1700s (decade)
| Millennium: | 2nd millennium |
| Centuries: | 17th century – 18th century – 19th century |
| Decades: | 1670s 1680s 1690s – 1700s – 1710s 1720s 1730s |
| Years: | 1700 1701 1702 1703 1704 1705 1706 1707 1708 1709 |
| 1700s-related categories: |
Births – Deaths – By country Establishments – Disestablishments |
Events
Contents: 1700 1701 1702 1703 1704 1705 1706 1707 1708 1709
1700
January–June
- January 1 – Protestant Western Europe, except England, starts using the Gregorian calendar
- January 1 (Julian) – Tsardom of Russia begins numbering its calendar from the birth of Christ (Anno Domini) instead of since the Creation (Anno Mundi).
- January 26 – At approximately 9 p.m., the Cascadia earthquake occurred with an estimated moment magnitude of 8.7–9.2. This megathrust earthquake ruptured about 1,000 kilometers (620 miles) of the Cascadia Subduction Zone and caused a tsunami that struck the coast of Japan approximately 10 hours later.
- February 3 – The 'Lesser Great Fire' destroys a substantial part of central Edinburgh, Scotland.[1]
- February 12 – The Great Northern War begins with a joint invasion of Swedish territory in Germany and Latvia by Denmark and Poland/Saxony. Sweden has control of the Baltic Sea and holds territory that includes Finland, Estonia, Latvia and parts of northern Germany. To challenge its power, an alliance is formed between Tsar Peter I of Russia, King Frederick IV of Denmark and Augustus II the Strong, King of Poland and Elector of Saxony. Sweden's ruler is the militaristic Charles XII, known as the "Swedish Meteor".
- February 27 – Island of New Britain discovered by William Dampier in the western Pacific.[2]
- March 1 (Gregorian) – Protestant Germany and Denmark–Norway adopt the Gregorian calendar.
- March 1 (Swedish), March 11 (Gregorian), February 29 (Julian) – Swedish calendar adopted.
- early March – William Congreve's comedy The Way of the World is first performed in London.[3][4]
- March 25 – Treaty of London signed between France, England and Holland.[5]
- April – Fire destroys many buildings in Gondar, the capital of Ethiopia, including two in the palace complex.
- May – In Rhode Island (American colony), Walter Clarke, three term former Governor of Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, is elected deputy governor for the second time, serving under is brother-in-law Samuel Cranston.
- May 5
- Within a few days of John Dryden's death (May 1 O.S.), his last written work (The Secular Masque) is performed as part of Vanbrugh's version of The Pilgrim.
- William Penn begins monthly meetings for blacks advocating emancipation.
July–December
- July 11 – The Prussian Academy of Sciences is founded with Gottfried Leibniz as president.[6]
- Summer – Charles XII of Sweden counter-attacks his enemies by invading Zealand (Denmark), assisted by an Anglo-Dutch naval squadron under Sir George Rooke, rapidly compelling the Danes to submit to peace.
- August 18 (August 7 O.S.) – Peace of Travendal concluded between the Swedish Empire, Denmark–Norway and Holstein-Gottorp in Traventhal. On the same day, Augustus II, King of Poland, and Peter the Great, Tsar of Russia, enter the war against Sweden.
- Late summer – A Russian army invades Swedish Estonia and besieges the town of Narva.
- November 1 – Charles II, last Spanish king of the House of Habsburg, dies insane at the Royal Alcazar of Madrid (aged 38) leaving no children.
- November 15 – Louis XIV accepts the Spanish crown on behalf of his grandson Philip of Anjou, who becomes Philip V of Spain (to 1746), thus triggering the War of the Spanish Succession (1701–1741).
- November 18 – Battle of Olkieniki, Lithuanian Civil War: victory for the anti-Sapieha coalition.
- November 23 – Pope Clement XI succeeds Pope Innocent XII as the 243rd pope.
- November 30 (November 19 O.S.; November 20 Swedish calendar) – Battle of Narva in Estonia. Having led his army of 8,000 on a forced march from Denmark to Estonia, Charles XII of Sweden routs the huge Russian army at Narva.
- December 28 – Laurence Hyde, 1st Earl of Rochester, is appointed Lord Lieutenant of Ireland.

Europe at the beginning of the 18th century
Date unknown
- Mission San Xavier del Bac is founded in New Spain near Tucson, as a Spanish Roman Catholic mission.
- An inventory made for the Medici family of Florence is the first documentary evidence for a piano, invented by their instrument keeper Bartolomeo Cristofori.
- An English translation of the novel Don Quixote, "translated from the original by many hands and published by Peter Motteux", begins publication in London. While popular among readers, it will eventually come to be known as one of the worst translations of the novel, totally betraying the spirit of Miguel de Cervantes's masterpiece.
- The value of sales of English manufactured products to the Atlantic economy is £3.9 million.
- approx. date – Lions become extinct in Libya.
Ongoing
- Nam tiến: southward expansion of the territory of Vietnam to cover the entire Indochina Peninsula.[7]
1701
January–June
- January 12 – Parts of Netherlands adopt the Gregorian calendar
- January 18 – The electorate of Brandenburg-Prussia becomes the Kingdom of Prussia as Elector Frederick III is proclaimed King Frederick I. Prussia remains part of the Holy Roman Empire. It consists of Brandenburg, Pomerania and East Prussia. Berlin is the capital. [8]
- January 28 – The Chinese storm Dartsedo.
- January – Robert Walpole enters the Parliament of England and soon makes his name as a spokesman for Whig policy.
- March 8 – Mecklenburg-Strelitz is created as a north German duchy.
- March – The War of the Spanish Succession begins. It is an international retaliation to Louis XIV’s acceptance in 1700 of the Spanish crown on behalf of his grandson Philip of Anjou, who became Philip V, first Bourbon king of Spain. Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor forms the Grand Alliance with Great Britain, the Netherlands, Denmark, Portugal, Savoy and Prussia. Louis XIV allies France with Spain and Bavaria.
- April 21 – In Japan, the young daimyo Asano Naganori is ordered to commit seppuku (ritual suicide). A group of 47 samurai of his service begin planning to avenge his death.
- May 23 – After being convicted of murdering William Moore and for piracy, Captain William Kidd is hanged in London.
- June 24 – The Act of Settlement 1701 is passed by the Parliament of England to exclude the Catholic Stuarts from the British monarchy. Under its terms, King William III, childless, would be succeeded by Queen Mary II's sister Princess Anne and her descendants. If Anne should have no descendants, she would be succeeded by Sophia of Hanover and her descendants (hence the Hanoverian Succession in 1714).
July–December
- July 9 – Crossing of the Düna: Following his victories over Denmark and Russia in 1700, Charles XII of Sweden escalates the conflict in the Great Northern War by an invasion of Poland. The Swedish defeat the army of Saxony (then in personal union with Poland) at the River Dvina.
- July 24 – Foundation of a French emporium named Fort Ponchartrain (later to become Detroit).
- August 4 – The Great Peace of Montreal is signed, ending 100 years of war between the Iroquois Confederacy and New France and its Huron and Algonquian allies. Formerly allied with the English, the treaty assured the Iroquois would be neutral if France and England were to ever resume hostilities.
- September 16 – Death of deposed King James II of England (James VII of Scotland) in exile at the Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye in France. His supporters, the Jacobites, turn to his son James Francis Edward Stuart (later called "The Old Pretender"), whom they recognise as James VIII and III. Louis XIV of France, the Papal States and Spain also recognise him as the rightful heir.[9]
- October 9 – The Collegiate School of Connecticut (later renamed Yale University) is chartered in Old Saybrook, Connecticut.
Date unknown
- English agriculturalist Jethro Tull invents a drill for planting seeds in rows.
- The Philharmonic Society (Academia Philharmonicorum) is established in Ljubljana, Slovenia.
1702
January–June
- January 12 – In North America, ships from Fort Maurepas arrive at Twenty-Seven Mile Bluff to build Fort Louis de la Mobile (future Mobile, Alabama) to become the capital of French Louisiana.
- March 8 (O.S.) – William III of England dies of complications following a fall from his horse on February 20; his sister-in-law Princess Anne Stuart becomes Queen Anne of England, Scotland and Ireland. Anne is the mother of 17 children by her husband Prince George of Denmark and Norway but none will survive childhood and she will die without heir to enable the Hanoverian Succession. The States General of the Netherlands do not appoint a new stadtholder and so the Dutch Republic becomes a true republic again.
- March 11 (O.S.) – The first regular English-language national newspaper, The Daily Courant, is published for the first time[2] in Fleet Street in the City of London; it covers only foreign news.
- May – Warsaw is conquered by Charles XII of Sweden .
- May 14 (N.S.) – The War of the Spanish Succession widens, as war is declared on France by the Grand Alliance (Kingdom of England, Dutch Republic and Holy Roman Empire).
- June – Queen Anne's Captain-General John Churchill forces the surrender of Kaiserswerth on the Rhine.
July–December
- July 19 (July 8 O.S.; July 9 Swedish calendar) – Battle of Klissow: Charles XII of Sweden decisively defeats the Polish–Lithuanian-Saxon army.
- September – John Churchill forces the surrender of Venlo on the Meuse River.
- October
- Sir George Rooke fails to take Cadiz, but captures a Spanish treasure fleet and destroys French and Spanish warships. Churchill forces the surrender of Liège.
- Battle of Flint River: failed attack by Spanish and Apalachee Indian forces against Creek Indians supported by English traders in what is now the state of Georgia.
- October 10 – Siege of St. Augustine opens: English forces besiege St. Augustine in Spanish Florida. First major action in Queen Anne's War in North America.
- October 27 – English troops plunder St. Augustine in Spanish Florida.
- December 14 – John Churchill is created duke of Marlborough.
- December 30 – Siege of St. Augustine lifted.
Date unknown
- Delaware designated a separate colony.
1703
January–June
- January 14 – An earthquake hits Norcia, Italy.
- January 30 (December 14 of previous year in the Chinese calendar) – In Japan, the revenge of the Forty-seven Ronin occurs, assassinating Daimyo Kira Yoshinaka, the enemy of their former lord Asano Naganori, at his own mansion as a vengeance. 46 of the 47 samurai commit seppuku, a ritual suicide on March 20 (February 4 in the Chinese calendar).
- February – Soldiers at Fort Louis de la Mobile celebrate Mardi Gras in Mobile, starting the tradition for Mobile, Alabama.
- February 3 – An earthquake hits the town of L'Aquila, Italy, killing 3000 and damaging many buildings.
- April 21 – The Company of Quenching of Fire (i.e., a fire brigade) is founded in Edinburgh, Scotland.
- May 26 – Portugal joins the Grand Alliance.
- May 27 (May 16 OS) – The city of Saint Petersburg is founded in Russia following Peter the Great's reconquest of Ingria from Sweden during the Great Northern War.
- June 15 – Hungarians rebel under Prince Francis II Rákóczi.
- June – The completed Icelandic census of 1703 is presented in the Althing, the first complete census of any country.
July–December

July 29: Daniel Defoe
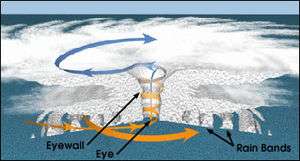
November 24: Great Storm of 1703
- July 29–July 31 – Daniel Defoe is placed in a pillory, then imprisoned for four months for the crime of seditious libel, after publishing his politically satirical pamphlet The Shortest Way with the Dissenters (1702) (his release is granted in mid-November).
- August 23 – Edirne event: Sultan Mustafa II of the Ottoman Empire is dethroned.
- September 12 – War of the Spanish Succession – Habsburg Archduke Charles is proclaimed King of Spain but never exercises full rule.
- October – A whirlwind blows down the tower of the Gan Takal in Gondar, capital of Ethiopia, killing 30.
- November 15 – The Kurucs defeated the Austrians and its allies (from Denmark, Hungary and the Serbs) near Zvolen (present day Slovakia)
- November 19 – The Man in the Iron Mask dies in the Bastille.
- November 24–December 2 – The Great Storm of 1703, an Atlantic hurricane, ravages southern England and the English Channel, killing nearly 8,000, mostly at sea.
- November 30 – Isaac Newton is elected president of the Royal Society in London, a position he will hold until his death in 1727.
- December 27 – Portugal and England sign the Methuen Treaty, which gives preference to Portuguese wines imported into England.
- December 28 – Ahmed III succeeds the deposed Mustafa II as Ottoman Emperor.
Date unknown
- French-born imposter George Psalmanazar arrives in London.
- Between 1702 and 1703 in Quebec, epidemic of smallpox, in which 2,000 to 3,000 people died with 300 to 400 in Quebec City.[10]
1704
January–June
- January 25–26 – Apalachee massacre: English colonists from the Province of Carolina and their native allies stage a series of brutal raids against a largely pacific population of Apalachee in Spanish Florida.
- February 29 – Raid on Deerfield (Queen Anne's War): French Canadians and Native Americans sack Deerfield, Massachusetts, killing over 50 English colonists.
- February – In America, Mardi Gras is celebrated with the Masque de la Mobile in the capital of Louisiana (New France), Mobile, Alabama.
- April 21 – Battle of Biskupice between the Hungarians (Kurucs) and Danes.
- April 24 – The first regular newspaper in the Thirteen Colonies of British North America, The Boston News-Letter, is published.
- May 28 – Battle of Smolenice: Kuruc rebels defeat the Austrian army and its allies.
- June 13 – Battle of Koroncó: Austrians and their allies from Denmark, Prussia, Croatia, Germany and Vojvodina defeat the Kurucs.
July–December
- July – Daniel Defoe documents the Great Storm of 1703 in England with eyewitness testimonies in The Storm.
- July 12 – Great Northern War – King Charles XII of Swedish forces the election of his ally Stanisław Leszczyński as King of Poland in place of Augustus II the Strong.
- August 3 (July 23 Old Style) – War of the Spanish Succession – Capture of Gibraltar from Spain by English and Dutch forces under Sir George Rooke.
- August 13 (August 2 OS) – War of the Spanish Succession – Battle of Blenheim: Allied troops under John Churchill, Earl of Marlborough and Prince Eugene of Savoy defeat the Franco-Bavarian army.
- August 24 (August 13 OS) – War of the Spanish Succession – French and English fleets clash off Málaga, causing heavy casualties in both sides but without sinking any ships.
- September – War of the Spanish Succession – The Twelfth Siege of Gibraltar by French and Spanish troops begins.
Date unknown
- Great Northern War: Russian troops under Tsar Peter the Great capture Tartu and Narva.
- The Sultanate of Brunei cedes its north-east territories to the Sultanate of Sulu.
- The lower three counties of the Province of Pennsylvania become the colony of Delaware.
- An earthquake strikes Gondar in Ethiopia.
- A Tale of a Tub, the first major satire by Jonathan Swift (written 1694–1697), is published in London, running through three editions this year.
- Isaac Newton publishes his Opticks.
- The Students' Monument is built in Aiud, Romania.
- Rome decrees that Roman ceremonial practice in Latin (not in Chinese) is to be the law for Chinese missions.
- Thomas Darley purchases the bay Arabian horse Darley Arabian in Aleppo, Syria, and ships him to stud in England where he becomes the most important foundation sire of all modern thoroughbred racing bloodstock.
1705
January–June
- March 8 – The Province of Carolina incorporates the town of Bath, making it the first incorporated town in present day North Carolina. The town becomes the political center and de facto capital of the northern portion of the Province of Carolina until Edenton is incorporated in 1722.
- April 16 – Anne, Queen of Great Britain honours Isaac Newton with a Knight Bachelor
- May – The Twelfth Siege of Gibraltar ends with the defending Confederate forces retaining control of the town.
- May 5 – Joseph I, Holy Roman Emperor succeeds his father Leopold I.[11]
July–December

November: Williamsburg Capitol (replica).
- November – In Williamsburg, capital of the Virginia colony in America, construction of the Capitol building is completed.
- November 5 – The Dublin Gazette publishes its first edition.
- November 15 – The Battle of Zsibó - the Austrian-Danish forces defeated the Kurucs (Hungarians)
- December – The Sophia Naturalization Act is passed by the English Parliament, which naturalizes Sophia of Hanover and the "issue of her body" as English subjects.
- December 25 – In Munich, capital of Bavaria, 1,100 militiamen from the Oberland are killed during the Sendlinger Mordweihnacht, after a failed attempt to break through several gates and capture a depot to seize better weaponry; many men were slaughtered by German federal infantry and Hungarian Husars, despite their capitulation to Austrian officers.
Date unknown
- Construction begins on Blenheim Palace, in Oxfordshire, England. It is completed in 1724.
- Taichung City, Taiwan is founded as the village of Dadun.
- With the interest paid from daimyo loans, the Konoike buy a tract of ponds and swampland, turn the land into rice paddies and settle 480 households numbering perhaps 2,880 peasants on the land.
- The Shogunate confiscates the property of a merchant in Osaka "for conduct unbecoming a member of the commercial class". The government seizes 50 pairs of gold screens, 360 carpets, several mansions, 48 granaries and warehouses scattered around the country and hundreds of thousands of gold pieces.
1706
January–June
- March 27 – Concluding that Emperor Iyasus I of Ethiopia has abdicated by retiring to a monastery, a council of high officials appoint Tekle Haymanot I Emperor of Ethiopia.
- March 31 – The last Courts (parliament) of the Principality of Catalonia are finished, presided by the king Charles III of Spain.
- May 23 – War of the Spanish Succession – Battle of Ramillies: English, Dutch, German, Swiss and Scottish troops led by John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, defeat Franco-Bavarian forces in the Low Countries.
July–December
- July 22 – Treaty of Union between Scotland and England agreed in London for ratification by the national legislatures.[12]
- September 7 – War of the Spanish Succession – Battle of Turin: Forces of Austria and Savoy defeat the French.
- October – Twinings founder, Thomas Twining, opens the first known tea room at 216 Strand, London, still open as of 2015.[13][14][15]
Date unknown
- English Parliament establishes the first turnpike trusts which place a length of road under the control of trustees drawn from local landowners and traders. The turnpike trusts borrow capital for road maintenance against the security of tolls and this arrangement becomes the common method of road maintenance for the next 150 years.
1707
January–June
- January 1 – John V is crowned King of Portugal and the Algarves in Lisbon.
- January 16 – The Treaty (or Act) of Union of the two Kingdoms of Scotland and England is ratified by the Parliament of Scotland.
- March 3 – Death of the Emperor Aurangzeb in Delhi.
- March 19 – The Act of Union with Scotland is ratified by the Parliament of England.
- April 25 (April 14 Old Style) – At the Battle of Almansa (Spain) in the War of the Spanish Succession, the Bourbon army of Spain and France (with Irish mercenaries) under the French-born Englishman James FitzJames, 1st Duke of Berwick, soundly defeats the allied forces of Portugal, England, and the Dutch Republic led by the French-born Huguenot in English service Henri de Massue, Earl of Galway. Following this, Philip V of Spain promulgates the first Nueva Planta decrees, bringing the Kingdoms of Valencia and Aragon under the laws of the Crown of Castile.[16]
- May 1 – The new sovereign state of Great Britain comes into being as a result of the Acts of Union which combine the Kingdoms of Scotland and England into a single united Kingdom of Great Britain[17] and merge the Parliaments of England and Scotland to form the Parliament of Great Britain.[18]

The Isles of Scilly, scene of the naval disaster in October 1707.
July–December
- July 29–August 21 – War of the Spanish Succession: Battle of Toulon – Allies are obliged to withdraw, but the French fleet is effectively put out of action.
- October 22 – Scilly naval disaster: four Royal Navy ships run aground in the Isles of Scilly because of faulty navigation. Admiral Sir Cloudesley Shovell and at least 1450 sailors all drown.
- October 23 – The Parliament of the Kingdom of Great Britain first meets in London.
- October 28 – Hōei earthquake, the most powerful in Japan until 2011, with an estimated local magnitude of 8.6.
- December 16 – The last recorded eruption of Mount Fuji begins in Japan.

Mount Fuji, last erupts in December 1707.
- December 24 – The first British Governor of Gibraltar, directly appointed by Queen Anne, Roger Elliott, takes up his residence in the Convent of the Franciscan Friars.
- December – Charles XII of Sweden launches his campaign to conquer Russia, marching to the east from Leipzig with 60,000 coalition troops. Another 16,000 soldiers are waiting on the outskirts of Riga, guarding the Swedish supply lines.
Date unknown
- A fortress is founded on the future site of Ust-Abakanskoye (modern Abakan).
- The Lao empire of Lan Xang officially ends and splits into the kingdoms of Vientiane, Luang Prabang, and Champasak.
- Hacienda Juriquilla is built in Querétaro, Mexico.
1708
January–June
- March 11 – Queen Anne withholds Royal Assent from the Scottish Militia Bill, the last time a British monarch vetoes legislation.
- March 23 – James Francis Edward Stuart, Jacobite pretender to the throne of Great Britain, unsuccessfully tries to land from a French fleet in the Firth of Forth in Scotland.
July–December
- July 1 – Tewoflos becomes Emperor of Ethiopia.
- July 11 – War of the Spanish Succession: Allied victory under the command of John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, against the French at the Battle of Oudenarde.[19]
- August – The future Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor weds Elisabeth Christine of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel.
- August 18 – War of the Spanish Succession: Capture of Minorca by British forces.[19]
- August 23 – Meidingu Pamheiba is crowned King of Manipur.
- August 29 – A native American attack in Haverhill, Massachusetts, kills 16 settlers.
- September 28 (O.S.); September 29 (Swedish calendar); October 9 (N.S.) – Battle of Lesnaya (Great Northern War): Peter the Great of Russia defeats the forces of the Swedish Empire.
- October 12 – War of the Spanish Succession: British forces capture Lille after a two-month siege, although the citadel continues to hold out for another six weeks.[20]
- October 26 – Completion of the construction of St Paul's Cathedral in London.[21]
Date unknown
- Kandahar is conquered by Mir Wais.
- Fearful of a Swedish attack, the Russians blow up the city of Tartu in Estonia.
- One third of the population of Masuria dies of the plague.
- Johann Sebastian Bach is appointed as chamber musician and organist at the court in Weimar.
- Italian philosopher Giambattista Vico delivers his inaugural lecture to the University of Naples, published as his first book, De Nostri Temporis Studiorum Ratione ("On the Order of the Scholarly Disciplines of Our Times"), in 1709.
- Calcareous hard-paste porcelain is produced for the first time in Europe at Dresden in Saxony by Ehrenfried Walther von Tschirnhaus and developed after his death (October) by Johann Friedrich Böttger.
- Merger (with consent of the Parliament of Great Britain) of the Company of Merchants of London Trading into the East Indies and the more recently established English Company Trading to the East Indies to form the United Company of Merchants of England Trading to the East Indies, known as the Honourable East India Company.[22]
1709
January–June
- January 6 – Western Europe's Great Frost of 1709, the coldest period in 500 years, begins during the night, lasting three months and with its effects felt for the entire year.[23] In France, the coast of the Atlantic and Seine river freeze, crops fail, and 24,000 Parisians die. Floating ice enters the North Sea.
- January 10 – Abraham Darby I successfully produces cast iron using coke fuel at his Coalbrookdale blast furnace in Shropshire, England.[24][25][19]
- February – In America, Mardi Gras is celebrated one more time with Masque de la Mobile in the capital of French Louisiana, Mobile, Alabama, before Mobile is moved 27 miles (43 km) down the Mobile River to Mobile Bay in 1711.
- February 1 or 2 – During his first voyage, Captain Woodes Rogers encounters marooned privateer Alexander Selkirk and rescues him after four years living on one of the Juan Fernández Islands, inspiring Defoe's book Robinson Crusoe.[2][26] After sacking Guayaquil, he and Selkirk will visit the Galápagos Islands.[27]
- March 28 – Johann Friedrich Böttger reports the first production of hard-paste porcelain in Europe, at Dresden.
- May – First influx into Britain of poor refugee families of German Palatines from the Rhenish Palatinate, mostly Protestants en route to the New World colonies.[28]
- June 27 (June 28 in the Swedish calendar; July 8 New Style) – Great Northern War: Battle of Poltava: In the Ukraine, Peter the Great, Tsar of Russia, defeats Charles XII of Sweden, thus effectively ending Sweden's role as a major power in Europe.
July–December
- July 27 – Emperor Nakamikado accedes to the throne of Japan.
- July 30 – War of the Spanish Succession: Capture of Tournai by John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough and Prince Eugene of Savoy.[19]
- August 8 – The hot air balloon of Bartolomeu de Gusmão flies in Portugal.
- August 28 – Pamheiba is crowned King of Manipur.
- September 11 (August 31 Old Style) – War of the Spanish Succession: Battle of Malplaquet - Troops of the Dutch Republic, Habsburg Austria, the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Prussia led by the Duke of Marlborough drive the French from the field but suffer twice as many casualties.[19]
- October 9 – War of the Spanish Succession: British army captures Mons.[29]
- October 12 – The city of Chihuahua in Mexico is founded.
- December 25 – From London, ten ships leave for the New York Colony, carrying over 4,000 people.
Date unknown
- Trinity School is founded as the Charity School of Trinity Church in New York City.
- The second Eddystone Lighthouse, erected off the south west coast of England by John Rudyerd, is completed.[30]
- Publication of the first modern edition of William Shakespeare's plays in London, edited by Nicholas Rowe.
- De Nostri Temporis Studiorum Rationae (On the Study Methods of Our Times) is published by Neapolitan philosopher Giambattista Vico.
- Priceless medieval altarpieces by Michael Pacher are destroyed.
References
- ↑ Colville, Ian (2011-02-08). "The Lesser Great Fire of 1700 in Edinburgh". On this day in Scotland. Retrieved 2011-11-21.
- 1 2 3 Penguin Pocket On This Day. Penguin Reference Library. 2006. ISBN 0-14-102715-0.
- ↑ Williams, Hywel (2005). Cassell's Chronology of World History. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. p. 289. ISBN 0-304-35730-8.
- ↑ Hochman, Stanley. McGraw-Hill Encyclopedia of World Drama. 4. p. 542.
- ↑ "The House Laws of the German Habsburgs". Retrieved 2011-11-21.
- ↑ O'Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F. (August 2004). "Berlin Academy of Science". MacTutor History of Mathematics. Retrieved 21 November 2011.
- ↑ Nguyen The Anh (1989). "Le Nam tien dans les textes Vietnamiens". In Lafont, P. B. (ed). Les frontieres du Vietnam. Paris: Edition l’Harmattan.
- ↑ "Historical Events for Year 1701 | OnThisDay.com". Historyorb.com. Retrieved 2016-07-05.
- ↑ "What Happened in 1701; History-Page.com". History-page.com. Retrieved 2016-08-01.
- ↑ Lessard, Rénald (1995). "L'Épidémie de variole de 1702-1703". Cap-aux-Diamants : La Revue d'histoire du Québec (pdf) (in French). 42: 51.
- ↑ "Historical Events for Year 1705 | OnThisDay.com". Historyorb.com. Retrieved 2016-06-30.
- ↑ Palmer, Alan; Veronica (1992). The Chronology of British History. London: Century Ltd. pp. 204–205. ISBN 0-7126-5616-2.
- ↑ "Icons, a portrait of England 1700-1750". Archived from the original on August 17, 2007. Retrieved 2007-08-24.
- ↑ Button, Henry G.; Lampert, Andrew P. (1976). The Guinness Book of the Business World. Enfield: Guinness Superlatives. ISBN 0-900424-32-X.
- ↑ "About Twinings - 216 Strand". Twinings. 2015. Retrieved 2015-02-13.
- ↑ Payne, Stanley G. "Chapter 16: The Eighteenth-Century Bourbon Regime in Spain". A History of Spain and Portugal. 2. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press. ISBN 0-299-06270-8. Retrieved 2008-04-17.
- ↑ Acts of Union 1707 parliament.uk, accessed 31 December 2010.
- ↑ Williams, Hywel (2005). Cassell's Chronology of World History. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. p. 291. ISBN 0-304-35730-8.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Williams, Hywel (2005). Cassell's Chronology of World History. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. p. 292. ISBN 0-304-35730-8.
- ↑ Palmer, Alan; Veronica (1992). The Chronology of British History. London: Century Ltd. pp. 205–206. ISBN 0-7126-5616-2.
- ↑ "Stamps celebrate St Paul's with Wren epitaph". Evening Standard. Retrieved 2008-06-05.
- ↑ Landow, George P. (2010). "The British East India Company — the Company that Owned a Nation (or Two)". The Victorian Web. Retrieved 2011-11-22.
- ↑ Pain, Stephanie. "1709: The year that Europe froze." New Scientist, 7 February 2009.
- ↑ Mott, R. A. (5 January 1957). "The earliest use of coke for ironmaking". The Gas World, coking section supplement. 145: 7–18.
- ↑ Raistrick, Arthur (1953). Dynasty of Ironfounders: the Darbys and Coalbrookdale. London: Longmans, Green. p. 34.
- ↑ Ober, Frederick A. (1912). Our West Indian Neighbors: the Islands of the Caribbean Sea. New York: James Pott & Company. p. 11.
- ↑ Jackson, Michael H. (1993). Galapagos: a Natural History. University of Calgary Press. ISBN 1-895176-07-7.
- ↑ Gardiner, Juliet (1995). Wenborn, Neil, ed. The History Today Companion to British History. London: Collins & Brown. p. 577. ISBN 1-85585-178-4.
- ↑ Palmer, Alan; Veronica (1992). The Chronology of British History. London: Century Ltd. pp. 207–208. ISBN 0-7126-5616-2.
- ↑ Majdalany, Fred (1959). The Red Rocks of Eddystone. London: Longmans. p. 86.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/19/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.