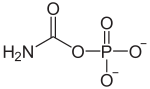
Carbamoyl phosphate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(Carbamoyloxy)phosphonic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 590-55-6 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:17672 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL369105 |
| ChemSpider | 272 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.230.975 |
| KEGG | C00169 |
| MeSH | Carbamoyl+phosphate |
| PubChem | 278 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CH2NO5P2− | |
| Molar mass | 141.020 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Carbamoyl phosphate is an anion of biochemical significance. In land-dwelling animals, it is an intermediary metabolite in nitrogen disposal through the urea cycle and the synthesis of pyrimidines.
Production
It is produced from bicarbonate, ammonia (derived from glutamine), and phosphate (from ATP). The synthesis is catalysed by the enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthetase, as follows:
- HCO−
3 + ATP → ADP + HO–C(O)–OPO2−
3 (carboxyl phosphate) - HO–C(O)–OPO2−
3 + NH3 + OH− → HPO2−
4 + −O–C(O)NH2 + H2O - −O–C(O)NH2 + ATP → ADP + H
2NC(O)OPO2−
3
See also
References
- Nelson, David L.; Cox, Michael M. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry fourth edition. New York: W. H. Freeman and company.
| Urea cycle Metabolic Pathway | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/7/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.