Quasi-crystals (supramolecular)
Quasi-crystals are supramolecular aggregates exhibiting both crystalline (solid) properties as well as amorphous, liquid-like properties.
Self-organized structures termed "quasi-crystals" were originally described in 1978 by the Israeli scientist Valeri A. Krongauz of the Weizmann Institute of Science, in the Nature paper, Quasi-crystals from irradiated photochromic dyes in an applied electric field. [1]
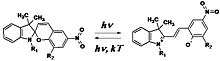
In his 1978 paper Krongauz coined the term “Quasi-Crystals” for the new self-organized colloidal particles . The Quasi-crystals are supramolecular aggregates manifesting both crystalline properties e.g. Bragg scattering, as well as amorphous, liquid-like properties i.e. drop-like shapes, fluidity, extensibility and elasticity in electric field. The supramolecular Quasi-crystals are produced in photochemical reaction by exposing solutions of photochromic spiropyran molecules to UV radiation. The ultraviolet light induces the conversion of the spiropyrans to merocyanine molecules that manifest electric dipole moments. (see Scheme 1). The quasi-crystals have external shape of submicron globules and their internal structure consists of crystals enveloped by an amorphous matter(see Fig. 1).The crystals are formed by self-assembled stacks of the merocyanine molecular dipoles aligningthemselves in a parallel manner, while amorphous envelopes consist of thesame merocyanine dipoles aligned in an anti-parallel manner (Fig.1, Scheme2).[2][3][4] In an applied electrostatic field, quasi-crystals form macroscopic threads that show linear optical dichroism.[1][5]
Later Krongauz described unusual phase transitions of molecules composedof mesogenic and spiropyran moieties, which he named "quasi-liquidcrystals." A micrograph of their mesophase appeared on the cover of Nature in a 1984 paper, “Quasi-Liquid Crystals.”[6] The investigation of spiropyran-merocyanineself-organized systems, including macromolecules (see, for example, Fig. 2),has continued over the years.[7][8][9][10][11]
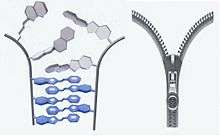
These studies have resulted in discoveries ofunusual and practically significant phenomena. Thus, in the electrostatic field, quasi-crystals andquasi-liquid crystals have exhibited 2nd order non-linear opticalproperties.[12][13][14]
Potential applications of these fascinating materials have been described and patented.[15][16][17]
Work on spiropyran-merocyanineself-assemblies currently continues in several laboratories –see, for example,reference [18] and the references cited in that study.[18]
References
- 1 2 V. A. Krongauz; E. S. Goldburt (5 January 1978). "Quasi-crystals from irradiated photochromic dyes in an applied electric field,". Nature. 271 (5640): 43–45. Bibcode:1978Natur.271...40V. doi:10.1038/271040b0. Retrieved 24 April 2014.
- ↑ V. A. Krongauz; S. N. Fishman; E. S. Goldburt (1978). "Quasi-crystals. Growth from photochromic spiropyrans on irradiation in a constant electric field". J. Phys. Chem. 82 (23): 2469–2474. doi:10.1021/j100512a004. Retrieved 24 April 2014.
- ↑ V. A. Krongauz (1979). "Quasi-Crystals". Israel Journal of Chemistry. 18 (3–4): 304–311. doi:10.1002/ijch.197900047. Retrieved 25 April 2014.
- ↑ V. A. Krongauz (1979). B. R. Jennings, ed. Electro-Optics and Dielectrics of Macromolecules and Colloids. U.S.A: Springer US. pp. 329–336. ISBN 978-1-4684-3497-2. Retrieved 25 April 2014.
- ↑ V.A. Krongauz; A.A. Parshutkin (May 1972). "The effect of the electric field on photochromism of spiropyrans. The dipole crystallization of a dye along the lines of force". Photochemistry & Photobiology. 15 (5): 503–507. doi:10.1111/j.1751-1097.1972.tb06261.x. Retrieved 25 April 2014.
- ↑ V. A. Krongauz; F. Shvartsman (14 June 1984). "Quasi-liquid crystals". Nature. 309 (5969): 608–611. Bibcode:1984Natur.309..608S. doi:10.1038/309608a0. Retrieved 25 April 2014.
- 1 2 T. Wismontski – Knittel; V.A. Krongauz (November 1985). "Self-Assembling of Spiropyran Polymers by Zipper Crystallization". Macromolecules. 18 (11): 2124–2126. Bibcode:1985MaMol..18.2124W. doi:10.1021/ma00153a009. Retrieved 25 April 2014.
- ↑ V. A. Krongauz; F. P. Shvartsman; I. R. Cabrera; A. L. Weis; E. J. Wachtel (1985). "Investigation of the quasi-liquid crystal structure". J. Phys. Chem. 89 (18): 3941–3946. doi:10.1021/j100264a037. Retrieved 25 April 2014.
- ↑ I. Cabrera; V. A. Krongauz (9 April 1987). "Dynamic ordering of aggregated mesomorphic macromolecules". Nature. 326 (362): 582–585. Bibcode:1987Natur.326..582C. doi:10.1038/326582a0. Retrieved 25 April 2014.
- ↑ I. Cabrera; V. A. Krongauz; H. Ringsdorf (November 1987). "Photo- and Thermochromic Liquid Crystal Polysiloxanes". Chem. English Int. Ed. 26 (11): 1178–1180. doi:10.1002/anie.198711781. Retrieved 25 April 2014.
- ↑ V. A. Krongauz (1992). C. B. McArdle, ed. Photochromic Liquid Crystal Polymers in Applied Photochromic Polymer Systems. New York: Springer Science, Blackie & Son Ltd. pp. 121–171. ISBN 9780412029714.
- ↑ V. A. Krongauz; G. R. Meredith; D. J. Williams; S. N. Fishman; E. S. Goldburt (1983). "Optical frequency doubling and the internal structure of quasi-crystals". J. Phys. Chem. 87 (10): 1697–1701. doi:10.1021/j100233a012. Retrieved 25 April 2014.
- ↑ V. A. Krongauz; G. R. Meredith and , D. J. Williams, S. N. Fishman, , E. S. Goldburt (1983). "6". In D. J. Williams. Second-Order Nonlinear Media from Spiropyran Merocyanine Quasicrystals in Nonlinear Optical Properties of Organic and Polymeric Materials. ACS Symposium Series. 233. AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY. pp. 135–152. doi:10.1021/bk-1983-0233.ch006. ISBN 9780841208025. Retrieved 25 April 2014. Cite uses deprecated parameter
|coauthors=(help) - ↑ V. A. Krongauz; H. Hsiung, Th. Rasing, Y.R. Shen, F. P. Shvartsman, I. Cabrera (1987). "Polar ordering of quasiliquid crystals—An optical second harmonic generation study". J. Chem. Phys. 87 (5): 3127. Bibcode:1987JChPh..87.3127H. doi:10.1063/1.453050. Retrieved 25 April 2014. Cite uses deprecated parameter
|coauthors=(help) - ↑ G. Berkovic; V. A. Krongauz; V. Weiss (2000). "Spiropyrans and Spirooxazines for Memories and Switches". Chem. Rev. 100 (5): 1741–1754. doi:10.1021/cr9800715. PMID 11777418. Retrieved 25 April 2014.
- ↑ A Lapsed US4405733 A, David J. Williams, Gerald R. Meredith, George R. Olin, "Composite quasi-crystalline material", published 1983-9-20, assigned to Xerox Corporation
- ↑ A Lapsed US4927917 A, Valeri A. Krongauz, Felix P. Shvartsman, "Quasi-liquid crystals", published 1990-5-22, assigned to Yeda Research And Development Co., Ltd.
- ↑ R. Klajn (2014). "Spiropyran-based dynamic materials". Chem. Soc. Rev. 43: 148–184. doi:10.1039/C3CS60181A. Retrieved 26 April 2014.