Ugocsa County
| Ugocsa County Comitatus Ugotsensis Ugocsa vármegye Komitat Ugotsch Comitatul Ugocea Комітат Уґоча | |||||
| County of the Kingdom of Hungary | |||||
| |||||
|
Coat of arms | |||||
 | |||||
| Capital | Nagyszőllős 48°8′N 23°2′E / 48.133°N 23.033°ECoordinates: 48°8′N 23°2′E / 48.133°N 23.033°E | ||||
| History | |||||
| • | Established | 1876 | |||
| • | Treaty of Trianon | June 4, 1920 | |||
| Area | |||||
| • | 1910 | 1,213 km2 (468 sq mi) | |||
| Population | |||||
| • | 1910 | 91,800 | |||
| Density | 75.7 /km2 (196 /sq mi) | ||||
| Today part of | | ||||
| Vynohradiv is the current name of the capital. | |||||
Ugocsa was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now in north-western Romania (1/4) and western Ukraine (3/4). The capital of the county was Nagy-Szőllős (Vynohradiv Ukrainian,Sevlush in Rusyn, Vinogradov in Russian).
Geography
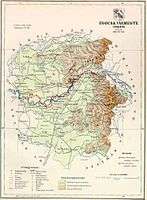
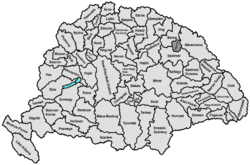
Ugocsa county shared borders with the Hungarian counties Máramaros, Szatmár and Bereg. It was situated on both sides of the river Tisza. Its area was 1208 km² around 1910.
History
In 1920, by the Treaty of Trianon most of the county (including Nagy-Szőllős) became part of newly formed Czechoslovakia. The southern part (including Halmi, Halmeu in Romanian language) became part of Romania except from 1940 until the end of the World War II when it was returned to Hungary by the Second Vienna Award.
In 1938, the western part of the former Czechoslovak part was returned to Hungary by the First Vienna Award and after, in 1939 the rest became part of Hungary when the remainder of Carpathian Ruthenia was annexed after Czechoslovakia ceased to exist. The county Ugocsa was recreated, again with Nagy-Szőllős as capital.
After World War II, the formerly Czechoslovak part of Ugocsa county became part of the Soviet Union, Ukrainian SSR, Zakarpattia Oblast. Since 1991, when the Soviet Union split up, the Zakarpattia Oblast is part of Ukraine.
The southern part of the county is now part of the Romanian county Satu Mare.
Demographics
1900
In 1900, the county had a population of 83,316 people and was composed of the following linguistic communities:[1]
Total:
- Hungarian: 35,702 (42.9%)
- Ruthenian: 32,721 (39.3%)
- Romanian: 9,270 (11.1%)
- German: 5,505 (6.6%)
- Slovak: 16 (0.0%)
- Croatian: 3 (0.0%)
- Serbian: 1 (0.0%)
- Other or unknown: 98 (0.1%)
According to the census of 1900, the county was composed of the following religious communities:[2]
Total:
- Greek Catholic: 52,417 (62.9%)
- Calvinist: 12,928 (15.5%)
- Jewish: 10,556 (12.7%)
- Roman Catholic: 7,264 (8.7%)
- Lutheran: 108 (0.2%)
- Greek Orthodox: 14 (0.0%)
- Unitarian: 10 (0.0%)
- Other or unknown: 9 (0.0%)
1910
In 1910, the county had a population of 91,755 people and was composed of the following linguistic communities:[3]
Total:
- Hungarian: 42,677 (46.5%)
- Ruthenian: 34,415 (37.5%)
- Romanian: 9,750 (10.6%)
- German: 4,632 (5.1%)
- Slovak: 37 (0.0%)
- Croatian: 4 (0.0%)
- Serbian: 1 (0.0%)
- Other or unknown: 239 (0.3%)
According to the census of 1910, the county was composed of the following religious communities:[4]
Total:
- Greek Catholic: 57,550 (62.7%)
- Calvinist: 14,002 (15.3%)
- Jewish: 11,850 (12.9%)
- Roman Catholic: 8,173 (8.9%)
- Lutheran: 120 (0.1%)
- Greek Orthodox: 48 (0.1%)
- Unitarian: 8 (0.0%)
- Other or unknown: 4 (0.0%)
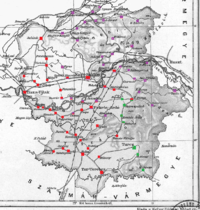
Subdivisions
In the early 20th century, the subdivisions of Ugocsa county were:
| Districts (járás) | |
|---|---|
| District | Capital |
| Tiszáninnen | Nagyszőllős, UA Vynohradiv |
| Tiszántúl | Halmi, RO Halmeu |
Vynohradiv is now in Ukraine; Halmeu is now in Romania.
References
- ↑ "KlimoTheca :: Könyvtár". Kt.lib.pte.hu. Retrieved 2012-06-26.
- ↑ "KlimoTheca :: Könyvtár". Kt.lib.pte.hu. Retrieved 2012-06-26.
- ↑ "KlimoTheca :: Könyvtár". Kt.lib.pte.hu. Retrieved 2012-06-26.
- ↑ "KlimoTheca :: Könyvtár". Kt.lib.pte.hu. Retrieved 2012-06-26.
.svg.png)
