Protein topology
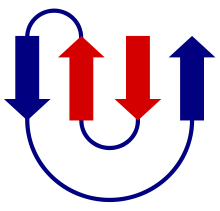
Topology of beta-strands in "Greek-key" protein motif.
Protein topology refers to mutual orientation of regular secondary structures, such as alpha-helices and beta strands in protein structure [1] . For example, two adjacent interacting alpha-helices or beta-strands can go in the same or in opposite directions. Topology diagrams of different proteins with known three-dimensional structure are provided by PDBsum (an example).
See also
References
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 12/8/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.