Pseudoterminal
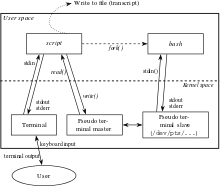
scriptIn some operating systems, including Unix, a pseudoterminal, pseudotty, or PTY is a pair of pseudo-devices, one of which, the slave, emulates a real text terminal device, the other of which, the master, provides the means by which a terminal emulator process controls the slave.
History
Pseudoterminals were present in the DEC PDP-6 Timesharing Monitor at least as early as 1967, and were used to implement batch processing.[1] They are described in the documentation for the succeeding TOPS-10 on the PDP-10.[2] Other DEC operating systems also had PTYs, including RSTS/E for the PDP-11, as did the third-party TENEX operating system for the PDP-10.
Unix pseudoterminals originated in 1983 during the development of Eighth Edition Unix and were based on a similar feature in TENEX.[3] They were part of the 4.2 release of BSD. AT&T's System V included support for pseudoterminals as a driver in their STREAMS device model, along with the pseudoterminal multiplexer.
The Linux Programming Interface from 2010 contains an entire chapter (chapter 64 "Pseudoterminals" p1375–1399.) explaining pseudoterminals. Then there is another one, Chapter 62 "Terminals", dedicated to terminals.
Applications
The role of the terminal emulator process is:
- to interact with the user.
- to feed text input to the master pseudo-device for use by the shell (such as bash), which is connected to the slave pseudo-device.
- to read text output from the master pseudo-device and show it to the user.
The terminal emulator process must also handle terminal control commands, e.g., for resizing the screen. Widely used terminal emulator programs include xterm, GNOME Terminal, Konsole, and Terminal. Remote login handlers such as ssh and telnet servers play the same role but communicate with a remote user instead of a local one. Also consider programs such as expect.
Screen and Tmux are used to add a session context to a pseudoterminal, making for a much more robust and versatile solution. For example, each provides terminal persistence, allowing a user to disconnect from one computer and then connect later from another computer.
Variants
In the BSD PTY system, the slave device file, which generally has a name of the form /dev/tty[p-za-e][0-9a-f], supports all system calls applicable to text terminal devices. Thus it supports login sessions. The master device file, which generally has a name of the form /dev/pty[p-za-e][0-9a-f], is the endpoint for communication with the terminal emulator. With this [p-za-e] naming scheme, there can be at most 256 tty pairs. Also, finding the first free pty master can be racy unless a locking scheme is adopted. For that reason, recent BSD operating systems, such as FreeBSD, implement Unix98 PTYs.[4]
BSD PTYs have been rendered obsolete by Unix98 ptys whose naming system does not limit the number of pseudo-terminals and access to which occurs without danger of race conditions. /dev/ptmx is the "pseudo-terminal master multiplexer". Opening it returns a file descriptor of a master node and causes an associated slave node /dev/pts/N to be created.[5]
References
- ↑ http://groups.google.com/group/alt.sys.pdp10/msg/5d96697ebf5c7bcf[]
- ↑ PDP-10 Timesharing Monitors Programmer's Reference Manual section 5.10
- ↑ Ritchie, D. M. "A stream input-output system". AT&T Bell Laboratories Technical Journal. 63 (8): 1897–1910. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.48.3730
 .
. - ↑ "pty". man page. FreeBSD.
- ↑ pts(4): pseudo-terminal master/slave - Linux man page
External links
- Containers, pseudo TTYs, and backward compatibility, LWN.net, June 1, 2016, by Neil Brown