Xiangjiaba–Shanghai HVDC system
| Xiangjiaba–Shanghai HVDC system | |
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Country | China |
| Coordinates |
28°32′47″N 104°25′04″E / 28.54639°N 104.41778°E 30°55′32″N 121°46′16″E / 30.92556°N 121.77111°E |
| From | Xiangjiaba Dam |
| To | Shanghai |
| Ownership information | |
| Owner | State Grid Corporation of China |
| Construction information | |
| Manufacturer of substations | State Grid Corporation of China, ABB, Siemens |
| Installer of substations | State Grid Corporation of China |
| Commissioned | 2010 |
| Technical information | |
| Type | Transmission |
| Type of current | HVDC |
| Total length | 2,000 km (1,200 mi) |
| Power rating | 6400 MW |
| DC Voltage | ±800 kV |
| Number of poles | 2 |
The Xiangjiaba–Shanghai HVDC system is a ±800 kV, 6400 MW high-voltage direct current transmission system in China. The system was built to export hydro power from Xiangjiaba Dam in Sichuan province, to the major city of Shanghai. Built and owned by State Grid Corporation of China (SGCC), the system became the world’s largest-capacity HVDC system when it was completed in July 2010, although it has already been overtaken by the 7200 MW Jinping–Sunan HVDC scheme which was put into operation in December 2012. It also narrowly missed becoming the world’s first 800 kV HVDC line, with the first pole of the Yunnan–Guangdong project having been put into service 6 months earlier. It was also the world’s longest HVDC line when completed, although that record is also expected to be overtaken early in 2013 with the completion of the first bipole of the Rio Madeira project in Brazil.
Various values are quoted for the length of the Xiangjiaba–Shanghai DC line, ranging from 1,907 kilometres (1,185 mi)[1] to 2,070 kilometres (1,290 mi),[2] but in any event the line is significantly longer than that of the 1,700 kilometres (1,100 mi) Inga–Shaba project in Democratic Republic of Congo which had held the record since 1982. Significant design and development work had to be performed to qualify the specialised equipment for operation at 800 kV.[3][4]
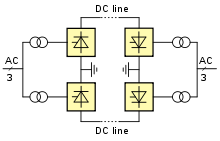
The scheme is a bipolar system with overhead lines for the high-voltage conductors and ground return for the neutral current. However, because of the very high operating voltage and power, each pole contains two twelve pulse bridges in series at each end.
Converter stations
The Fulong (rectifier) converter station is located approximately 10 km south of Xiangjiaba Dam and is connected to the power plant by four 500 kV AC lines. The thyristor valves were supplied by Siemens together with its partner XD Xi’an Power Rectifier Works. The valves use state of the art 8.5 kV rated, 150 mm diameter electrically triggered thyristors. Ten of the converter transformers were also supplied by Siemens.[2]
The Fengxia (inverter) converter station is located some 45 km south-east from the centre of Shanghai and feeds power to the Nanhui AC substation via three 500 kV AC lines. Much of the DC equipment at the Fengxia station was provided by ABB, including the thyristor valves and converter transformers.[5] In common with the valves at the Fulong station, the valves use 8.5 kV rated, 150 mm diameter electrically triggered thyristors. At Fengxia, each valve consists of 56 series connected thyristor levels (of which two are redundant), arranged in 8 thyristor modules of 7 thyristor levels each.[4]
Waypoints
| Site | Coordinates |
|---|---|
| Fulong HVDC Static Inverter | 28°32′47″N 104°25′04″E / 28.54639°N 104.41778°E |
| Fengxia Electrode Line Branch | 30°54′39″N 121°08′00″E / 30.91083°N 121.13333°E |
| Fengxia Electrode | 30°47′4″N 121°08′09″E / 30.78444°N 121.13583°E |
| Fengxia HVDC Static Inverter | 30°55′32″N 121°46′16″E / 30.92556°N 121.77111°E |
See also
- High-voltage direct current
- HVDC converter station
- HVDC converter
- Xiangjiaba Dam
- Yunnan–Guangdong HVDC
References
- ↑ ABB Website: Xiangjiaba - Shanghai ±800 kV UHVDC transmission project, ABB publication POW0056, rev 1.
- 1 2
- ↑ Lescale, V. F., Åström, U.,Ma, W., Liu, Z. The Xiangjiaba-Shanghai 800kV UHVDC project - Status and special aspects, Paris, 2010, paper reference B4-102.
- 1 2 Sheng, B., Danielsson, J., Fu, Y., Liu, Z., Converter Valve Design and Valve Testing for Xiangjiaba – Shanghai ±800kV 6400MW UHVDC Power Transmission Project, PowerCon 2010, Hangzhou, China, Oct. 24th – 28th, 2010
- ↑ Kumar, A., Lescale, V., Åström, U., Hartings, R., Berglund, M., 800 kV UHVDC . From Test Station to Project Execution, CIGRÉ Second International Symposium on Standards for Ultra High Voltage Transmission, New Delhi, 2009.
External links
- SGCC Website: Xiangjiaba-Shanghai +/-800 kV UHV DC Transmission Pilot Project
- ABB HVDC References: Xiangjiaba - Shanghai