1979–80 Australian region cyclone season
1979–80 Australian region cyclone season
| |
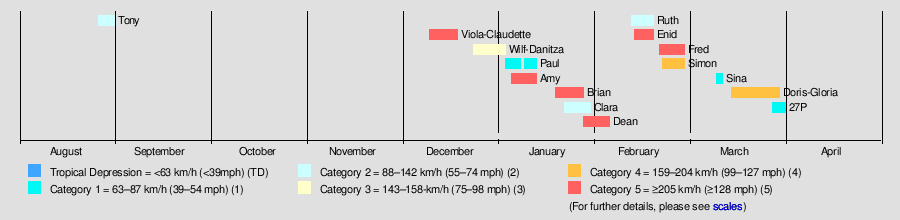
| Season summary map |
| First system formed |
26 August 1979 |
| Last system dissipated |
31 March 1980 |
| Strongest storm1 |
Amy – 915 hPa (mbar), |
| Tropical lows |
16 |
| Tropical cyclones |
15 |
| Severe tropical cyclones |
7 |
| Total fatalities |
Unknown |
| Total damage |
Unknown |
| 1Strongest storm is determined by lowest pressure |
Australian region tropical cyclone seasons
1977–78, 1978–79, 1979–80, 1980–81, 1981–82 |
| Related articles |
|
|
The 1979–80 Australian region cyclone season saw above normal activity.
Seasonal summary
Storms
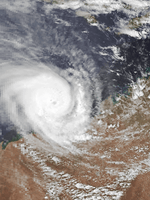
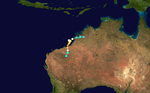
Severe Tropical Cyclone Viola-Claudette
| Category 5 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Category 3 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
9 December – 18 December (Crossed 80°E) |
| Peak intensity |
205 km/h (125 mph) (10-min) 930 hPa (mbar) |
Severe Tropical Cyclone Wilf-Danitza
| Category 3 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
23 December – 2 January (Crossed 80°E) |
| Peak intensity |
130 km/h (80 mph) (10-min) 973 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Cyclone Paul
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
2 January – 12 January |
| Peak intensity |
85 km/h (50 mph) (10-min) 989 hPa (mbar) |
On 2 January, the BoM reported that a tropical depression had developed in the Southwest Gulf of Carpentaria.[1] During that day the depression moved towards the southwest and developed early signs of having a cyclonic circulation, however before it could intensify into a tropical cyclone, the system made landfall near the Northern Territory border with Queensland at 135°E.[1] Over the next couple of days the depression weakened slightly, as it moved in a general east-southeast direction across the Carpentaria and Central Coast districts of Queensland.[1] On 7 January, the depression moved out into the Coral Sea just to the south of Sarina with a central pressure of 995 hPa.[1] During that day the depression developed gale force windspeeds and was named as Paul by TCWC Brisbane.[1] Before later that day, Paul reached its peak intensity as a tropical cyclone with 10-minute sustained windspeeds of 75 km/h (45 mph) and its lowest central pressure of 989 hPa as it moved rapidly towards the southeast.[1] This southeastern movement continued until 1200 UTC on 8 January when it slowed down and started to move to the southwest as it developed a cold core and became extratropical.[1] The extratropical remnants of Paul subsequently lingered in the Australian region and peaked with stronger windspeeds then when it was a tropical cyclone.[1] The US Navy's analysis of this system shows that they would have considered Paul a tropical storm with peak 1-minute sustained windspeeds of 110 km/h (70 mph). As a tropical depression, Paul forced a strong area of convergence in the moist airstream onto the tropical Queensland coast.[1] As a result of the moisture, very heavy rain caused one of the highest floods of the 20th Century down the Don River through Bowen.[1] In its lower reaches the river changed its course and washed away two homes and caused several million Australian dollars worth of damage to the market garden industry.[1]
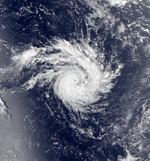
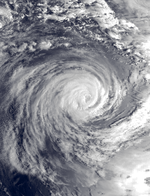
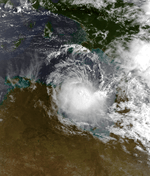
Severe Tropical Cyclone Amy
| Category 5 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Category 3 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
4 January – 12 January |
| Peak intensity |
230 km/h (145 mph) (10-min) 915 hPa (mbar) |
Severe Tropical Cyclone Brian
| Category 5 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Category 2 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
18 January – 27 January |
| Peak intensity |
205 km/h (125 mph) (10-min) 930 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Cyclone Clara
| Category 2 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
21 January – 29 January |
| Peak intensity |
100 km/h (65 mph) (10-min) 980 hPa (mbar) |
Severe Tropical Cyclone Dean
| Category 5 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Category 4 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
27 January – 4 February |
| Peak intensity |
215 km/h (130 mph) (10-min) 930 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Cyclone Ruth
| Category 2 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
11 February – 18 February |
| Peak intensity |
110 km/h (70 mph) (10-min) 980 hPa (mbar) |
Severe Tropical Cyclone Enid
| Category 5 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Category 4 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
12 February – 18 February |
| Peak intensity |
215 km/h (130 mph) (10-min) 930 hPa (mbar) |
Severe Tropical Cyclone Fred
| Category 5 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Category 4 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
20 February – 28 February |
| Peak intensity |
215 km/h (130 mph) (10-min) 930 hPa (mbar) |
On 19 February, TCWC Perth reported that a tropical depression had developed out of an active area of convection that was associated with a monsoonal shear line about midway between the Cocos and Christmas Islands.
Fred developed from an active area of convection associated with the monsoon shear line about midway between Cocos and Christmas Islands late on 19 February 1980. It reached tropical cyclone strength early on 21 February 1980 and attained its maximum intensity on the afternoon of 24 February 1980 when the central pressure was estimated to be near 930 hPa. Despite the small size of the cyclone it maintained this intensity with minor fluctuations until about 1200 UTC 25 February 1980. Early on 26 February the direction of movement changed from southwestward to southward as Fred came under the influence of a northwesterly upper-level flow. It weakened rapidly as it moved into a strong ridge of high pressure located at about latitude 33°S.
Severe Tropical Cyclone Simon
| Category 4 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Category 3 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
21 February – 28 February (Crossed 160°E) |
| Peak intensity |
175 km/h (110 mph) (10-min) 950 hPa (mbar) |
Severe Tropical Cyclone Doris-Gloria
| Category 4 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Category 3 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
14 March – 29 March |
| Peak intensity |
165 km/h (105 mph) (10-min) 955 hPa (mbar) |
Unnamed Tropical Cyclone (27P)
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
27 March – 30 March |
| Peak intensity |
65 km/h (40 mph) (10-min) 998 hPa (mbar) |
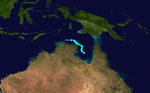
On 27 March, TCWC Darwin reported that a tropical depression had developed in the Gulf of Carpentraria about 300 km (190 mi) to the southwest of Wallaby island. During that day the system intensified enough to produce localized and intermittent gale force winds, over the northeast Arnhem land as it moved into the Arafura sea. Early on 28 March, TCWC Darwin reported that despite the depression having reached cyclone intensity of 65 km/h (40 mph), it was not a tropical cyclone as the system had not developed a "deep convective warm cored structure". However, during post storm analysis TCWC Darwin reported that the depression had become a tropical cyclone at 0000 UTC (0800 WST) on 28 March. During 28 March, the system moved towards the north, before during the next day as the cyclone turned towards the west and moved into the Arafura sea it reached its lowest central pressure of 998 hPa (29.47 inHg). As the system moved further into the Arafura sea, a very strong amount of vertical windshear and an intrusion of dry air made the cyclone rapidly weaken into a tropical depression before the residual depression dissipated on 31 March just to the north of the Cobourg peninsular. The Cyclone caused no deaths and only minor damage was reported to have occurred.
Other systems
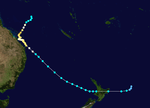
During March 11, the precursor tropical low to Severe Tropical Cyclone Sina, moved south-westwards into the region from the South Pacific.[2] The system subsequently developed into a tropical cyclone and was named Sina by the BoM, before it moved south-eastwards out of the region early the next day.[2]
Seasonal effects
See also
- Atlantic hurricane seasons: 1979, 1980
- Eastern Pacific hurricane seasons: 1979, 1980
- Western Pacific typhoon seasons: 1979, 1980
- North Indian Ocean cyclone seasons: 1979, 1980
References
External links