Zadoff–Chu sequence
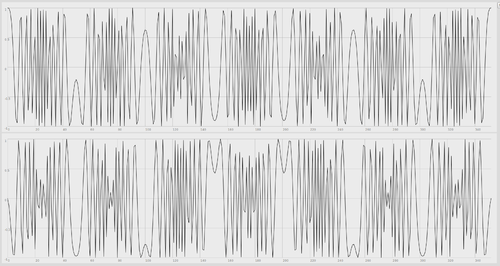
A Zadoff–Chu (ZC) sequence, also referred to as Chu sequence or Frank–Zadoff–Chu (FCZ) sequence,[1] is a complex-valued mathematical sequence which, when applied to radio signals, gives rise to an electromagnetic signal of constant amplitude, whereby cyclically shifted versions of the sequence imposed on a signal result in zero correlation with one another at the receiver. A generated Zadoff–Chu sequence that has not been shifted is known as a "root sequence".
These sequences exhibit the useful property that cyclically shifted versions of themselves are orthogonal to one another, provided, that is, that each cyclic shift, when viewed within the time domain of the signal, is greater than the combined propagation delay and multi-path delay-spread of that signal between the transmitter and receiver.
The complex value at each position n of each root Zadoff–Chu sequence parametrised by u is given by
where
- ,
- and ,
- ,
- .
Zadoff–Chu sequences are CAZAC sequences (constant amplitude zero autocorrelation waveform).
They are named after Solomon A. Zadoff and D. C. Chu. Note that the special case results in a Chu sequence.
Properties of Zadoff-Chu sequences
1. They are periodic with period if is odd.
2. If is prime, Discrete Fourier Transform of Zadoff–Chu sequence is another Zadoff–Chu sequence conjugated, scaled and time scaled.
- where is the multiplicative inverse of u modulo .
3. The auto correlation of a Zadoff–Chu sequence with a cyclically shifted version of itself is zero, i.e., it is non-zero only at one instant which corresponds to the cyclic shift.
4. The cross-correlation between two prime length Zadoff–Chu sequences, i.e. different values of , is constant , provided that is relative prime to [2]
Usages
Zadoff–Chu sequences are used in the 3GPP LTE Long Term Evolution air interface in the Primary Synchronization Signal (PSS), random access preamble (PRACH), uplink control channel (PUCCH), uplink traffic channel (PUSCH) and sounding reference signals (SRS).
By assigning orthogonal Zadoff–Chu sequences to each LTE eNodeB and multiplying their transmissions by their respective codes, the cross-correlation of simultaneous eNodeB transmissions is reduced, thus reducing inter-cell interference and uniquely identifying eNodeB transmissions.
Zadoff–Chu sequences are an improvement over the Walsh–Hadamard codes used in UMTS because they result in a constant-amplitude output signal, reducing the cost and complexity of the radio's power amplifier.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Zepernick, Hans-Jurgen; Finger, Adolf (2013). Pseudo Random Signal Processing: Theory and Application. Wiley. ISBN 9781118691212.
- ↑ Popovic, B.M. (1992). "Generalized Chirp-Like polyphase sequences with optimum correlation properties". IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory. 38 (4): 1406–9. doi:10.1109/18.144727.
- ↑ Song, Lingyang; Shen, Jia, eds. (2011). Evolved Cellular Network Planning and Optimization for UMTS and LTE. New York: CRC Press. ISBN 1439806500.
Further reading
- Frank, R. L. (Jan 1963). "Polyphase codes with good nonperiodic correlation properties". IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory. 9 (1): 43–45. doi:10.1109/TIT.1963.1057798.
- Chu, D. C. (July 1972). "Polyphase codes with good periodic correlation properties". IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory. 18 (4): 531–2. doi:10.1109/TIT.1972.1054840.
- S. Beyme and C. Leung (2009). "Efficient computation of DFT of Zadoff-Chu sequences". Electron. Lett. 45 (9): 461–3. doi:10.1049/el.2009.3330.
- Khan, Farooq. "9.2: Zadoff Chu (ZC) Sequences". IHS Engineering360.
- "Wideband CDMA 3GPP Specification Library". QT Corporation.