Whiting reaction
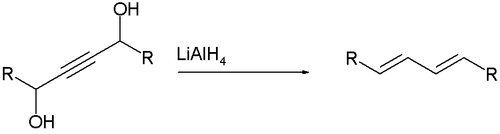
The Whiting reaction is an organic reaction converting a propargyl diol into a diene using lithium aluminium hydride.[1]
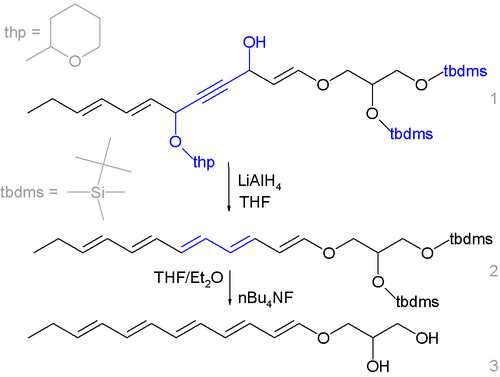
This organic reduction has been applied in the synthesis of fecapentaene.[2][3][4]
References
- ↑ Nayler, P.; Whiting, M. C. J. Chem. Soc. 1954, 4006–09.
- ↑ Synthesis of crystalline (.+-.)-fecapentaene Hans Rudolf Pfaendler, Franz Karl Maier, and Sonja Klar J. Am. Chem. Soc.; 1986; 108(6) pp. 1338–39. (doi:10.1021/ja00266a057)
- ↑ a mutagenic glyceryl ether lipid which can occur in trace amounts in the feces of people living in industrialized countries and are suspected to be a cause for colon cancer
- ↑ protecting groups are tetrahydropyranyl and TBSMS, the final step is deprotection with tetra-n-butylammonium fluoride
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/28/2013. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.