Viti Levu
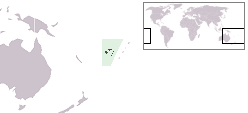
 Map of Fiji showing Viti Levu (one of its major islands) | |
 | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Pacific Ocean |
| Coordinates | 17°48′S 178°0′E / 17.800°S 178.000°E |
| Archipelago | Viti Levu Group |
| Area | 10,388 km2 (4,011 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 75th |
| Length | 146 km (90.7 mi) |
| Width | 106 km (65.9 mi) |
| Highest elevation | 1,324 m (4,344 ft) |
| Highest point | Tomanivi |
| Administration | |
|
Fiji | |
| Division | Western Division and Central Division |
| Largest settlement | Suva (pop. 77,366) |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 600,000 |
| Pop. density | 55.83 /km2 (144.6 /sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups |
Native Fijians (54.3%), Indo-Fijians (38.1%); other (Asian, Europeans, other Pacific Islander) (7.6%) |
Viti Levu (pronounced [ˈβitʃi ˈleβu]) is the largest island in the Republic of Fiji, the site of the nation's capital, Suva, and home to a large majority of Fiji's population.
Geography and economy

The largest island, Viti Levu is home to 70% of the population (about 600,000) and is the hub of the entire Fijian archipelago. It measures 146 kilometers long and 106 kilometers wide and has an area of 10,389 square kilometers comparable to the size of The Big Island of Hawaii or slightly smaller than Connecticut. Geologists believe that Viti Levu has been submerged a number of times, and has been covered by lava and other volcanic materials. Earthquakes and volcanic eruptions account for the somewhat rugged terrain of the island, which is divided into roughly equal halves by a north-south mountain range. The eastern side of the island experiences heavy rainfall, while the western side is noticeably drier. Accordingly, sugar cane production thrives in the west, while a dairy industry is being built in the east. Fiji's biggest cattle ranch, with 7000 head of cattle in its 70 square kilometres, is at Yaqara, halfway between Tavua and Rakiraki. The centre of the island is forested and includes the nation's highest peak Mount Tomanivi (otherwise Mount Victoria) rising to 1,324 meters. The island is the only known home of one of the world's largest insects, the Giant Fijian long-horned beetle.
Localities


Viti Levu hosts the capital city of Suva, and is home to nearly three quarters of the population of the Republic (about 580,000). Other important towns, all around the coast, include Ba, Lautoka, Nadi, Nausori, Rakiraki, and Sigatoka. One major road has been built around the perimeter of Viti Levu. Well-known localities include Natadola Beach, Pacific Harbour (a resort center about 50 kilometers from Suva).
Politics
Eight of Fiji's fourteen Provinces are in Viti Levu. The Provinces of Ba, Nadroga-Navosa, and Ra comprise the Western Division, while Naitasiri, Namosi, Rewa, Serua, and Tailevu form the Central Division. In part because of its high concentration of Indo-Fijians, whose ancestors came mostly as indentured workers from India between 1879 and 1916, the political dynamics of western Viti Levu are somewhat different from those of eastern Viti Levu, where, apart from the multi-racial urban areas, indigenous Fijians are more heavily concentrated.
History
Viti Levu is believed to have been inhabited longer than the northern island of Vanua Levu. According to oral traditions, the first Melanesian settlers landed at Vuda Point and established Viseisei, believed to be Fiji's oldest settlement, although archaeologists refute this claim.
Other
The Canadian entrepreneur Peter Munk named his Klosters house after the island, as Viti Levu was where he and David Gilmour started the Southern Pacific Hotel chain in the 1960s.[1]
References
- ↑ "Peter Munk: A mining magnate nears the end of his golden reign" ERIC REGULY. The Globe and Mail 15 March 2014
External links
 Viti Levu travel guide from Wikivoyage
Viti Levu travel guide from Wikivoyage
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Viti Levu. |
Coordinates: 17°48′S 178°0′E / 17.800°S 178.000°E