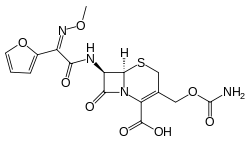
Cefuroxime
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Zinacef, Ceftin |
| MedlinePlus | a601206 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | intramuscular, intravenous |
| ATC code | J01DC02 (WHO) S01AA27 (WHO) QJ51DC02 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 37% on an empty stomach, up to 52% if taken after food |
| Biological half-life | 80 minutes |
| Excretion | Urine 66–100% unchanged |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
55268-75-2 |
| PubChem (CID) | 5361202 |
| DrugBank |
DB01112 |
| ChemSpider |
4514699 |
| UNII |
O1R9FJ93ED |
| KEGG |
D00262 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL466 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.054.127 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H16N4O8S |
| Molar mass | 424.386 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Cefuroxime is an enteral second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic. It was discovered by the Glaxo, now GlaxoSmithKline and first marketed in 1978 as Zinacef. It received approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in October 1983.[1]
Cefuroxime axetil is an acetoxyetyl-ester-prodrug of cefuroxime which is effective orally.[2]
Medical uses
As with the other cephalosporins, although as a second-generation variety, it is less susceptible to beta-lactamase. Hence, it may have greater activity against Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Lyme disease. Unlike most other second-generation cephalosporins, cefuroxime can cross the blood-brain barrier.
Side effects
Cefuroxime is generally well-tolerated and its side effects are usually transient. If ingested after food, this antibiotic is both better absorbed and less likely to cause its most common side effects of diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, headaches/migraines, dizziness, and abdominal pain compared to most antibiotics in its class.
Although a widely stated cross-allergic risk of about 10% exists between cephalosporins and penicillin, recent assessments have shown no increased risk for a cross-allergic reaction for cefuroxime and several other second-generation or later cephalosporins.[3]
Trade names
In US it is available as Zinacef by Covis Pharmaceuticals as the company acquired the US rights of the product from GSK.[4] In Bangladesh it is available as Xorimax by Sandoz. In India it is available as Supacef by GSK.[5] In Poland it is available as Zamur by Mepha, subsidiary of Teva Pharmaceutical Industries.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ "Cefuroxime medical facts from". Drugs.com.
- ↑ Walter Sneader. "Drug Discovery: History".
- ↑ Pichichero ME (2006). "Cephalosporins can be prescribed safely for penicillin-allergic patients" (PDF). The Journal of family practice. 55 (2): 106–12. PMID 16451776.
- ↑ http://www.covispharma.ch/assets/pdf/covis-pharma-acquires-portfolio-of-drugs-from-glaxosmithkline.pdf
- ↑ "GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals Limited – Prescription Medicines – Anti-Infective". Gsk-india.com. 26 March 2013.
- ↑ "Charakterystyka produktu lecznicznego" (PDF). Urząd Rejestracji Produktów Leczniczych, Wyrobów Medycznych i Produktów Biobójczych. 12 November 2015.