Backpack palsy
| Backpack palsy | |
|---|---|
|
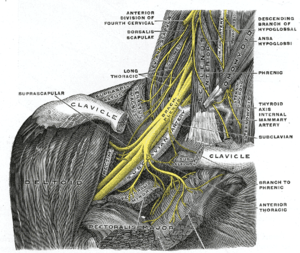
The right brachial plexus with its short branches, viewed from in front. | |
| Classification and external resources |
Backpack palsy (BPP) — or rucksack palsy or rucksack paralysis — is a type of brachial plexus injury associated with carrying a heavy backpack or similar load with excessive compression of the shoulder areas by straps. It is a known hazard for ruckmarching soldiers and for certain outdoor recreationalists (hikers, trekkers, mountaineers, etc) and certain labors (e.g., those carrying sandbags). A particular risk factor is bearing heavy backpack loads without any waist support (i.e., all the weight borne by the shoulders).
Presentation
Typical upper extremity symptoms are paresis (i.e., weakness of voluntary movement, or partial loss of voluntary movement or impaired movement), numbness, and paresthesias (“pins and needles” sensation) after carrying a heavy load with shoulder-straps of a backpack, or similar burden. The syndrome is generally painless. Neuralgic pain, as seen with other acute brachial neuropathies (see Parsonage–Turner syndrome), is not a feature. The long thoracic nerve is often the critically affected organ. (In this case the serratus anterior muscle is palsied and a "winged scapula" may be the result.[1]) The shoulder girdle and elbow flexors are usually the most severely affected. Sensory disturbances can occur in the lateral shoulder and arm region and in forearm and hand (especially the radial aspects). Atrophy of the affected muscles may develop long term in a minority of cases.
Prognosis
Prognosis is not well understood: about two-thirds of victims recover completely, or mostly, within 6 months; for the remainder, the duration of prolonged recovery is unknown.
Prevention
Backpack palsy can be prevented by making change in backpack design. If the straps design in the way that be less concentrated on shoulder, then the pressure will be decreased on shoulder and can be helpful in decreasing the chance of backpack palsy.[2]
References
Citations
- ↑ Clarke, Charles, "Wilderness Neurology", Chapter 33 in: Auerbach, Paul S. (2012), Wilderness Medicine, 6th edition, Elsevier/Mosby, pg 642.
- ↑ http://content.iospress.com/articles/work/wor2293
Further reading
- Daube J (1969), "Rucksack paralysis", JAMA, 208:2447–2452.
- Bessen R, Belcher V, Franklin R (1987), "Rucksack paralysis with and without rucksack frames", Mil Med, 152:372–375.
- Wilson W (1987), "Brachial plexus palsy in basic trainees", Mil Med, 152:519–522.