Royal Yugoslav Air Force
| Royal Yugoslav Air Force | |
|---|---|
| Active | 1918–1941 |
| Country | Kingdom of Yugoslavia |
| Branch | Air Force |
| HQ |
Petrovaradin (1918–1936) Zemun (1936–1941) |
| Engagements | World War II |
| Commanders | |
| Notable commanders | Dušan Simović, Borivoje Mirković |
| Insignia | |
| Roundel |
 |
| Fin flash |
|
| Aircraft flown | |
| Bomber | Dornier Do Y, Bristol Blenheim, Dornier Do 17, Caproni Ca.310, Savoia-Marchetti SM.79 |
| Fighter | Hawker Hurricane, Ikarus IK-2, Hawker Fury Mk.II, Messerschmitt Bf 109, Rogožarski IK-3 |
| Trainer | Rogožarski SIM-Х, Rogožarski SIM-XII-H, Rogožarski PVT, Rogožarski R-100, Bücker Bü 131 |
The Royal Yugoslav Air Force (Serbo-Croatian: Jugoslavensko kraljevsko ratno zrakoplovstvo, Југословенско краљевско ратно ваздухопловство), officially the Kingdom of Yugoslavia Army Air Force (Vazduhoplovstvo vojske Kraljevine Jugoslavije, VVKJ),[1] was formed in 1918 in the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (renamed to Kingdom of Yugoslavia in 1929) and existed until Yugoslavia's surrender to the Axis powers in 1941 following the Invasion of Yugoslavia during World War II.
Some 18 aircraft and several hundred aircrew escaped the Axis invasion of April 1941 to the Allied base in Egypt, eventually flying with the Royal Air Force in the Northern Africa initially and then with the Balkan Air Force in Italy and Yugoslavia, with some even going on to join the Soviet Air Force, returning to Yugoslavia in 1944.
Germany distributed captured Royal Yugoslav Air Force aircraft and spare-parts to Romania, Bulgaria, Finland and the newly created Independent State of Croatia.
History
Origins and establishment
The Royal Yugoslav Air Force developed out of the Serbian Aviation Command, which had been created on 24 December 1912, and had been active during the Balkan Wars of 1912–1913.[2] During World War I, the small Serbian Aviation Command had initially operated in support of the Royal Serbian Army and its defence of the country against concerted attacks by Austria-Hungary. After initial Serbian successes, in 1915 the Central Powers forced the Serbian Army to withdraw to Albania where the surviving elements of the army were evacuated. Serbian aviators were absorbed into French squadrons to support the French-led Allied force that pushed north from Salonika,[3] and towards the end of the war, separate Serbian squadrons were again raised. After the end of World War I, in 1919 the South Slav peoples determined to form a new country, the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, and the existing Serbian air corps became the basis for the military air service of the new state. The chief of the fledgling air force was the former head of the Austro-Hungarian Imperial and Royal Aviation Troops, Emil Uzelac.[4]
Early developments
Lack of funds meant that little could be done to improve military aviation in the first years of the new state, although in 1922, Uzelac went on a European tour to study military aviation in foreign armies. Efforts were also made to develop a civil aviation sector with a view to forming a reserve pool of pilots and mechanics.[5] The following year, Uzelac retired, and the British military attache noted that there were several former Russian Empire aviators serving in the air force, two of whom attempted to defect to the Soviet Union with an aircraft during that year.[6] In 1924, the first Yugoslav-built aircraft was produced at the Ikarus plant in Novi Sad, albeit with a foreign-made engine. The next year, 150 Breguet 19 biplane light bomber and reconnaissance aircraft were purchased on credit from the French government, signalling the first significant expansion of the air force. The new aircraft were assembled at Novi Sad, then distributed to the other military aerodromes at Sarajevo, Mostar, Zagreb and Skopje. The Ikarus plant was producing training aircraft and seaplanes using Austrian engines captured at the end of World War I, and imported steel tubing and wire stays. [7] In 1926, the aerodrome at Zemun was developed in order to provide a military airfield near the capital, Belgrade, and a military air race was held for the first time, with a gold cup presented by King Alexander.[8]
By 1927, the air force had acquired Potez 25 biplanes and Dewoitine single-seater fighter aircraft, as well as some Hansa-Brandenburg and Hanriot training aircraft.[9] The following year, a government aircraft factory at Kraljevo was completed, and a privately owned factory near Belgrade went into production, building French aircraft engines under licence. By the same year, the air force had also acquired Fizir F1V reconnaissance aircraft.[10] In 1929, the British military attaché reported that the air force was making slow but steady improvements, but observed that the airfield at Novi Sad was the only one capable of supporting night flying. Chief among the deficiencies of the air arm were the lack of advanced repair and maintenance facilities at the various regional airfields such as those at Zagreb or Sarajevo. It was concluded that this meant the Yugoslav air force would be unable to keep aircraft in the air for any period of conflict beyond a few weeks. The factory at Kraljevo was apparently capable of producing around 50 licence-built Breguet 19 aircraft per year.[11]
1930s
In 1930, workshops were completed at the airfields at Zagreb and Mostar, allowing for repairs and modifications to be carried out without transferring aircraft to the main factories and workshops closer to the capital. In May of that year, the first aircraft of entirely Yugoslav manufacture was completed at Kraljevo, and it was estimated that factory was capable of producing 100 Breguet 19 aircraft per year. At this time, the factory had a French workforce and was under French management, but the contract was due to expire in 1932, after which the Yugoslav government would be at liberty to produce whichever aircraft it could obtain licences to build. The privately-owned Ikarus plant at Zemun continued to produce seaplanes of its own design as well as Potez 25 aircraft under licence. The strength of the air force was estimated at 26 squadrons of about twelve aircraft each, indicating a total of approximately 312 aircraft, although there were almost no reserve aircraft.[12]
.jpg)
During 1931, no additional squadrons were raised, but a reserve of aircraft was built up, so that around 200 machines were stored at the various regional airfields. The British military attache assessed that the standard of pilot training remained deficient, with a significant number of aircraft being put out of action each year due to accidents. During the same year, the air force obtained three Hawker Fury aircraft for evaluation, two fitted with Rolls Royce engines, and one with a Hispano-Suiza engine. This was viewed with alarm by the French, who had thus far had a strong influence over Yugoslav aviation procurement.[13]
During 1932, there were significant problems of morale and discipline due to subversion within the 2nd Air Regiment near Sarajevo.[14] Steady progress continued to made in developing the air force, but several weaknesses were evident, including; lack of first-class aircraft, dependence on foreign sources for the bulk of aviation construction material, inadequate repair and maintenance facilities, the slow development of the home-grown aircraft industry, and the negative influence exerted by senior army officers with no aviation experience or knowledge. It was acknowledged that the air force had no difficulty in attracting high quality recruits, and the Sarajevo incident aside, that morale and discipline were high within the air arm. Two additional squadrons were added to each of the six air regiments during 1932. As a result, the number of aircraft in service increased to approximately 430, with a reserve of 300. The state factory at Kraljevo produced about 150 Breguet 19 aircraft during the year, with forty Potez 25s also being delivered from the Ikarus factory. Six bombers were obtained for evaluation during the year; two each from Junkers, Dornier and Fokker.[15]
In the early months of 1933, a war scare with Italy betrayed significant deficiencies in stocks of aircraft bombs and fuel reserves. During that year the Yugoslav government tendered for twenty single-seat fighter aircraft. Six aircraft were recommended for consideration, in priority order; a Polish PZL, the Hawker Fury, a Dewoitine, two Fokkers and a Czechoslovak Avia. The tender included the production of another twenty aircraft under licence, and a further fifty machines to either be purchased or built locally under licence. An acquisition program for medium reconnaissance aircraft was also being considered, while evaluation of bombers continued. Also in 1933, the headquarters of the 1st Air Brigade was transferred to Zemun. There were thirty-six squadrons in the six air regiments, with each regiment consisting of six squadrons split between three groups, with an additional squadron at regimental level maintained for liaison duties and skill maintenance of reserve pilots. In addition to these forty-two squadrons, there were a number of training squadrons and an experimental group. The reserve aircraft numbered approximately 250. Night flying training was carried out throughout the summer over Belgrade, and anti-aircraft training in the city was carried out in cooperation with the air force. Each regiment conducted air gunnery training once per year.[16] Despite the availability of funds for the acquisition of new modern aircraft, no decision was made during 1934, although the Polish PZL fighter was ruled out as unsuitable. Little night flying was conducted, and it became apparent that reserves of aircraft were not as high as believed.[17]
On 19 September 1935, the Yugoslav government signed a contract to purchase ten Hawker Fury fighters and sixty-five Rolls-Royce engines. At the same time, a licence was obtained to build the Hawker Fury locally, and an option was also taken out on building Rolls-Royce engines in-country. Despite funds being available, no other purchases were made during the year, with air force strength being estimated at 400 Breguet 19s, 200 Potez 25s, a few Avia and Dewoitine aircraft, and the six bombers previously purchased for trial purposes. Basic pilot training was fair, with less accidents, but instrument flying training was rare. The Yugoslav air service was almost entirely equipped with obsolete aircraft, but despite this, the morale of aircrew was good and there was no shortage of young men wishing to fly. A licence was also obtained for the local manufacture of captive balloons.[18]
In 1936, General Milutin Nedić was replaced as chief of the VVKJ by General Dušan Simović upon the appointment of the former as Chief of the General Staff. Simović had previously served as second-in-command of the VVKJ.[19] There were few developments of note during the year, with the obsolete fleet continuing to decline, and even the state aircraft factory at Kraljevo was largely idle except for the production of spare parts for the large number of Breguet 19 aircraft still in service. The Ikarus and Zmaj factories at Zemun installed plant and equipment for the production of the Hawker Fury under licence, but the delivery of the ten purchased aircraft was not expected until March 1937, and it was not expected that any of the locally made aircraft would be delivered until May of that year. Ikarus also produced several Avia BH-33E fighters, and overhauled a large number of Potez 25 aircraft during the year. A prototype Dornier Do 17 light bomber with Gnome-Rhône engines was ordered, with a further order for nineteen more aircraft pending a successful trial.[20]
Consolidation and modernization

By 1941 the JKRV, with a strength of 1,875 officers and 29,527 other ranks,[21] had over 460 front-line aircraft of domestic (notably the IK-3), German, Italian, French, and British origin, of which most were modern types. Organized into twenty-two bomber squadrons and nineteen fighter squadrons, the main aircraft types in operational use included seventy-three Messerschmitt Bf 109 E, forty-seven Hawker Hurricane I (with more being built under licence in Yugoslavia), thirty Hawker Fury II, eleven Rogozarski IK-3 fighters (plus more under construction), ten Ikarus IK-2, 2 Potez 63, one Messerschmitt Bf 110C-4 (captured in early April due to a navigational error) and one Rogozarski R 313 fighters, sixty-nine Dornier Do 17 K (including 40 plus licence-built), sixty-one Bristol Blenheim I (including some 40 licence-built) and forty Savoia Marchetti SM-79 K bombers. Army reconnaissance units comprised seven Groups with 130 obsolete Yugoslav-built Breguet 19 and Potez 25 light bombers. The Naval Aviation units comprised 75 aircraft in eight squadrons equipped with, amongst other auxiliary types, twelve German-built Dornier Do 22 K and fifteen Rogozarski SIM-XIV-H locally designed and built maritime patrol float-planes.[22]
The aircraft of the Yugoslav airline Aeroput, consisting mainly of six Lockheed Model 10 Electras, three Spartan Cruisers, and one de Havilland Dragon were mobilised to provide transport services to the VVKJ.[23]
The situation whereby the Kingdom of Yugoslavia had to acquire or manufacture aircraft from whatever source presented itself meant that by 1941, the VVKJ was rather uniquely equipped with 11 different types of operational aircraft, 14 different types of trainers and five types of auxiliary aircraft, with 22 different engine models, four different machine guns and two types of aircraft cannon.[24]
The Yugoslav manufactured Dornier Do-17K, for example, was a German aircraft with French 1000 hp Gnome-Rhone engines, Belgian armament from Fabrique Nationale, Czech photo-recon equipment and locally produced Yugoslav instrumentation.
During 1938, the Yugoslav government purchased 12 Hurricane Is for the Royal Yugoslav Air Force and followed this up with an order for another 12 together with a manufacturing licence to allow production of the fighter at the Rogozarski (orders for 60) and Zmaj (orders for 40) factories. These plants, together with the Ikarus concern, had been designing and manufacturing sporting and training aircraft since the 1920s. Production was expected to reach eight per month from each assembly line by mid-1941. In the event, by the time of the German onslaught of April 1941, which put an end to further production, Zmaj had delivered 20 Hurricanes but Rogorzarski had delivered none.
The local design team working on improved versions of the IK-3 fighter had originally planned to power later IK-3s with new 1,100 h.p. Hispano-Suiza 12Y-51 engine. The German occupation of France had frustrated this plan, and British or German engines were considered. The Air Ministry favoured the DB 601 A, and as part of IK-3 development program, a Daimler-Benz engine was installed experimentally in a Hurricane airframe in 1940.
Engineers Ilic and Sivcev at the Ikarus plant Zemun, outside Belgrade, made the conversion by the fitting of new engine bearers, cowlings and cooling system manufactured at the Ikarus factory. The one Hurricane fitted with a DB601A engine for comparison with the Merlin-engined version was tested early in 1941. It was given the designation "LVT-1".
The conversion was extremely successful, and experimental aircraft displayed better take-off performance and climb rate than either the standard Hurricane or the Bf 109 E-3 and was only slightly slower than the latter. VVKJ pilots who flew the Hurricane conversion considered it to be superior to the standard model.[25]
At the same time, a 1,030 h.p. Rolls-Royce Merlin III was installed in one of the IK-3 airframes, but this machine had only just been completed at the time of the German attack, and as enemy forces neared Belgrade it was destroyed by the factory workers, together with four other IK-3s undergoing overhaul or modification and a further 25 on the production line.
World War II

During 1940 Britain supplied significant military aid to the VVKJ, to strengthen its forces against the increasing German threat. In early March 1941, the German Luftwaffe forces started arriving in neighboring Bulgaria. On March 12, 1941, VVKJ units began to deploy to their wartime airfields. The overthrow of the pro-German government in Belgrade on March 27 brought an end to hopes of a settlement with Germany. On April 6, 1941, Luftwaffe units in Bulgaria and Romania attacked Yugoslavia in what was known as the Bombing of Belgrade. Equipped with a combination of obsolete equipment and new aircraft still being introduced into service, the VVKJ was forced to defend the country's long borders against multiple attacks from many directions. The dubious loyalty of some military personnel did not help matters. Yugoslav fighter aircraft and anti-aircraft artillery brought down about 90-100 enemy aircraft, but defending forces were unable to make any significant impact on the enemy advance. During the attack of German aircraft on Niš Airport Medoševac on 6 April around 08:00, fire from the ground shot down the plane of German fighter ace Herbert Ihlefeld. Captain Ihlefeld, who was credited with over forty air victories, was shot down by Corporal Vlasta Belić, firing a Darne machine gun, caliber 7.69 mm, taken from a Yugoslav Breguet 19. Having received a shot in the oil cooler, the Bf 109's engine stopped, and the pilot was forced to leave the plane. He rescued himself with a parachute about 35 miles southeast of Nis. The German ace was captured by Serbian peasants who handed him over to the gendarmes. On April 17, 1941 the Yugoslav government surrendered. Several VVKJ aircraft escaped to Egypt via the Kingdom of Greece, and the crews then served with the British Royal Air Force (RAF).
By the outbreak of the Second World War, Yugoslavia had a substantial air force with their own aircraft, aircraft from Allied countries like Britain and aircraft from Axis countries like Germany and Italy. In 1940, Britain attempted to bring Yugoslavia to the Allied side by supplying military aide to the Royal Yugoslav Air Force, including new Hawker Hurricane fighter aircraft. However Germany sold a large number of Messerschmitt Bf 109 fighters to Yugoslavia and in early 1941, and German dismay towards a Balkans campaign convinced Yugoslavia to join the Axis forces.
Although Yugoslavia joined the Axis powers, Fascist Italy demanded that their ally Nazi Germany invade Yugoslavia in order to reach Greece and help their disastrous campaign there and in the process break up Yugoslavia since Italians were laying claim on certain territories (mostly Dalmatia). The German Luftwaffe then began to mass at the borders of Yugoslavia from allied Axis nations. The VVKJ was forced to stretch out to defend Yugoslavia from an apparent invasion and imminent air war.[26]
Following the coup d'état on March 25, 1941, the Yugoslav armed forces were put on alert, although the army was not fully mobilized for fear of provoking Hitler – to no avail. The VVKJ command decided to disperse its forces away from their main bases to a system of auxiliary airfields that had previously been prepared. However many of these airfields lacked facilities and had inadequate drainage which prevented the continued operation of all but the very lightest aircraft in the adverse weather conditions encountered in April 1941).[27]
Despite having, on paper at any rate, a substantially stronger force of relatively modern aircraft than the combined British and Greek air forces to the south, the VVKJ could simply not match the overwhelming Luftwaffe and Regia Aeronautica superiority in terms of numbers, tactical deployment and combat experience.[28]
The bomber eskadrilla (the equivalent of 22 squadrons) and maritime air force hit targets in Italy, Germany (Austria), Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria, Albania and Greece, as well as attacking German, Italian and Hungarian troops. Meanwhile the fighter eskadrilla (the equivalent of 19 squadrons) inflicted not insignificant losses on escorted Luftwaffe bomber raids on Belgrade and Serbia, as well as upon Regia Aeronautica raids on Dalmatia and Herzegovina, whilst also providing air support to the hard pressed Yugoslav Army by strafing attacking troop columns in Croatia, Bosnia, Macedonia and Serbia (sometimes taking off and strafing the troops attacking the very base being evacuated).[29]
Little wonder then that after a combination of air combat losses, losses on the ground to enemy air attack on bases and the overrunning of airfields by enemy troops that after 11 days the VVKJ almost ceased to exist. It must, however, be noted that between 6 and 17 April 1941 the VVKJ received an additional 8 Hawker Hurricane Is, 6 Dornier Do-17Ks, 4 Bristol Blenheim Is, 2 Ikarus IK 2s, 1 Rogozarski IK-3 and 1 Messerschmitt Bf 109 from the aircraft factories and workshops.[30]
Some 70 or so operational and training aircraft succeeded in escaping to Greece and 4 to Russia (8 Do 17Ks and SM.79Ks set out, but half were lost due to poor weather conditions, mountainous terrain and/or overloading). But further tragedy was to befall even these escapees with some 44 destroyed on the ground at the airfield of Paramitia in Greece by marauding German and Italian fighters. In the end only 3 Lockheed 10s, 2 Do-17Ks, 4 SM.79Ks, 8 Do 22K floatplanes and 1 SIM XIVH floatplane reached the Allied base of Egypt in May 1941.
The Air Force of the Independent State of Croatia came into existence in July 1941 with over 200 captured aircraft. Yugoslav Partisans were themselves able to form an air force in 1943 from captured aircraft from the Croatian Air Force.
Inventory
Aircraft (April 1941)
Markings
 Royal Yugoslav Air Force roundel from 1918-1929.
Royal Yugoslav Air Force roundel from 1918-1929. Royal Yugoslav Air Force roundel from 1929-1941.
Royal Yugoslav Air Force roundel from 1929-1941.
Gallery
 Rogožarski SIM-Х Yugoslav aircraft trainer.
Rogožarski SIM-Х Yugoslav aircraft trainer.- Rogožarski R-100 Yugoslav aircraft advanced trainer.
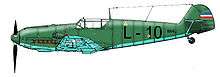 A Yugoslav Messerschmitt Bf 109E-3
A Yugoslav Messerschmitt Bf 109E-3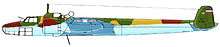 Dornier Do 17K from the 3rd bomber regiment of Royal Yugoslav Air Force, April 1941.
Dornier Do 17K from the 3rd bomber regiment of Royal Yugoslav Air Force, April 1941. Savoia-Marchetti SM.79 of the Yugoslav Air Force.
Savoia-Marchetti SM.79 of the Yugoslav Air Force. Zmaj Fizir FN of the Yugoslav Air Force.
Zmaj Fizir FN of the Yugoslav Air Force.
See also
- Invasion of Yugoslavia
- Bombing of Belgrade
- SFR Yugoslav Air Force
- Hawker Hurricane in Yugoslav service
Footnotes
- ↑ Ciglić & Savić 2007, p. 4.
- ↑ Boyne 2002, p. 66.
- ↑ Sanger 2002, p. 121.
- ↑ Chant 2012, p. 8.
- ↑ Jarman 1997a, p. 579.
- ↑ Jarman 1997a, pp. 624–625.
- ↑ Jarman 1997a, p. 730.
- ↑ Jarman 1997a, pp. 775 & 777.
- ↑ Jarman 1997b, p. 59.
- ↑ Jarman 1997b, pp. 123–124.
- ↑ Jarman 1997b, pp. 180–181.
- ↑ Jarman 1997b, pp. 244–245.
- ↑ Jarman 1997b, p. 318.
- ↑ Jarman 1997b, p. 385.
- ↑ Jarman 1997b, pp. 389–390.
- ↑ Jarman 1997b, pp. 448–450.
- ↑ Jarman 1997b, pp. 536–537.
- ↑ Jarman 1997b, pp. 638–639.
- ↑ Jarman 1997b, p. 735.
- ↑ Jarman 1997b, pp. 739–741.
- ↑ Ciglić & Savić 2007, p. 22.
- ↑ Shores, Cull & Malizia 1987, pp. 187–192.
- ↑ Shores, Cull & Malizia 1987, p. 260.
- ↑ Shores, Cull & Malizia 1987, p. 173.
- ↑ Half-Century Hurricane in AIR International, Vol. 33, No. 1, July 1987. Fine Scroll, London ISSN 0306-5634
- ↑
- ↑ Shores, Cull & Malizia 1987, pp. 177.
- ↑ Shores, Cull & Malizia 1987, p. 178.
- ↑ Shores, Cull & Malizia 1987, pp. 178–229.
- ↑ Ciglić & Savić 2002, p. 8.
References
- Boyne, Walter J. (2002). Air Warfare: An International Encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1-57607-345-2.
- Chant, Chris (2012). Austro-Hungarian Aces of World War 1. Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 978-1-78200-890-3.
- Јанић, Чедомир; Огњан Петровић (2010.). Век авијације у Србији 1910-2010 225 значајних летилица (на ((sr))). YU-Београд: Аерокомуникације. ISBN 978-86-913973-0-2.
- Jarman, Robert L., ed. (1997a). Yugoslavia Political Diaries 1918–1965. 1. Slough, Berkshire: Archives Edition. ISBN 978-1-85207-950-5.
- Jarman, Robert L., ed. (1997b). Yugoslavia Political Diaries 1918–1965. 2. Slough, Berkshire: Archives Edition. ISBN 978-1-85207-950-5.
- Jarman, Robert L., ed. (1997c). Yugoslavia Political Diaries 1918–1965. 3. Slough, Berkshire: Archives Edition. ISBN 978-1-85207-950-5.
- Sanger, Ray (2002). Nieuport Aircraft of World War One. Crowood.
- Shores, Christopher F.; Cull, Brian; Malizia, Nicola (1987). Air War for Yugoslavia, Greece, and Crete, 1940–41. London: Grub Street. ISBN 978-0-948817-07-6.
- Half-Century Hurricane in AIR International, Vol. 33, No. 1, July 1987. Fine Scroll, London ISSN 0306-5634.
- Станојевић, Драгољуб.; Чедомир Јанић (12/1982.). "Животни пут и дело једног великана нашег ваздухопловства - светао пример и узор нараштајима". Машинство 31: 1867 - 1876.
- Микић, В. Војислав (2000). Зракопловство Независне Државе Хрватске 1941-1945. године (на ((sr))). Београд: Војноисторијски институт Војске Југославије. ID=72669708.
- Savic, D. and Ciglic, B. Croatian Aces of World War II Osprey Aircraft of the Aces - 49, Oxford, 2002 ISBN 1-84176-435-3.
- Ciglic, B. and Savic, D., Dornier Do 17 The Yugoslav story, Operational Record 1937-1947 Jeroplan, Belgrade, 2007 ISBN 978-86-909727-0-8
- Likso, T. and Canak, D., Hrvatsko Ratno Zrakoplovstvo u Drugome Svjetskom Ratu (The Croatian Airforce in the Second World War) Zagreb, 1998 ISBN 953-97698-0-9.
- Jelavic, T., No.352 RAF Sqd. Zagreb, 2003 ISBN 953-97698-2-5.