Restrictive flow orifice
A Restrictive Flow Orifice (RFO) is a type of orifice plate. They are used to limit the potential danger of an uncontrolled flow from, for example, a compressed gas cylinder by:[1][2]
- limiting the accidental release of a hazardous gas (flammable, toxic, etc.) resulting from regulator or other component failure,
- restricting flow in a system in order to assure adequate pressure relief valve sizing and system over pressure protection, or
- restricting flow from bulk sources.[3]
Predicting Flow
Correlations assist in predicting the flow of a particular gas or gas mixture through a RFO. This is done by first determining the flow through the same RFO at the required pressure with a reference gas and then adjusting the specific gravity accordingly.
The pertinent equation for the reference gas of nitrogen (N2) is presented below.
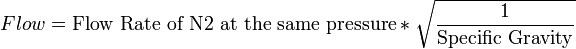
Other applications
River flood control
In the natural environment, large orifice plates are used to control onward flow in flood relief dams. In these structures a low dam is placed across a river and in normal operation the water flows through the orifice plate unimpeded as the orifice is substantially larger than the normal flow cross section. However, in floods, the flow rate rises and floods out the orifice plate which can then only pass a flow determined by the physical dimensions of the orifice. Flow is then held back behind the low dam in a temporary reservoir which is slowly discharged through the orifice when the flood subsides.
Notes
4. Types and applications of restriction orifice plates
5. Notes on Orifice Flow Meter