Stenosis of pulmonary artery
| Stenosis of pulmonary artery | |
|---|---|
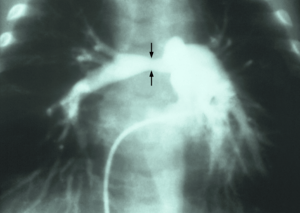 | |
| Stenosis of the right pulmonary artery in a patient which was due to a case of congenital rubella. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | medical genetics |
| ICD-10 | Q25.6 |
| ICD-9-CM | 747.3 |
Stenosis of the pulmonary artery is a condition where the pulmonary artery is subject to an abnormal constriction (or stenosis).[1] Peripheral pulmonary artery stenosis may occur as an isolated event or in association with Alagille syndrome, Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy type 1, Costello syndrome, Keutel syndrome, nasodigitoacoustic syndrome (Keipert syndrome), Noonan syndrome or Williams syndrome.
It should not be confused with a pulmonary valve stenosis, which is in the heart, but can have similar hemodynamic effects. Both stenosis of the pulmonary artery and pulmonary valve stenosis are causes of pulmonic stenosis.
In some cases it is treated with surgery.[2]
References
- ↑ "Pulmonary Artery Stenosis". Retrieved 2009-01-18.
- ↑ Saidi AS, Kovalchin JP, Fisher DJ, Ferry GD, Grifka RG (1998). "Balloon pulmonary valvuloplasty and stent implantation. For peripheral pulmonary artery stenosis in Alagille syndrome". Tex Heart Inst J. 25 (1): 79–82. PMC 325508
 . PMID 9566070.
. PMID 9566070.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/26/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.