Eclipse season
Eclipse seasons are the only times during a year eclipses can occur, due to the inclination of the Moon's orbit. Each season lasts for approximately 34 days and repeats just short of six months, thus there are always two full eclipse seasons each year. Two to three eclipses always occur each eclipse season. During the season the inclination of the Moon is low, hence the Sun, Moon and Earth become close enough in alignment (syzygy) for an eclipse to occur.
Details
An eclipse season is the only time during which the Sun (from the perspective of the Earth) is close enough to one of the Moon's nodes to allow for an eclipse to occur. During the season, whenever there is a full moon a lunar eclipse will occur and whenever there is a new moon a solar eclipse will occur. If the Sun is close enough to a node, then a total eclipse will occur. Each season lasts from 31 to 37 days, recurring about every 6 months. At least two (one solar and one lunar, in any order), and at most three eclipses (solar, lunar, then solar again, or vice versa), will occur during every eclipse season. This is because it is about 15 days (a fortnight) between full moon and new moon and vice versa. If there is an eclipse at the very beginning of the season, then there is enough time (30 days) for two more eclipses.
In other words, because the eclipse season (34 days long on average) is longer than the synodic month (one lunation, or the time for the Moon to return to a particular phase and about 29.5 days), the Moon will be new or full at least two, and up to three, times during the season. Eclipse seasons occur slightly shy of six months apart (successively occurring every 173.31 days - half of an eclipse year), the time it takes the Sun to travel from one node to the next along the ecliptic. If the last eclipse of an eclipse season occurs at the very beginning of a calendar year, it is possible for a total of seven eclipses to occur since there is still time before the end of the calendar year for two full eclipse seasons, each having up to three eclipses.[1][2][3]
Examples
Visual sequence of two particular eclipse seasons
In each sequence below, each eclipse is separated by a fortnight. The first and last eclipse in each sequence is separated by one synodic month. See eclipse cycles.
| May 26th Descending Node (Full Moon) | June 10th Ascending Node (New Moon) | June 24th Descending Node (Full Moon) |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
| Penumbral lunar eclipse Lunar saros 111 |
Annular solar eclipse Solar saros 137 |
Penumbral lunar eclipse Lunar saros 148 |
| June 1st Descending Node (New Moon) | June 15th Ascending Node (Full Moon) | July 1st Descending Node (New Moon) |
|---|---|---|
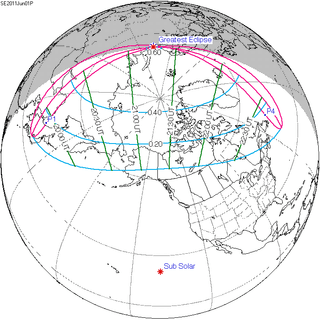 |  |  |
| Partial solar eclipse Solar saros 118 |
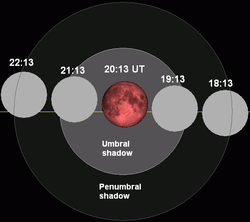
Total lunar eclipse Lunar saros 130 |
Partial solar eclipse Solar saros 156 |
(The two eclipse seasons above share similarities (lunar or solar centrality and gamma of each eclipse in the same column) because they are a half saros apart.)[4]
Two year chart of eclipses (2013–2014) demonstrating seasons
| Date | Type (phase) | Time of season | next eclipse will occur... |
|---|---|---|---|
| April 25, 2013 | lunar (full) | beginning | next new moon |
| May 10, 2013 | solar (new) | middle | next full moon |
| May 25, 2013 | lunar (full) | end | next eclipse season |
| ... no eclipses for about 5 months... | |||
| October 18, 2013 | lunar (full) | beginning | next new moon |
| November 3, 2013 | solar (new) | end | next eclipse season |
| ... no eclipses for about 5 and a half months... | |||
| April 15, 2014 | lunar (full) | beginning | next new moon |
| April 29, 2014 | solar (new) | end | next eclipse season |
| ... no eclipses for about 5 and a half months... | |||
| October 8, 2014 | lunar (full) | beginning | next new moon |
| October 23, 2014 | solar (new) | end | next eclipse season (spring of 2015) |
See also
References
- ↑ Littmann, Mark; Fred Espenak; Ken Willcox (2008). Totality: Eclipses of the Sun. Oxford University Press. pp. 18–19. ISBN 0-19-953209-5.
- ↑ Periodicity of Lunar and Solar Eclipses, Fred Espenak
- ↑ Five Millennium Catalog of Lunar and Solar Eclipses: -1999 to +3000, Fred Espenak and Jean Meeus
- ↑ A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles, Robert Harry van Gent