Mesna
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈmɛznə/ |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | Oral, intravenous |
| ATC code | R05CB05 (WHO) V03AF01 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 45–79% (Oral) |
| Metabolism | Oxidised in circulation |
| Biological half-life | 0.36–8.3 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
19767-45-4 |
| PubChem (CID) | 29769 |
| ChemSpider |
27663 |
| UNII |
NR7O1405Q9 |
| KEGG |
D01459 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL975 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.039.336 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
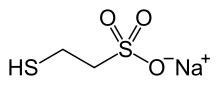
| Formula | C2H5NaO3S2 |
| Molar mass | 164.181 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Mesna is an organosulfur compound used as an adjuvant in cancer chemotherapy involving cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide. It is marketed by Baxter as Uromitexan and Mesnex. The name of the substance is an acronym for 2-mercaptoethane sulfonate Na (Na being the chemical symbol for sodium).
It is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, the most important medications needed in a basic health system.[1]
Medical uses
Chemotherapy adjuvant
Mesna is used therapeutically to reduce the incidence of haemorrhagic cystitis and haematuria when a patient receives ifosfamide or cyclophosphamide for cancer chemotherapy. These two anticancer agents, in vivo, may be converted to urotoxic metabolites, such as acrolein.
Mesna assists to detoxify these metabolites by reaction of its sulfhydryl group with α,β-unsaturated carbonyl containing compounds such as acrolein.[2] This reaction is known as a Michael addition. Mesna also increases urinary excretion of cysteine.
Other
Outside North America, mesna is also used as a mucolytic agent, working in the same way as acetylcysteine; it is sold for this indication as Mistabron[3] and Mistabronco.
Administration
It is administered intravenously or orally (per mouth).[4] The IV mesna infusions would be given with IV ifosfamide, while oral mesna would be given with oral cyclophosphamide. The oral doses must be double the intravenous (IV) mesna dose due to bioavailability issues. The oral preparation allows patients to leave the hospital sooner, instead of staying four to five days for all the IV mesna infusions.
Mechanism
Mesna reduces the toxicity of urotoxic compounds that may form after chemotherapy administration. Mesna is a water-soluble compound with antioxidant properties, and is given concomitantly with the chemotherapeutic agents cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide. Mesna concentrates in the bladder where acrolein accumulates after administration of chemotherapy and through a Michael addition, forms a conjugate with acrolein and other urotoxic metabolites.[2] This conjugation reaction inactivates the urotoxic compounds to harmless metabolites. The metabolites are then excreted in the urine.[5]
See also
- Coenzyme M—a coenzyme with the same parent structure used by methanogenic bacteria
References
- ↑ "19th WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (April 2015)" (PDF). WHO. April 2015. Retrieved May 10, 2015.
- 1 2 Thurston DE (2007). Chemistry and Pharmacology of Anticancer Drugs. Boca Raton: CRC Press/Taylor & Francis. pp. 53–54. ISBN 978-1-4200-0890-6.
- ↑ "Mistabron Ampoules". South African Electronic Package Inserts. August 1973. Retrieved 2008-08-12.
- ↑ Mace JR, Keohan ML, Bernardy H, et al. (December 2003). "Crossover randomized comparison of intravenous versus intravenous/oral mesna in soft tissue sarcoma treated with high-dose ifosfamide". Clin. Cancer Res. 9 (16 Pt 1): 5829–34. PMID 14676103.
- ↑ Shaw IC, Graham MI (1987). "Mesna—a short review". Cancer Treat. Rev. 14 (2): 67–86. doi:10.1016/0305-7372(87)90041-7. PMID 3119211.
External links
- BC Cancer Agency
- NIH/MedlinePlus patient information
- Mesna at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)