Slepian's lemma
In probability theory, Slepian's lemma (1962), named after David Slepian, is a Gaussian comparison inequality. It states that for Gaussian random variables 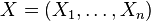 and
and 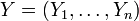 in
in 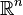 satisfying
satisfying ![E[X] = E[Y] = 0](../I/m/912202b436582edacb88eee9dc8945c7.png) ,
,
![E[X_i^2]=E[Y_i^2], i=1,\dots,n, \text{ and } \ E[X_iX_j] \le E[Y_i Y_j]](../I/m/0554040058bce40c331a46ef7a3b8689.png) for
for 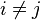 ,
,
the following inequality holds for all real numbers 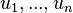 :
:
![P[X_1 \le u_1, \dots, X_n \le u_n] \le P[Y_1 \le u_1, \dots, Y_n \le u_n ]](../I/m/4cd4d3aead8921661cd09bebfd081f8a.png) ,
,
While this intuitive-seeming result is true for Gaussian processes, it is not in general true for other random variables—not even those with expectation 0.
As a corollary, if 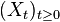 is a centered stationary Gaussian process such that
is a centered stationary Gaussian process such that ![E[X_0X_t] \geq 0](../I/m/143db5a58aa44d634c8d5cf353787ea7.png) for all t, it holds for any real number c that
for all t, it holds for any real number c that
![P\left[\sup_{t \in [0,T+S]} X_t \leq c\right] \ge P\left[\sup_{t \in [0,T]} X_t \leq c\right] P\left[\sup_{t \in [0,S]} X_t \leq c\right], \quad T,S > 0](../I/m/8b64259e3417f916f21145553a3d4ad1.png) .
.
History
Slepian's lemma was first proven by Slepian in 1962, and has since been used in reliability theory, extreme value theory and areas of pure probability. It has also been reproven in several different forms.
References
- Slepian, D. "The One-Sided Barrier Problem for Gaussian Noise", Bell System Technical Journal (1962), pp 463–501.
- Huffer, F. "Slepian's inequality via the central limit theorem", Canadian Journal of Statistics (1986), pp 367–370.
- Ledoux, M., Talagrand, M. "Probability in Banach Spaces", Springer Verlag, Berlin 1991, pp 75.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 1/20/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.