Conivaptan
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Vaprisol |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | intravenous |
| ATC code | C03XA02 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | N/A |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
210101-16-9 |
| PubChem (CID) | 151171 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 2203 |
| DrugBank |
DB00872 |
| ChemSpider |
133239 |
| UNII |
0NJ98Y462X |
| KEGG |
D01236 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:681850 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1755 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
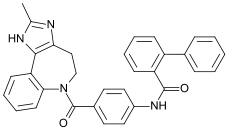
| Formula | C32H26N4O2 |
| Molar mass | 498.583 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Conivaptan (YM 087, brand name Vaprisol) is a non-peptide inhibitor of antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin receptor antagonist). It was approved in 2004 for hyponatremia (low blood sodium levels) caused by syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH), and there is some evidence it may be effective in heart failure. It is marketed by Cumberland Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Conivaptan inhibits two of the three subtypes of the vasopressin receptor (V1a and V2). Effectively, it causes iatrogenic nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.
Conivaptan has not been approved by the FDA for the treatment of decompensated congestive heart failure. However, in theory, vasopressin receptor antagonism would be particularly useful in this setting, and an initial study shows that it has some promise.[1]
References
- ↑ Udelson JE, Smith WB, Hendrix GH, et al. (November 2001). "Acute hemodynamic effects of conivaptan, a dual V(1A) and V(2) vasopressin receptor antagonist, in patients with advanced heart failure". Circulation. 104 (20): 2417–23. doi:10.1161/hc4501.099313. PMID 11705818.