Phosducin
| PDC | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
|||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | PDC, MEKA, PHD, PhLOP, PhLP, phosducin | ||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | MGI: 98090 HomoloGene: 1950 GeneCards: PDC | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||||||
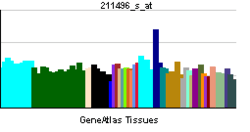 | |||||||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||||||
| Entrez | |||||||||||||||||
| Ensembl | |||||||||||||||||
| UniProt | |||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | |||||||||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 1: 186.44 – 186.46 Mb | Chr 1: 150.32 – 150.33 Mb | |||||||||||||||
| PubMed search | [1] | [2] | |||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
Phosducin, also known as PDC, is a human protein and gene.[3] It belongs to phosducin family of proteins.
This gene encodes a phosphoprotein, which is located in the outer and inner segments of the rod cells in the retina. This protein may participate in the regulation of visual phototransduction or in the integration of photoreceptor metabolism. It modulates the phototransduction cascade by interacting with the beta and gamma subunits of the retinal G-protein transducin. By associating with these subunits only, the Transducin alpha subunit will remain active for longer. This will increase the amount of time of visual excitation.
This gene is a potential candidate gene for retinitis pigmentosa and Usher syndrome type II. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified.[3]
See also
References
Further reading
- Abe T, Nakabayashi H, Tamada H, et al. (1990). "Analysis of the human, bovine and rat 33-kDa proteins and cDNA in retina and pineal gland". Gene. 91 (2): 209–15. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(90)90090-E. PMID 2210381.
- Watanabe Y, Kawasaki K, Miki N, Kuo CH (1990). "Isolation and analysis of the human MEKA gene encoding a retina-specific protein". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 170 (2): 951–6. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(90)92183-Z. PMID 2383274.
- Lee RH, Brown BM, Lolley RN (1990). "Protein kinase A phosphorylates retinal phosducin on serine 73 in situ". J. Biol. Chem. 265 (26): 15860–6. PMID 2394752.
- Hawes BE, Touhara K, Kurose H, et al. (1994). "Determination of the G beta gamma-binding domain of phosducin. A regulatable modulator of G beta gamma signaling". J. Biol. Chem. 269 (47): 29825–30. PMID 7961975.
- Abe T, Kikuchi T, Shinohara T (1994). "The sequence of the human phosducin gene (PDC) and its 5'-flanking region". Genomics. 19 (2): 369–72. doi:10.1006/geno.1994.1072. PMID 8188267.
- Sparkes RS, Lee RH, Shinohara T, et al. (1994). "Assignment of the phosducin (PDC) gene to human chromosome 1q25-1q32.1 by somatic cell hybridization and in situ hybridization". Genomics. 18 (2): 426–8. doi:10.1006/geno.1993.1490. PMID 8288249.
- Ding C, Li X, Griffin CA, et al. (1994). "The gene for human phosducin (PDC), a soluble protein that binds G-protein beta gamma dimers, maps to 1q25-q31.1". Genomics. 18 (2): 457–9. doi:10.1006/geno.1993.1501. PMID 8288259.
- Boekhoff I, Touhara K, Danner S, et al. (1997). "Phosducin, potential role in modulation of olfactory signaling". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (7): 4606–12. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.7.4606. PMID 9020189.
- Barhite S, Thibault C, Miles MF (1998). "Phosducin-like protein (PhLP), a regulator of G beta gamma function, interacts with the proteasomal protein SUG1". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1402 (1): 95–101. doi:10.1016/S0167-4889(97)00141-9. PMID 9551090.
- Zhu X, Craft CM (1998). "Interaction of phosducin and phosducin isoforms with a 26S proteasomal subunit, SUG1". Mol. Vis. 4: 13. PMID 9701609.
- Craft CM, Xu J, Slepak VZ, et al. (1998). "PhLPs and PhLOPs in the phosducin family of G beta gamma binding proteins". Biochemistry. 37 (45): 15758–72. doi:10.1021/bi980921a. PMID 9843381.
- Carpten JD, Makalowska I, Robbins CM, et al. (2000). "A 6-Mb high-resolution physical and transcription map encompassing the hereditary prostate cancer 1 (HPC1) region". Genomics. 64 (1): 1–14. doi:10.1006/geno.1999.6051. PMID 10708513.
- Zhu X, Craft CM (2000). "The carboxyl terminal domain of phosducin functions as a transcriptional activator". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 270 (2): 504–9. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2000.2414. PMID 10753654.
- Zhu X, Craft CM (2000). "Modulation of CRX transactivation activity by phosducin isoforms". Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (14): 5216–26. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.14.5216-5226.2000. PMC 85970
 . PMID 10866677.
. PMID 10866677. - Ruiz-Gómez A, Humrich J, Murga C, et al. (2000). "Phosphorylation of phosducin and phosducin-like protein by G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (38): 29724–30. doi:10.1074/jbc.M001864200. PMID 10884381.
- Nakano K, Chen J, Tarr GE, et al. (2001). "Rethinking the role of phosducin: light-regulated binding of phosducin to 14-3-3 in rod inner segments". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98 (8): 4693–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.071067198. PMC 31896
 . PMID 11287646.
. PMID 11287646. - Thulin CD, Savage JR, McLaughlin JN, et al. (2001). "Modulation of the G protein regulator phosducin by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II phosphorylation and 14-3-3 protein binding". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (26): 23805–15. doi:10.1074/jbc.M101482200. PMID 11331285.
- Wistow G, Bernstein SL, Wyatt MK, et al. (2002). "Expressed sequence tag analysis of human retina for the NEIBank Project: retbindin, an abundant, novel retinal cDNA and alternative splicing of other retina-preferred gene transcripts". Mol. Vis. 8: 196–204. PMID 12107411.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241
 . PMID 12477932.
. PMID 12477932. - Margulis A, Dang L, Pulukuri S, et al. (2002). "Presence of phosducin in the nuclei of bovine retinal cells". Mol. Vis. 8: 477–82. PMID 12500174.
