenna and then it is safe to work on the antenna until the fieldSENSE raise an alarm to warn RF technicians that the antenna is live and that any work on the antennas should be ceased until deactivation is confirmed. A few of the newer models of RF monitors such as the EME Guard also have a data logging functionality that can log the RF exposure of a worker over time.[15][11]
List of personal RF monitors
- EME Guard [16]
- EME Guard XS[17]
- EME SPY 201[18]
- Narda Radman Mobile [19]
- Narda Radman XT [20]
- Nardalert S3[21]
- Occupational fieldSENSE [22]
- Public fieldSENSE [6]
- SafeOne® Pro SI-1100XT[9]
- FlashRad [23]
Gallery
-

Guard RF Safety Monitor
-

EME Guard XS Safety Monitor for RF
-

Occupational fieldSENSE unit
-

Narda Radman unit
-

Scan for leak in RF feeder
-

Nardalert S3
References
- ↑ https://books.google.com/books?id=V8Lk2ghPl7IC&pg=PA1904&lpg=PA1904&dq=fcc+rf+monitors+ppm&source=bl&ots=b0TqBCuBJ6&sig=9QyY-CcpuSi8i9vrc-ZaafMYpgY&hl=en&sa=X&ei=fEoQVYeFLY_5yQTD4oCQBA&ved=0CEkQ6AEwBw#v=onepage&q=fcc%20rf%20monitors%20ppm&f=false
- ↑ https://www.osha.gov/dts/osta/otm/otm_ii/otm_ii_3.html
- ↑ http://www.fcc.gov/oet/ea/eameasurements.html
- ↑ "WHO/ICNIRP Conference on EMF Biological Effects" (PDF). World Health Organization. 2001-12-10.
- ↑ http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/login.jsp?tp=&arnumber=1611107&url=http%3A%2F%2Fieeexplore.ieee.org%2Fxpls%2Fabs_all.jsp%3Farnumber%3D1611107|title"IEEE Recommended Practice for Radio Frequency Safety Programs, 3 kHz to 300 GHz," IEEE, International Committee on Electromagnetic Safety, New York, IEEE Std C95.7, 2014
- 1 2 "Public product info". fieldSENSE. Retrieved 2012-04-02.
- ↑ "EME Guard XS" (PDF). RF Monitors EME Guard XS. RSIcorp.com. Retrieved 7 June 2016.
- ↑ "Narda Safety Test Solutions RadMan Datasheet" (PDF). Narda-sts.us. Retrieved 2012-06-06.
- 1 2 http://www.lbagroup.com/products/safeone-rf-monitors
- ↑ "fieldSENSE" (PDF). fieldSENSE. Retrieved 2012-04-02.
- 1 2 "EME Guard" (PDF). RF Monitors EME Guard. RSIcorp.com. Retrieved 7 June 2016.
- ↑ "Narda Safety Test Solutions Nardalert S3 Datasheet" (PDF). Narda-sts.us. Retrieved 2016-06-06.
- ↑ "Radman - Measure and probe mode".
- ↑ "fieldSENSE - Measure and monitor mode".
- ↑ "Narda Safety Test Solutions" (PDF). Narda-sts.us. Retrieved 2012-04-02.
- ↑ "EME Guard - MVG (Satimo)". RSIcorp.com. 2016-06-06. Retrieved 2016-06-06.
- ↑ "EME Guard XS - RSIcorp.com MVG (Satimo)". RSIcorp.com. 2016-06-06. Retrieved 2016-06-06.
- ↑ "EME SPY 201 - MVG (Satimo)".
- ↑ "Narda Radman Mobile" (PDF). Narda-sts.us. 2011-06-06. Retrieved 2012-06-06.
- ↑ "Narda Radman (XT)". Narda-sts.de. 2011-12-15. Retrieved 2012-04-02.
- ↑ "Nardalert S3 - NARDA STS". Narda-sts.us. 2016-06-06. Retrieved 2012-06-06.
- ↑ "Occupational product info". fieldSENSE. Retrieved 2012-04-02.
- ↑ "FlashRad - RSIcorp.com MVG (Satimo)" (PDF). RSIcorp.com. 2015-08-31.