Pessary
A pessary is a medical device inserted into the vagina, either to provide structural support, or as a method of delivering medication.[1]
Types of pessaries
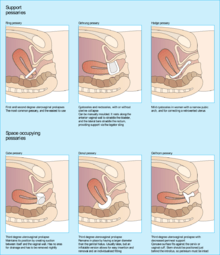
Therapeutic pessaries
A therapeutic pessary is a medical device similar to the outer ring of a diaphragm. Therapeutic pessaries are used to support the uterus, vagina, bladder, or rectum. Pessaries are a treatment option for pelvic organ prolapse.[2] A pessary is most commonly used to treat prolapse of the uterus. It is also used to treat stress urinary incontinence, a retroverted uterus, cystocele and rectocele. Historically, pessaries may have been used to perform abortions.
The Cerclage Pessary is used to treat pregnant women with cervical incompetence in order to support the cervix and turn it backward towards the sacrum. It may be indicated in pregnancies with a history of premature labor, multiple pregnancies or mothers who are exposed to physical strain (e.g. standing for a long time). It may also be indicated in pregnant women suffering from prolapse of the genital organs.[3]
The pessary can be placed temporarily or permanently, and must be fitted by a physician, physician assistant, midwife, or advanced practice nurse. Some pessaries can be worn during intercourse.
Pharmaceutical pessaries
A pharmaceutical pessary is used as a very effective means of delivery of pharmaceutical substances easily absorbed through the skin of the vagina, or intended to have action in the locality, for example against inflammation or yeast infection, or on the uterus. Pessaries were used as birth control in ancient times.
Occlusive pessaries
An occlusive pessary is generally used in combination with spermicide as a contraceptive.
Stem pessary
The stem pessary, a type of occlusive pessary, was an early form of the cervical cap. Shaped like a dome, it covered the cervix, and a central rod or "stem" entered the uterus through the os, to hold it in place.[4]
General side effects
Side effects that are shared among most different types of pessaries are risks of increased vaginal discharge, vaginal irritation, ulceration, bleeding, and dyspareunia (painful intercourse for the male or female).
See also
References
- ↑ http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/pessary?s=t
- ↑ American Urogynecologic Society (May 5, 2015), "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question", Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the ABIM Foundation, American Urogynecologic Society, retrieved June 1, 2015, which cites: * Culligan, PJ (April 2012). "Nonsurgical management of pelvic organ prolapse.". Obstetrics and gynecology. 119 (4): 852–60. doi:10.1097/aog.0b013e31824c0806. PMID 22433350.
- ACOG Committee on Practice, Bulletins--Gynecology (September 2007). "ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 85: Pelvic organ prolapse.". Obstetrics and gynecology. 110 (3): 717–29. doi:10.1097/01.aog.0000263925.97887.72. PMID 17766624..
- ↑ http://www.dr-arabin.de/e/cerclage.html
- ↑ Contraceptive Stem Pessary in Aluminium
-solution.jpg)


