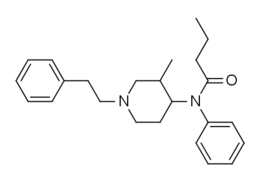
3-Methylbutyrfentanyl
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | 97605-09-9 |
| PubChem (CID) | 86130531 |
| UNII |
875L53T89N |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C24H32N2O |
| Molar mass | 364,533 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
3-Methylbutyrfentanyl (3-MBF) is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of butyrfentanyl.[1][2] 3-Methylbutyrfentanyl is one of the most potent drugs that have been sold online as a designer drug.[3][4]
Side effects of fentanyl analogs are similar to those of fentanyl itself, which include itching, nausea and potentially serious respiratory depression, which can be life-threatening. Fentanyl analogs have killed hundreds of people throughout Europe and the former Soviet republics since the most recent resurgence in use began in Estonia in the early 2000s, and novel derivatives continue to appear.[5]
See also
- 3-Methylfentanyl
- 4-Fluorobutyrfentanyl
- 4-Fluorofentanyl
- α-Methylfentanyl
- Acetylfentanyl
- Furanylfentanyl
- List of Fentanyl analogues
References
- ↑ Yoshiyasu Higashikawa; Shinichi Suzuki (June 2008). "Studies on 1-(2-phenethyl)-4-(N -propionylanilino)piperidine (fentanyl) and its related compounds. VI. Structure-analgesic activity relationship for fentanyl, methyl-substituted fentanyls and other analogues". Forensic Toxicology. 26 (5): 1–5. doi:10.1007/s11419-007-0039-1.
- ↑ Ruben S. Vardanyan; Victor J. Hruby (August 2014). "Fentanyl-related compounds and derivatives: current status and future prospects for pharmaceutical applications". Future medicinal chemistry. 6 (4): 385–412. doi:10.4155/fmc.13.215. PMC 4137794
 . PMID 24635521.
. PMID 24635521. - ↑ Jin, W. Q.; Xu, H.; Zhu, Y. C.; Fang, S. N.; Xia, X. L.; Huang, Z. M.; Ge, B. L.; Chi, Z. Q. (1981). "Studies on synthesis and relationship between analgesic activity and receptor affinity for 3-methyl fentanyl derivatives". Scientia Sinica. 24 (5): 710–720. PMID 6264594.
- ↑ Huang, Z. M.; Zhou, J.; Chen, X. J.; Zheng, W. J.; Zhang, H. P.; Chi, Z. Q.; Li, Z. G.; Chen, W. L. (1984). "Analgesic activity and toxicity of potent analgesics, ohmefentanyl and mefentanyl". Zhongguo yao li xue bao = Acta pharmacologica Sinica. 5 (3): 153–158. PMID 6239505.
- ↑ Jane Mounteney; Isabelle Giraudon; Gleb Denissov; Paul Griffiths (July 2015). "Fentanyls: Are we missing the signs? Highly potent and on the rise in Europe.". The international journal of drug policy. 26 (7): 626–631. doi:10.1016/j.drugpo.2015.04.003. PMID 25976511.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/18/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.