Rhodamine B
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
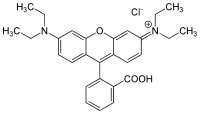
| IUPAC name
[9-(2-carboxyphenyl)-6-diethylamino-3-xanthenylidene]-diethylammonium chloride | |
| Other names
Rhodamine 610, C.I. Pigment Violet 1, Basic Violet 10, C.I. 45170 | |
| Identifiers | |
| 81-88-9 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:52334 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL428971 |
| ChemSpider | 6439 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.259 |
| KEGG | C19517 |
| PubChem | 6694 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C28H31ClN2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 479.02 |
| Appearance | red to violet powder |
| Melting point | 210 to 211 °C (410 to 412 °F; 483 to 484 K) (Decomposes) |
| ~15 g/L (20 °C) [1] | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | MSDS |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Rhodamine B /ˈroʊdəmiːn/ is a chemical compound and a dye. It is often used as a tracer dye within water to determine the rate and direction of flow and transport. Rhodamine dyes fluoresce and can thus be detected easily and inexpensively with instruments called fluorometers. Rhodamine dyes are used extensively in biotechnology applications such as fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry, fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and ELISA.
Rhodamine B is used in biology as a staining fluorescent dye, sometimes in combination with auramine O, as the auramine-rhodamine stain to demonstrate acid-fast organisms, notably Mycobacterium.
Rhodamine B is tunable around 610 nm when used as a laser dye.[2] Its luminescence quantum yield is 0.65 in basic ethanol,[3] 0.49 in ethanol,[4] 1.0,[5] and 0.68 in 94% ethanol.[6] The fluorescence yield is temperature dependent.[7]
Solubility

The solubility of rhodamine B in water is ~15 g/L.[8] However, the solubility in acetic acid solution (30 vol.%) is ~400 g/L. Chlorinated tap water decomposes rhodamine B. Rhodamine B solutions adsorb to plastics and should be kept in glass.[9]
Synthesis
Other uses
Rhodamine B is being tested for use as a biomarker in oral rabies vaccines for wildlife, such as raccoons, to identify animals that have eaten a vaccine bait. The rhodamine is incorporated into the animal's whiskers and teeth.[10]
It is also often mixed with herbicides to show where they have been used.
Rhodamine B (BV10) is mixed with Quinacridone Magenta (PR122) to make the bright pink watercolor known as Opera Rose.[11]
Safety and health
In California, rhodamine B is suspected to be carcinogenic and thus products containing it must contain a warning on its label.[12] Cases of economically motivated adulteration, where it has been illegally used to impart a red color to chili powder, have come to the attention of food safety regulators.
References
- ↑ Sicherheitsdatenblatt Rhodamin B by Roth, 2013
- ↑ Rhodamine B
- ↑ Kubin, R (1983). "Fluorescence quantum yields of some rhodamine dyes". Journal of Luminescence. 27 (4): 455–462. doi:10.1016/0022-2313(82)90045-X.
- ↑ Casey, Kelly G.; Quitevis, Edward L. (1988). "Effect of solvent polarity on nonradiative processes in xanthene dyes: Rhodamine B in normal alcohols". The Journal of Physical Chemistry. 92 (23): 6590–6594. doi:10.1021/j100334a023.
- ↑ Kellogg, R. E.; Bennett, R. G. (1964). "Radiationless Intermolecular Energy Transfer. III. Determination of Phosphorescence Efficiencies". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 41 (10): 3042. doi:10.1063/1.1725672.
- ↑ Snare, M (1982). "The photophysics of rhodamine B". Journal of Photochemistry. 18 (4): 335–346. doi:10.1016/0047-2670(82)87023-8.
- ↑ Karstens, T.; Kobs, K. (1980). "Rhodamine B and rhodamine 101 as reference substances for fluorescence quantum yield measurements". The Journal of Physical Chemistry. 84 (14): 1871–1872. doi:10.1021/j100451a030.
- ↑ Sicherheitsdatenblatt Rhodamin B by Roth, 2013
- ↑ Detection and prevention of leaks from dams By Antonio Plata Bedmar and Luís Araguás Araguás, Taylor & Francis, 2002, ISBN 90-5809-355-7
- ↑ Slate, Dennis; Algeo, Timothy P.; Nelson, Kathleen M.; Chipman, Richard B.; Donovan, Dennis; Blanton, Jesse D.; Niezgoda, Michael; Rupprecht, Charles E. (2009). Bethony, Jeffrey M., ed. "Oral Rabies Vaccination in North America: Opportunities, Complexities, and Challenges". PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 3 (12): e549. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0000549. PMC 2791170
 . PMID 20027214.
. PMID 20027214. - ↑ http://www.handprint.com/HP/WCL/waterc.html
- ↑ Naval Jelly msds with Rhodamine B
