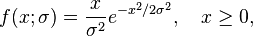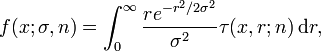Rayleigh mixture distribution
In probability theory and statistics a Rayleigh mixture distribution is a weighted mixture of multiple probability distributions where the weightings are equal to the weightings of a Rayleigh distribution.[1] Since the probability density function for a (standard) Rayleigh distribution is given by[2]
Rayleigh mixture distributions have probability density functions of the form
where 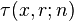 is a well-defined probability density function or sampling distribution.[1]
is a well-defined probability density function or sampling distribution.[1]
The Rayleigh mixture distribution is one of many types of compound distributions in which the appearance of a value in a sample or population might be interpreted as a function of other underlying random variables. Mixture distributions are often used in mixture models, which are used to express probabilities of sub-populations within a larger population.