Inositol
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(1R,2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol | |
| Other names
cis-1,2,3,5-trans-4,6-Cyclohexanehexol , Cyclohexanehexol, Mouse antialopecia factor, Nucite, Phaseomannite, Phaseomannitol, Rat antispectacled eye factor, and Scyllite (for the structural isomer scyllo-Inositol) | |
| Identifiers | |
| 87-89-8 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:17268 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1222251 |
| ChemSpider | 10239179 |
| 4495 | |
| KEGG | D08079 |
| PubChem | 892 |
| UNII | 4L6452S749 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H12O6 | |
| Molar mass | 180.16 g/mol |
| Density | 1.752 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 225 to 227 °C (437 to 441 °F; 498 to 500 K) |
| Pharmacology | |
| A11HA07 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 143 °C (289 °F; 416 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Inositol or cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol is a chemical compound with formula C6H12O6 or (-CHOH-)6, a six-fold alcohol (polyol) of cyclohexane. It exists in nine possible stereoisomers, of which the most prominent form, widely occurring in nature, is cis-1,2,3,5-trans-4,6-cyclohexanehexol, or myo-inositol (former names meso-inositol or i-inositol).[2][3] Inositol is a sugar alcohol. Its taste has been assayed at half the sweetness of table sugar (sucrose).
myo-Inositol plays an important role as the structural basis for a number of secondary messengers in eukaryotic cells, the various inositol phosphates. In addition, inositol serves as an important component of the structural lipids phosphatidylinositol (PI) and its various phosphates, the phosphatidylinositol phosphate (PIP) lipids.
Inositol or its phosphates and associated lipids are found in many foods, in particular fruit, especially cantaloupe and oranges.[4] In plants, the hexaphosphate of inositol, phytic acid or its salts, the phytates, are found. These serve as phosphate stores in the seed. Phytic acid occurs also in cereals with high bran content and also nuts and beans. Yet, inositol, when present as phytate, is not directly bioavailable to humans in the diet, since it is not digestible. Some food preparation techniques partly break down phytates to change this. Inositol as it occurs in certain plant-derived substances such as lecithins, however, is well-absorbed and relatively bioavailable.
myo-Inositol (free of phosphate) was once considered a member of the vitamin B complex (formerly Vitamin B8); however, because it is produced by the human body from glucose, it is not an essential nutrient.[5] Some substances such as niacin can also be synthesized in the body, but are not made in amounts considered adequate for good health, thus are still classified as essential nutrients. However, no convincing evidence indicates this is the case for myo-inositol.
Isomers and structure
The isomer myo-inositol is a meso compound possessing an optically inactive plane of symmetry through the molecule (meso-inositol is an obsolete name that refers to myo-inositol). Besides myo-inositol, the other naturally occurring stereoisomers (though in minimal quantities) are scyllo-, muco-, D-chiro-, and neo-inositol. The other possible isomers are L-chiro-, allo-, epi-, and cis-inositol. As their name denotes, the two chiro inositols are the only pair of inositol enantiomers, but they are enantiomers of each other, not of myo-inositol.
 |
 |
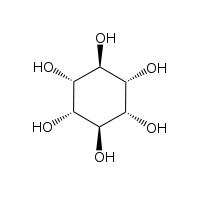 |
 |
| myo- | scyllo- | muco- | chiro- |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| neo- | allo- | epi- | cis- |
In its most stable conformational geometry, the myo-inositol isomer assumes the chair conformation, which puts the maximum number of hydroxyls to the equatorial position, where they are farthest apart from each other. In this conformation, the natural myo isomer has a structure in which five of the six hydroxyls (the first, third, fourth, fifth, and sixth) are equatorial, whereas the second hydroxyl group is axial.[6]
Biosynthesis
myo-Inositol is synthesized from glucose-6-phosphate (G-6-P) in two steps. First, G-6-P is isomerised by an inositol-3-phosphate synthase enzyme (for example, ISYNA1) to myo-inositol 1-phosphate, which is then dephosphorylated by an inositol monophosphatase enzyme (for example, IMPA1) to give free myo-inositol. In humans, most inositol is synthesized in the kidneys, in typical amounts of a few grams per day.[7]
Function
Inositol and some of its mono- and polyphosphates function as the basis for a number of signaling and secondary messenger molecules. They are involved in a number of biological processes, including:
- Insulin signal transduction[8]
- Cytoskeleton assembly
- Nerve guidance (epsin)
- Intracellular calcium (Ca2+) concentration control[9]
- Cell membrane potential maintenance[10]
- Breakdown of fats [11]
- Gene expression[12][13]
Phytic acid in plants
Phytic acid (IP6 or phytate), a derivative of inositol with six phosphate groups, is the principal storage form of phosphorus in many plant tissues, especially bran and seed.[14] Neither the inositol nor the phosphate in phytic acid in plants is available to humans, or to animals that are not ruminants, since it cannot be broken down, except by bacteria. Moreover, phytic acid also chelates important minerals such as calcium, magnesium, iron, and zinc, making them unabsorbable, and contributing to mineral deficiencies in people whose diets rely highly on bran and seeds for their mineral intake, such as occurs in developing countries.[15][16]
Inositol penta- (IP5), tetra- (IP4), and triphosphate (IP3) are also called "phytates".
Use in explosives manufacture
At the 1936 meeting of the American Chemical Society, professor Edward Bartow of the University of Iowa presented a commercially viable means of extracting large amounts of inositol from the phytic acid naturally present in waste corn. As a possible use for the chemical, he suggested 'inositol nitrate' as a more stable alternative to nitroglycerin.[17] Today, inositol nitrate is used to gelatinize nitrocellulose, thus can be found in many modern explosives and solid rocket propellants.[18]
Counter to road salt
When plants are exposed to increasing concentrations of road salt, the plant cells become dysfunctional and undergo apoptosis, leading to an inhibition of growth in plants. Inositol pretreatment could reverse the effects of salt on plants.[19][20]
Research and clinical applications
Large doses of inositol have been studied for treatment of depression: the evidence is insufficient to determine whether inositol treatment can reduce depression symptoms, but no evidence of harm or negative side effects is seen.[21]
Inositol is effective in reducing adverse neonatal outcomes in preterm babies who either have or are at a risk of developing respiratory distress syndrome (RDS).[22]
Common use as a "cutting" agent
Inositol has been used as an adulterant (or cutting agent) in many illegal drugs, such as cocaine, methamphetamine, and sometimes heroin.[23] This use is presumed to be connected with one or more of the substance's properties of solubility, powdery texture, or reduced sweetness (50%) as compared with more common sugars.
Inositol is also used as a stand-in for cocaine on television and in film.[24]
Nutritional sources
myo-Inositol is naturally present in a variety of foods, although tables of this do not always distinguish between the bioavailable lecithin form, and the unavailable phytate form in grains.[25] According to research, foods containing the highest concentrations of myo-inositol (including its compounds) include fruits, beans, grains, and nuts.[25] Beans and grains, however, as seeds, contain large amounts of inositol as phytate. Some energy drinks also contain inositol.
See also
References
- ↑ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 4883.
- ↑ Synonyms in PubChem
- ↑ Synonyms in Commonchemistry.org
- ↑ Clements RS Jr; Darnell B (1980). "Myo-inositol content of common foods: development of a high-myo-inositol diet" (PDF). American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 33 (9): 1954–1967. PMID 7416064.
- ↑ Reynolds, James E. F. (January 1, 1993). Martindale: The Extra Pharmacopoeia. 30. Pennsylvania: Rittenhouse Book Distributors. p. 1379. ISBN 0-85369-300-5.
An isomer of glucose that has traditionally been considered to be a B vitamin although it has an uncertain status as a vitamin and a deficiency syndrome has not been identified in man
- ↑ S. M. N. Furse (2006). The Chemical and Bio-physical properties of Phosphatidylinositol phosphates, Thesis for M.Res. Imperial College London.
- ↑ Subcell Biochem. 2006;39:293-314. Mammalian inositol 3-phosphate synthase: its role in the biosynthesis of brain inositol and its clinical use as a psychoactive agent. Parthasarathy LK, Seelan RS, Tobias C, Casanova MF, Parthasarathy RN.
- ↑ Larner J (2002). "D-chiro-inositol--its functional role in insulin action and its deficit in insulin resistance". Int J Exp Diabetes Res. 3 (1): 47–60. doi:10.1080/15604280212528. PMC 2478565
 . PMID 11900279.
. PMID 11900279. - ↑ Gerasimenko, Julia V; et al; "Bile Acids Induce Ca2+ Release from Both the Endoplasmic Reticulum and Acidic Intracellular Calcium Stores through Activation of Inositol Trisphosphate Receptors and Ryanodine Receptors" Journal of Biological Chemistry; December 29, 2006; Volume 281: Pp 40154-40163.
- ↑ Kukuljan M, Vergara L, Stojilkovic SS (February 1997). "Modulation of the kinetics of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced [Ca2+]i oscillations by calcium entry in pituitary gonadotrophs". Biophysical Journal. 72 (2 Pt 1): 698–707. Bibcode:1997BpJ....72..698K. doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(97)78706-X. PMC 1185595
 . PMID 9017197.
. PMID 9017197. - ↑ Rapiejko PJ, Northup JK, Evans T, Brown JE, Malbon CC (November 1986). "G-proteins of fat-cells. Role in hormonal regulation of intracellular inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate". The Biochemical Journal. 240 (1): 35–40. PMC 1147372
 . PMID 3103610.
. PMID 3103610. - ↑ Shen, X.; Xiao, H; Ranallo, R; Wu, WH; Wu, C (2003). "Modulation of ATP-dependent chromatin-remodeling complexes by inositol polyphosphates". Science. 299 (5603): 112–4. doi:10.1126/science.1078068. PMID 12434013.
- ↑ Steger, D. J.; Haswell, ES; Miller, AL; Wente, SR; O'Shea, EK (2003). "Regulation of chromatin remodelling by inositol polyphosphates". Science. 299 (5603): 114–6. doi:10.1126/science.1078062. PMC 1458531
 . PMID 12434012.
. PMID 12434012. - ↑ Phytic acid
- ↑ Hurrell RF (September 2003). "Influence of vegetable protein sources on trace element and mineral bioavailability". The Journal of Nutrition. 133 (9): 2973S–7S. PMID 12949395.
- ↑ Committee on Food Protection; Food and Nutrition Board; National Research Council (1973). "Phytates". Toxicants Occurring Naturally in Foods. National Academy of Sciences. pp. 363–371. ISBN 978-0-309-02117-3.
- ↑ Laurence, William L. "Corn by-product yields explosive", The New York Times. April 17, 1936. Page 7.
- ↑ Ledgard, Jared. The Preparatory Manual of Explosives, 2007. p. 366.
- ↑ Chaterjee, J.; Mujumder, AL. (September 2010). "Salt-induced abnormalities on root tip mitotic cells of Allium cepa: prevention by inositol pretreatment.". Protoplasma. 245 (1-4): 165–72. doi:10.1007/s00709-010-0170-4. PMID 20559853.
- ↑ Theerakulpisut, P.; Gunnula, W. (2012). "Exogenous Sorbitol and Trehalose Mitigated Salt Stress Damage in Salt-sensitive but not Salt-tolerant Rice Seedlings.". Asian Journal of Crop Science. 4: 165–170. doi:10.3923/ajcs.2012.165.170. Retrieved 16 October 2014.
- ↑ Taylor MJ, Wilder H, Bhagwagar Z, Geddes J (2004). Taylor MJ, ed. "Inositol for depressive disorders". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (2): CD004049. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004049.pub2. PMID 15106232.
- ↑ Howlett A, Ohlsson A, Plakkal N (2015). "Inositol in preterm infants at risk for or having respiratory distress syndrome.". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (2): CD000366. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000366.pub3.
- ↑ http://feedadditivechina.com/6-16-inositol.html
- ↑ Golianopoulos, Thomas. "Drug Doubles: What Actors Actually Toke, Smoke and Snort on Camera". Wired Magazine. Retrieved 14 May 2012.
- 1 2 Clements, Rex; Betty Darnell (1980). "Myo-inositol content of common foods: development of a high-myo-inositol diet" (PDF). American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 33 (9): 1954–1967. PMID 7416064. Retrieved 2009-05-18.
External links
- Inositol MS Spectrum
- Cancer Inhibition by Inositol Hexaphosphate (IP6) and Inositol: From Laboratory to Clinic (scientific publication)
- Myo-inositol Content of Various Foods
- U.S. National Library of Medicine: Drug Information Portal – Inositol
- Inositol bound to proteins in the PDB
