Voacanga africana
| Voacanga africana | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Asterids |
| Order: | Gentianales |
| Family: | Apocynaceae |
| Genus: | Voacanga |
| Species: | V. africana |
| Binomial name | |
| Voacanga africana Stapf[1] | |
Voacanga africana is a small tropical African tree that grows to 6m in height. It has leaves that are up to 30 cm in length, and the tree produces yellow or white flowers, which become berries with yellow seeds.
Uses

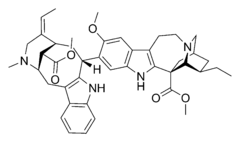
The bark and seeds of the tree are used in Ghana as a poison, stimulant, aphrodisiac, and ceremonial psychedelic. These effects are due to the presence of a complex mixture of iboga alkaloids such as voacangine, voacamine, vobtusine, amataine, akuammidine, tabersonine, coronaridine and vobtusine.
Medicinal uses
A number of these compounds have pharmaceutical uses. [2] Of particular pharmaceutical interest is voacangine, which is a common precursor in the semi-synthesis of the anti-addiction medication ibogaine. Small amounts of ibogaine are found in Voacanga Africana root bark but not in sufficient quantity to have much medicinal effect.
References
Notes
- ↑ "Voacanga africana information from NPGS/GRIN". www.ars-grin.gov. Retrieved 2008-04-05.
- ↑ Review of Voacanga africana taxonomy, phytochemistry, ethnobotany and pharmacology.