Resolution (electron density)
Resolution in terms of electron density is a measure of the resolvability in the electron density map of a molecule. In X-ray crystallography, resolution is the highest resolvable peak in the diffraction pattern, while resolution in cryo-electron microscopy is a frequency space comparison of two halves of the data, which strives to correlate with the X-ray definition.[1]
Qualitative measures
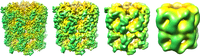
In structural biology, resolution can be broken down into 4 groups:
- sub-atomic, individual elements are distinguishable and quantum effects can be studied
- atomic, individual atoms are visible and an accurate three-dimensional model can be constructed
- helical, secondary structure, such as alpha helices and beta sheets; RNA helices (in ribosomes)
- domain, no secondary structure is resolvable
X-ray crystallography
As the crystal's repeating unit, its unit cell, becomes larger and more complex, the atomic-level picture provided by X-ray crystallography becomes less well-resolved (more "fuzzy") for a given number of observed reflections. Two limiting cases of X-ray crystallography are often discerned, "small-molecule" and "macromolecular" crystallography. Small-molecule crystallography typically involves crystals with fewer than 100 atoms in their asymmetric unit; such crystal structures are usually so well resolved that its atoms can be discerned as isolated "blobs" of electron density. By contrast, macromolecular crystallography often involves tens of thousands of atoms in the unit cell. Such crystal structures are generally less well-resolved (more "smeared out"); the atoms and chemical bonds appear as tubes of electron density, rather than as isolated atoms. In general, small molecules are also easier to crystallize than macromolecules; however, X-ray crystallography has proven possible even for viruses with hundreds of thousands of atoms.[2]
| Resolution (Å) | Meaning |
| >4.0 | Individual coordinates meaningless. Secondary structure elements can be determined. |
| 3.0 - 4.0 | Fold possibly correct, but errors are very likely. Many sidechains placed with wrong rotamer. |
| 2.5 - 3.0 | Fold likely correct except that some surface loops might be mismodelled. Several long, thin sidechains (lys, glu, gln, etc.) and small sidechains (ser, val, thr, etc.) likely to have wrong rotamers. |
| 2.0 - 2.5 | As 2.5 - 3.0, but number of sidechains in wrong rotamer is considerably less. Many small errors can normally be detected. Fold normally correct and number of errors in surface loops is small. Water molecules and small ligands become visible. |
| 1.5 - 2.0 | Few residues have wrong rotamer. Many small errors can normally be detected. Folds are rarely incorrect, even in surface loops. |
| 0.5 - 1.5 | In general, structures have almost no errors at this resolution. Individual atoms in a structure can be resolved. Rotamer libraries and geometry studies are made from these structures. |
Cryo-electron microscopy
In cryo-electron microscopy, resolution is typically measured by the Fourier shell correlation (FSC),[5] a three-dimensional extension of the Fourier ring correlation (FRC),[6] which is also known as the spatial frequency correlation function.[7] The FSC is a comparison of two different Fourier transforms over different shells on frequency space. To measure the FSC, the data needs to be separated into two groups. Typically, the even particles form the first group and odd particles the second based on their order. This is commonly referred to as the even-odd test. Most publications quote the FSC 0.5 cutoff, which refers to when the correlation coefficient of the Fourier shells is equal to 0.5.[1][8]
Determining the resolution threshold remains a controversial topic and many other criteria using the FSC curve exist, including 3-σ criterion, 5-σ criterion, and the 0.143 cutoff. However, fixed-value thresholds (like 0.5, or 0.143) were argued to be based on incorrect statistical assumptions.[9] The new half-bit criterion indicates at which resolution one has collected enough information to reliably interpret the 3-dimensional volume, and the (modified) 3-sigma criterion indicates where the FSC systematically emerges above the expected random correlations of the background noise.[9] In 2007, a resolution criterion independent of the FSC was developed using the correlation between neighboring Fourier voxels to distinguish signal from noise.[10]
Notes
- 1 2 Frank, 2006, p250-251
- ↑ Hopper, P.; Harrison, S.C.; Sauer, R.T. (1984). "Structure of tomato bushy stunt virus. V. Coat protein sequence determination and its structural implications". Journal of Molecular Biology. Elsevier Ltd. 177 (4): 701–713. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(84)90045-7. PMID 6481803.
- ↑ Huang, Yu-Feng (2007). Study of Mining Protein Structural Properties and its Application (pdf) (Ph.D.). National Taiwan University. Retrieved Nov 4, 2014.
- ↑ Blow, David (June 20, 2002). Outline of Crystallography for Biologists. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 196. ISBN 978-0198510512. Retrieved Nov 4, 2014.
- ↑ Harauz & van Heel, 1986
- ↑ van Heel, 1982
- ↑ Saxton & Baumeister, 1982
- ↑ Böttcher et al., 1997
- 1 2 van Heel & Schatz, 2005
- ↑ Sousa & Grigoreiff, 2007
References
- Harauz, G.; M. van Heel (1986). "Exact filters for general geometry three dimensional reconstruction". Optik. 73: 146–156.
- van Heel, M.; Keegstra, W.; Schutter, W.; van Bruggen E.F.J. (1982). Arthropod hemocyanin studies by image analysis, in: Structure and Function of Invertebrate Respiratory Proteins,EMBO Workshop 1982, E.J. Wood. Life Chemistry Reports. Suppl. 1. pp. 69–73. ISBN 9783718601554.
- Saxton, W.O.; W. Baumeister (1982). "The correlation averaging of a regularly arranged bacterial cell envelope protein". J Microscopy. 127: 127–138. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2818.1982.tb00405.x.
- Böttcher, B.; Wynne, S.A.; Crowther, R.A. (1997). "Determination of the fold of the core protein of hepatitis B virus by electron microscopy". Nature. 386 (6620): 88–91. doi:10.1038/386088a0. PMID 9052786.
- van Heel, M.; Schatz, M. (2005). "Fourier shell correlation threshold criteria". Journal of Structural Biology. 151 (3): 250–262. doi:10.1016/j.jsb.2005.05.009. PMID 16125414.
- Frank, Joachim (2006). Three-Dimnsional Electron Microscopy of Macromolecular Assemblies. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-518218-9.
- Sousa, Duncan; Nikolaus Grigorieff (2007). "Ab initio resolution measurement for single particle structures". J Struct Biol. 157 (1): 201–210. doi:10.1016/j.jsb.2006.08.003. PMID 17029845.
External links
- PDB 101 Looking at Structures: Resolution
- EMstats Trends and distributions of maps in EM Data Bank (EMDB), e.g. resolution trends