Poekilopleuron
| Poekilopleuron Temporal range: Middle Jurassic, 167.7–166.1 Ma | |
|---|---|
| | |
| Cast of the holotype gastralia, Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Order: | Saurischia |
| Suborder: | Theropoda |
| Family: | †Megalosauridae |
| Subfamily: | †Afrovenatorinae |
| Genus: | †Poekilopleuron Eudes-Deslongchamps, 1838 |
| Type species | |
| Poekilopleuron bucklandii Eudes-Deslongchamps, 1838 | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
|
Genus synonyms
Species synonyms
| |
Poekilopleuron (meaning "varied ribs") is an extinct genus of megalosauroid tetanuran theropod dinosaur, which lived during the middle Bathonian of the Jurassic, about 168 to 166 million years ago. The genus has been used under many different spelling variants, although only one, Poekilopleuron, is valid. The type species is P. bucklandii, named after William Buckland, and many junior synonyms of it have also been erected. Few material is currently known, as the holotype was destroyed in World War II, although many casts of the material still exist.
Discovery and naming
Poekilopleuron is a genus of theropod with a long and complex history. The genus was first named and described by Jacques Amand Eudes-Deslongchamps in 1838, based on holotype material that is now destroyed. The holotype, which was housed in Musée de la Faculté des Sciences de Caen and destroyed during World War II, included gastralia, phalanges, a left forelimb, caudal vertebrae, chevrons, ribs and a hindlimb. Of all the material, few is still preserved, although the gastralia, phalanges and forelimb were casted and now represent the plastotype, with casts in the Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle (specimen MNHN 1897-2) and Yale Peabody Museum (specimen YPM 4938). The original material was uncovered in a layer of the Calcaire de Caen in Normandy, France. Poekilopleuron can be assigned to the middle Bathonian in age,[1] about 167.7 to 166 million years ago.[2]
In the same 1838 publication, Eudes-Deslongchamps also named the type species of Poekilopleuron, P. bucklandii.[3] Eudes-Deslongchapms noted similarities with some material of Megalosaurus bucklandii and Poekilopleuron, and chose the species name bucklandii for Poekilopleuron, so that it the two genera were synonymized, only the genus name would be suppressed.[1] The generic name is derived from Greek ποίκιλος, poikilos, "varied", and πλευρών, pleuron, "rib", a reference to the three types of rib present. The specific name, honouring William Buckland, was deliberately identical to that of Megalosaurus bucklandii.
Classification
Poekilopleuron is a hard taxon to classify, as its original material is lost, and few casts are known. Poekilopleuron has a history of being renamed under different species and genera, most of which are now its junior synonyms.[1]
Eudes-Deslongchamps thought the specimen might well be proven to belong to this earlier named species; if so, merely the generic name would have to be changed. Indeed, following 1879 Poekilopleuron was often subsumed under Megalosaurus bucklandii.[4] Eudes-Deslongchamps' choice caused problems however, when Friedrich von Huene in 1923 concluded it was part of Megalosaurus but as a separate species within that genus. As both species carried the same epithet bucklandii, they could no longer be distinguished. Von Huene therefore renamed the species into Megalosaurus poekilopleuron. Most later authors continued using the generic name Poekilopleuron.
Another problem was caused by the fact that the name was only partially Latinised. In correct Greek it would have been "poikilopleuron", in Latin "poecilopleurum". This induced later writers to improve the spelling, leading to such variants as Poecilopleuron and Poikilopleuron (still used as late as 2006). However, the original name has priority and is valid.
Five other species would be named in the genus. In 1869 Edward Drinker Cope renamed Laelaps gallicus into Poekilopleuron gallicum. In 1870 Joseph Leidy created a Poicilopleuron valens based on a fossil probably belonging to Allosaurus.[5] In 1876 Richard Owen named a Poikilopleuron pusillus, in 1879 renamed by Cope to Poekilopleuron minor; in 1887 Harry Govier Seeley made it a separate genus: Aristosuchus.[6] In 1883 W.A. Kiprijanow created a Poekilopleuron schmidti, of which the specific name honours Friedrich Schmidt, based on some indeterminate ribs and a sauropod metatarsal.[7] This chimaera is a nomen dubium. A much later named species is Poekilopleuron valesdunensis created by Ronan Allain in 2002.[8] In 2005 it was renamed Dubreuillosaurus.[9]
Because the original fossil was destroyed and no other remains of Poekilopleuron have since been found, and also because of its name change, there is much controversy surrounding its classification that cannot be resolved. Traditionally it has been assigned to the Megalosauridae, but some recent analyses showed a position in the Sinraptoridae; others had as result it was a member of Megalosauroidea, in a basal position or in the Eustreptospondylinae. Benson et al. (2010) found it and Lourinhanosaurus to belong to Sinraptoridae.[10] An earlier study found that it was a primitive allosauroid outside Sinraptoridae.[11]
Description
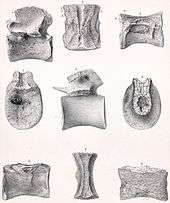
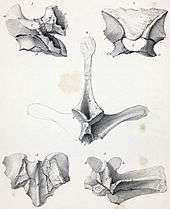
The most distinctive feature of Poekilopleuron were its forelimbs. Their length, about 60 cm, was a sign of this theropod's more original build. Unlike later Theropoda, whose forelimbs tended toward reduction in length in proportion to the animals' size, Poekilopleuron's were long and, by implication, potent. The length mostly resided in the elongated but powerfully muscled humerus. The antebrachia (forearms) were markedly short and robust, a characteristic shared with Poekilopleuron's slightly later and considerably larger American cousin Torvosaurus. A unique feature is a lack of the olecranon process on the ulna.[1]
The fossil of Poekilopleuron showed a rare complete set of gastralia: fourteen pair of belly ribs supported the body of the animal.[1]
Paleobiology
The material of Poekilopleuron bucklandii includes two tail vertebrae with the chevron of one vertebra ankylosed to the centrum of the next within the development of an exostosis. Two phalanges also preserve pathologies. One probable pedal phalanx shows three low, irregular exostosis-like projections. A second probable manual phalanx exhibits a "low rounded projection resembling a callus." Ralph Molnar considered the occurrence of three pathologies in one individual to be "noteworthy". Sadly the specimens cannot be examined further to determine the etiology of the pathologies because of their destruction during the British bombing raid in 1944.[12]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Allain R.; Chure D. J. (2002). "Poekilopleuron bucklandii, the theropod dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic (Bathonian) of Normandy" (PDF). Palaeontology. 45 (6): 1107–1121. doi:10.1111/1475-4983.00277.
- ↑ Holtz, T.R. Jr (2012). "Updated genus list for Holtz (2007) Dinosaurs" (PDF). University of Maryland. p. 8.
- ↑ Eudes-Deslongchamps A (1838). "Mémoire sur le Poekilopleuron bucklandii, grande saurien fossile, intermédiaire entre les crocodiles et les lézards, découvert dans les carrières de la Maladrerie, près Caen, au mois de juillet 1835". Mémoires de la Société Linnéenne Normandie. 6: 1–114.
- ↑ Hulke J.W. (1879). "Note on Poekilopleuron bucklandi of Eudes Deslongchamps (père), identifying it with Megalosaurus bucklandi". Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society. 35 (1-4): 233–238. doi:10.1144/GSL.JGS.1879.035.01-04.10.
- ↑ Leidy J (1870). "Remarks on Poicilopleuron valens, Clidastes intermedius, Leiodon proriger, Baptemys wyomingensis, and Emys stevensonianus". Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences. 22 (1): 3–4. JSTOR 4624064.
- ↑ Seeley H.G. (1887). "On Aristosuchus pusillus Owen, being further notes on the fossils described by Sir R. Owen as Poikilopleuron pusillus Owen". Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society of London. 43: 221–228. doi:10.1144/GSL.JGS.1887.043.01-04.22.
- ↑ Kiprijanow W.A. (1883). "Studien über die Fossilen Reptilien Russlands. IV. Theil. Ordnung Crocodilia Oppel. Indeterminierte Fossile Reptilien". Mémoires de l'Académie Impériale des Sciences de Saint-Pétersbourg. VIIe série. 31 (7): 1–29.
- ↑ Allain R (2002). "Discovery of megalosaur (Dinosauria, Theropoda) in the Middle Bathonian of Normandy (France) and its implications for the phylogeny of basal Tetanurae". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 22 (3): 548–563. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2002)022[0548:DOMDTI]2.0.CO;2.
- ↑ Allain R (2005). "The postcranial anatomy of the megalosaur Dubreuillosaurus valesdunensis (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Middle Jurassic of Normandy, France". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 25 (4): 850–858. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2005)025[0850:TPAOTM]2.0.CO;2.
- ↑ Benson, R.B.J., Carrano, M.T and Brusatte, S.L. (2010). "A new clade of archaic large-bodied predatory dinosaurs (Theropoda: Allosauroidea) that survived to the latest Mesozoic". Naturwissenschaften. 97 (1): 71–78. Bibcode:2010NW.....97...71B. doi:10.1007/s00114-009-0614-x. PMID 19826771. Supporting Information
- ↑ Allain R (2001). "Redescription de Streptospondylus altdorfensis, le dinosaure théropode de Cuvier, du Jurassique de Normandie [Redescription of Streptospondylus altdorfensis, Cuvier's theropod dinosaur from the Jurassic of Normandy]" (PDF). Geodiversitas. 23 (3): 349–367.
- ↑ Molnar, R. E., 2001, Theropod paleopathology: a literature survey: In: Mesozoic Vertebrate Life, edited by Tanke, D. H., and Carpenter, K., Indiana University Press, p. 337-363.