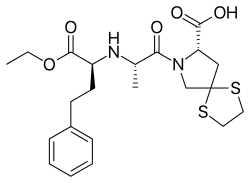
Spirapril
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Renormax |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | C09AA11 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 50% |
| Metabolism | converted to spiraprilat |
| Biological half-life | 30 to 35 hours |
| Excretion | Hepatic and renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
83647-97-6 |
| PubChem (CID) | 5311447 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 6575 |
| DrugBank |
DB01348 |
| ChemSpider |
4470933 |
| UNII |
96U2K78I3V |
| KEGG |
D08529 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL431 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H30N2O5S2 |
| Molar mass | 466.616 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Spirapril hydrochloride (Renormax) is an ACE inhibitor antihypertensive drug used to treat hypertension. It belongs to dicarboxy group of ACE inhibitors.
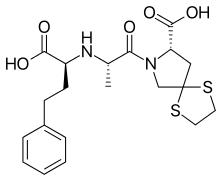
Spiraprilat — the active metabolite
Like many ACE inhibitors, this prodrug is converted to the active metabolite spiraprilat following oral administration. Unlike other members of the group, it is eliminated both by renal and hepatic routes, which may allow for greater use in patients with renal impairment.[1] However, data on its effect upon the renal function are conflicting.[2]
References
- ↑ Shohat J, Wittenberg C, Erman A, Rosenfeld J, Boner G (1999). "Acute and chronic effects of spirapril, alone or in combination with isradipine on kidney function and blood pressure in patients with reduced kidney function and hypertension.". Scand J Urol Nephrol. 33 (1): 57–62. doi:10.1080/003655999750016294. PMID 10100366.
- ↑ Noble S, Sorkin E (1995). "Spirapril. A preliminary review of its pharmacology and therapeutic efficacy in the treatment of hypertension.". Drugs. 49 (5): 750–66. doi:10.2165/00003495-199549050-00008. PMID 7601014.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/27/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.