Solar eclipse
 |
| A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon completely covers the Sun's disk, as seen in this 1999 solar eclipse. Solar prominences can be seen along the limb (in red) as well as extensive coronal filaments. |
  |
| An annular solar eclipse (left) occurs when the Moon is too far away to completely cover the Sun's disk (May 20, 2012). During a partial solar eclipse (right), the Moon blocks only part of the Sun's disk (October 23, 2014). |
As seen from the Earth, a solar eclipse is a type of eclipse that occurs when the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth, and the Moon fully or partially blocks ("occults") the Sun. This can happen only at new moon, when the Sun and the Moon are in conjunction as seen from Earth in an alignment referred to as syzygy. In a total eclipse, the disk of the Sun is fully obscured by the Moon. In partial and annular eclipses, only part of the Sun is obscured.
If the Moon were in a perfectly circular orbit, a little closer to the Earth, and in the same orbital plane, there would be total solar eclipses every month. However, the Moon's orbit is inclined (tilted) at more than 5 degrees to the Earth's orbit around the Sun (see ecliptic), so its shadow at new moon usually misses Earth. Earth's orbit is called the ecliptic plane as the Moon's orbit must cross this plane in order for an eclipse (both solar as well as lunar) to occur. In addition, the Moon's actual orbit is elliptical, often taking it far enough away from Earth that its apparent size is not large enough to block the Sun totally. The orbital planes cross each other at a line of nodes resulting in at least two, and up to five, solar eclipses occurring each year; no more than two of which can be total eclipses.[1][2] However, total solar eclipses are rare at any particular location because totality exists only along a narrow path on the Earth's surface traced by the Moon's shadow or umbra.
An eclipse is a natural phenomenon. Nevertheless, in some ancient and modern cultures, solar eclipses have been attributed to supernatural causes or regarded as bad omens. A total solar eclipse can be frightening to people who are unaware of its astronomical explanation, as the Sun seems to disappear during the day and the sky darkens in a matter of minutes.
Since looking directly at the Sun can lead to permanent eye damage or blindness, special eye protection or indirect viewing techniques are used when viewing a solar eclipse. It is technically safe to view only the total phase of a total solar eclipse with the unaided eye and without protection; however, this is a dangerous practice, as most people are not trained to recognize the phases of an eclipse, which can span over two hours while the total phase can only last up to 7.5 minutes for any one location. People referred to as eclipse chasers or umbraphiles will travel to remote locations to observe or witness predicted central solar eclipses.[3][4]
For the date of the next eclipse see the section Recent and forthcoming solar eclipses.
Types



There are four types of solar eclipses:
- A total eclipse occurs when the dark silhouette of the Moon completely obscures the intensely bright light of the Sun, allowing the much fainter solar corona to be visible. During any one eclipse, totality occurs at best only in a narrow track on the surface of Earth.[5]
- An annular eclipse occurs when the Sun and Moon are exactly in line with the Earth, but the apparent size of the Moon is smaller than that of the Sun. Hence the Sun appears as a very bright ring, or annulus, surrounding the dark disk of the Moon.[6]
- A hybrid eclipse (also called annular/total eclipse) shifts between a total and annular eclipse. At certain points on the surface of Earth it appears as a total eclipse, whereas at other points it appears as annular. Hybrid eclipses are comparatively rare.[6]
- A partial eclipse occurs when the Sun and Moon are not exactly in line with the Earth and the Moon only partially obscures the Sun. This phenomenon can usually be seen from a large part of the Earth outside of the track of an annular or total eclipse. However, some eclipses can only be seen as a partial eclipse, because the umbra passes above the Earth's polar regions and never intersects the Earth's surface.[6] Partial eclipses are virtually unnoticeable in terms of the sun's brightness, as it takes well over 90% coverage to notice any darkening at all. Even at 99% it would be no darker than civil twilight.[7] Of course, partial eclipses (and partial stages of other eclipses) can be observed if one is viewing the sun through a darkening filter (which should anyhow be used for safety).
The Sun's distance from Earth is about 400 times the Moon's distance, and the Sun's diameter is about 400 times the Moon's diameter. Because these ratios are approximately the same, the Sun and the Moon as seen from Earth appear to be approximately the same size: about 0.5 degree of arc in angular measure.[6]
A separate category of solar eclipses is that of the Sun being occluded by a body other than the Earth's moon, as can be observed at points in space away from the Earth's surface. Two examples are when the crew of Apollo 12 observed the Earth eclipse the Sun in 1969 and when the Cassini probe observed Saturn eclipsing the Sun in 2006.
The Moon's orbit around the Earth is an ellipse, as is the Earth's orbit around the Sun. The apparent sizes of the Sun and Moon therefore vary.[8] The magnitude of an eclipse is the ratio of the apparent size of the Moon to the apparent size of the Sun during an eclipse. An eclipse that occurs when the Moon is near its closest distance to Earth (i.e., near its perigee) can be a total eclipse because the Moon will appear to be large enough to completely cover the Sun's bright disk, or photosphere; a total eclipse has a magnitude greater than 1. Conversely, an eclipse that occurs when the Moon is near its farthest distance from Earth (i.e., near its apogee) can only be an annular eclipse because the Moon will appear to be slightly smaller than the Sun; the magnitude of an annular eclipse is less than 1. Slightly more solar eclipses are annular than total because, on average, the Moon lies too far from Earth to cover the Sun completely. A hybrid eclipse occurs when the magnitude of an eclipse changes during the event from less to greater than one, so the eclipse appears to be total at some locations on Earth and annular at other locations.[9]
Because the Earth's orbit around the Sun is also elliptical, the Earth's distance from the Sun similarly varies throughout the year. This affects the apparent size of the Sun in the same way, but not as much as does the Moon's varying distance from Earth.[6] When Earth approaches its farthest distance from the Sun in July, a total eclipse is somewhat more likely, whereas conditions favour an annular eclipse when Earth approaches its closest distance to the Sun in January.[10]
Terminology for central eclipse

Central eclipse is often used as a generic term for a total, annular, or hybrid eclipse.[11] This is, however, not completely correct: the definition of a central eclipse is an eclipse during which the central line of the umbra touches the Earth's surface. It is possible, though extremely rare, that part of the umbra intersects with the Earth (thus creating an annular or total eclipse), but not its central line. This is then called a non-central total or annular eclipse.[11] The last non-central solar eclipse was on April 29, 2014. This was an annular eclipse. The next non-central total solar eclipse will be on April 9, 2043.[12]
The phases observed during a total eclipse are called:[13]
- First contact—when the Moon's limb (edge) is exactly tangential to the Sun's limb.
- Second contact—starting with Baily's Beads (caused by light shining through valleys on the Moon's surface) and the diamond ring effect. Almost the entire disk is covered.
- Totality—the Moon obscures the entire disk of the Sun and only the solar corona is visible.
- Third contact—when the first bright light becomes visible and the Moon's shadow is moving away from the observer. Again a diamond ring may be observed.
- Fourth contact—when the trailing edge of the Moon ceases to overlap with the solar disk and the eclipse ends.
Predictions
Geometry

The diagrams to the right show the alignment of the Sun, Moon and Earth during a solar eclipse. The dark gray region between the Moon and Earth is the umbra, where the Sun is completely obscured by the Moon. The small area where the umbra touches Earth's surface is where a total eclipse can be seen. The larger light gray area is the penumbra, in which a partial eclipse can be seen. An observer in the antumbra, the area of shadow beyond the umbra, will see an annular eclipse.[14]
The Moon's orbit around the Earth is inclined at an angle of just over 5 degrees to the plane of the Earth's orbit around the Sun (the ecliptic). Because of this, at the time of a new moon, the Moon will usually pass to the north or south of the Sun. A solar eclipse can occur only when new moon occurs close to one of the points (known as nodes) where the Moon's orbit crosses the ecliptic.[15]
As noted above, the Moon's orbit is also elliptical. The Moon's distance from the Earth can vary by about 6% from its average value. Therefore, the Moon's apparent size varies with its distance from the Earth, and it is this effect that leads to the difference between total and annular eclipses. The distance of the Earth from the Sun also varies during the year, but this is a smaller effect. On average, the Moon appears to be slightly smaller than the Sun as seen from the Earth, so the majority (about 60%) of central eclipses are annular. It is only when the Moon is closer to the Earth than average (near its perigee) that a total eclipse occurs.[16][17]
| Moon | Sun | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| At perigee (nearest) |
At apogee (farthest) |
At perihelion (nearest) |
At aphelion (farthest) | |
| Mean radius | 1,737.10 km (1,079.38 mi) |
696,000 km (432,000 mi) | ||
| Distance | 363,104 km (225,622 mi) |
405,696 km (252,088 mi) |
147,098,070 km (91,402,500 mi) |
152,097,700 km (94,509,100 mi) |
| Angular diameter[18] |
33' 30" (0.5583°) |
29' 26" (0.4905°) |
32' 42" (0.5450°) |
31' 36" (0.5267°) |
| Apparent size to scale |
|
|
 |
 |
| Order by decreasing apparent size |
1st | 4th | 2nd | 3rd |
The Moon orbits the Earth in approximately 27.3 days, relative to a fixed frame of reference. This is known as the sidereal month. However, during one sidereal month, Earth has revolved part way around the Sun, making the average time between one new moon and the next longer than the sidereal month: it is approximately 29.5 days. This is known as the synodic month, and corresponds to what is commonly called the lunar month.[15]
The Moon crosses from south to north of the ecliptic at its ascending node, and vice versa at its descending node.[15] However, the nodes of the Moon's orbit are gradually moving in a retrograde motion, due to the action of the Sun's gravity on the Moon's motion, and they make a complete circuit every 18.6 years. This regression means that the time between each passage of the Moon through the ascending node is slightly shorter than the sidereal month. This period is called the nodical or draconic month.[19]
Finally, the Moon's perigee is moving forwards or precessing in its orbit, and makes a complete circuit in 8.85 years. The time between one perigee and the next is slightly longer than the sidereal month and known as the anomalistic month.[20]
The Moon's orbit intersects with the ecliptic at the two nodes that are 180 degrees apart. Therefore, the new moon occurs close to the nodes at two periods of the year approximately six months (173.3 days) apart, known as eclipse seasons, and there will always be at least one solar eclipse during these periods. Sometimes the new moon occurs close enough to a node during two consecutive months to eclipse the Sun on both occasions in two partial eclipses. This means that, in any given year, there will always be at least two solar eclipses, and there can be as many as five.[21]
Eclipses can occur only when the Sun is within about 15 to 18 degrees of a node, (10 to 12 degrees for central eclipses). This is referred to as an eclipse limit. In the time it takes for the Moon to return to a node (draconic month), the apparent position of the Sun has moved about 29 degrees, relative to the nodes.[1] Since the eclipse limit creates a window of opportunity of up to 36 degrees (24 degrees for central eclipses), it is possible for partial eclipses (or rarely a partial and a central eclipse) to occur in consecutive months.[22][23]
Path
During a central eclipse, the Moon's umbra (or antumbra, in the case of an annular eclipse) moves rapidly from west to east across the Earth. The Earth is also rotating from west to east, at about 28 km/min at the Equator, but as the Moon is moving in the same direction as the Earth's spin at about 61 km/min, the umbra almost always appears to move in a roughly west-east direction across a map of the Earth at the speed of the Moon's orbital velocity minus the Earth's rotational velocity.[24]
The width of the track of a central eclipse varies according to the relative apparent diameters of the Sun and Moon. In the most favourable circumstances, when a total eclipse occurs very close to perigee, the track can be up to 267 km (166 mi) wide and the duration of totality may be over 7 minutes.[25] Outside of the central track, a partial eclipse is seen over a much larger area of the Earth. Typically, the umbra is 100–160 km wide, while the penumbral diameter is in excess of 6400 km.[26]
Duration
The following factors determine the duration of a total solar eclipse (in order of decreasing importance):[27][28]
- The moon being almost exactly at perigee (making its angular diameter as large as possible).
- The earth being very near aphelion (furthest away from the sun in its elliptical orbit, making its angular diameter nearly as small as possible).
- The midpoint of the eclipse being very close to the earth's equator, where the orbital velocity is greatest.
- The vector of the eclipse path at the midpoint of the eclipse aligning with the vector of the earth's rotation (i.e. not diagonal but due east).
- The midpoint of the eclipse being near the subsolar point (the part of the earth closest to the sun).
The longest eclipse that has been calculated thus far is the eclipse of July 16, 2186 (with a maximum duration of 7 minutes 4 seconds over northern Guyana).
Occurrence and cycles
Total solar eclipses are rare events. Although they occur somewhere on Earth every 18 months on average,[30] it is estimated that they recur at any given place only once every 360 to 410 years, on average.[31] The total eclipse lasts for only a maximum of a few minutes at any location, because the Moon's umbra moves eastward at over 1700 km/h.[32] Totality currently can never last more than 7 min 32 s. This value changes over the millennia and is currently decreasing. By the 8th millennium, the longest theoretically possible total eclipse will be less than 7 min 2 s.[27] The last time an eclipse longer than 7 minutes occurred was June 30, 1973 (7 min 3 sec). Observers aboard a Concorde supersonic aircraft were able to stretch totality for this eclipse to about 74 minutes by flying along the path of the Moon's umbra.[33] The next total eclipse exceeding seven minutes in duration will not occur until June 25, 2150. The longest total solar eclipse during the 11,000 year period from 3000 BC to at least 8000 AD will occur on July 16, 2186, when totality will last 7 min 29 s.[27][34] For comparison, the longest total eclipse of the 20th century at 7 min 8 s occurred on June 20, 1955 and there are no total solar eclipses over 7 min in duration in the 21st century.[35]
If the date and time of any solar eclipse are known, it is possible to predict other eclipses using eclipse cycles. The saros is probably the best known and one of the most accurate. A saros lasts 6,585.3 days (a little over 18 years), which means that, after this period, a practically identical eclipse will occur. The most notable difference will be a westward shift of about 120° in longitude (due to the 0.3 days) and a little in latitude (north-south for odd-numbered cycles, the reverse for even-numbered ones). A saros series always starts with a partial eclipse near one of Earth's polar regions, then shifts over the globe through a series of annular or total eclipses, and ends with a partial eclipse at the opposite polar region. A saros series lasts 1226 to 1550 years and 69 to 87 eclipses, with about 40 to 60 of them being central.[36]
Frequency per year
Between two and five solar eclipses occur every year, with at least one per eclipse season. Since the Gregorian calendar was instituted in 1582, years that have had five solar eclipses were 1693, 1758, 1805, 1823, 1870, and 1935. The next occurrence will be 2206.[37] On average, there are about 240 solar eclipses each century.[38]
| January 5 | February 3 | June 30 | July 30 | December 25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Partial (south) |
Partial (north) |
Partial (north) |
Partial (south) |
Annular (south) |
 Saros 111 |
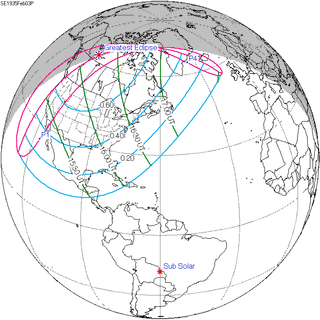 Saros 149 |
 Saros 116 |
 Saros 154 |
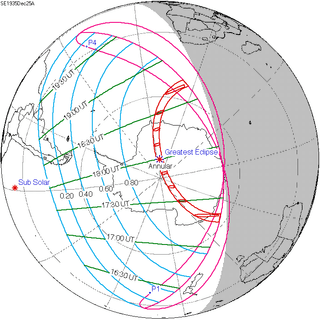 Saros 121 |
Final totality
Total solar eclipses are seen on Earth because of a fortuitous combination of circumstances. Even on Earth, the diversity of eclipses familiar to people today is a temporary (on a geological time scale) phenomenon. Hundreds of millions of years in the past, the Moon was closer to the Earth and therefore apparently larger, so every solar eclipse was total and there were no annular eclipses. Over a billion years in the future, the Moon will be too far away to fully occlude the Sun, and no total eclipses will occur.[39]
Due to tidal acceleration, the orbit of the Moon around the Earth becomes about 2.2 cm more distant each year. It is estimated that, in slightly less than 1.4 billion years, the distance from the Earth to the Moon will have increased by 30,400 km. During that period, the apparent angular diameter of the Moon will decrease in size, meaning that it will no longer be able to completely cover the Sun's disk as seen from the Earth. This will be true even when the Moon is at perigee, and the Earth at aphelion. Moreover, the Sun is increasing in diameter by about 5% per billion years.[40] Therefore, the last total solar eclipse on Earth will occur about six hundred million years from now.[39]
Historical eclipses

Historical eclipses are a very valuable resource for historians, in that they allow a few historical events to be dated precisely, from which other dates and ancient calendars may be deduced. A solar eclipse of June 15, 763 BC mentioned in an Assyrian text is important for the Chronology of the Ancient Orient.[41] There have been other claims to date earlier eclipses. The King Zhong Kang supposedly beheaded two astronomers, Hsi and Ho, who failed to predict an eclipse 4,000 years ago.[42] Perhaps the earliest still-unproven claim is that of archaeologist Bruce Masse, who putatively links an eclipse that occurred on May 10, 2807 BC with a possible meteor impact in the Indian Ocean on the basis of several ancient flood myths that mention a total solar eclipse.[43]
Eclipses have been interpreted as omens, or portents.[44] The ancient Greek historian Herodotus wrote that Thales of Miletus predicted an eclipse that occurred during a battle between the Medes and the Lydians. Both sides put down their weapons and declared peace as a result of the eclipse.[45] The exact eclipse involved remains uncertain, although the issue has been studied by hundreds of ancient and modern authorities. One likely candidate took place on May 28, 585 BC, probably near the Halys river in Asia Minor.[46] An eclipse recorded by Herodotus before Xerxes departed for his expedition against Greece,[47] which is traditionally dated to 480 BC, was matched by John Russell Hind to an annular eclipse of the Sun at Sardis on February 17, 478 BC.[48] Alternatively, a partial eclipse was visible from Persia on October 2, 480 BC.[49] Herodotus also reports a solar eclipse at Sparta during the Second Persian invasion of Greece.[50] The date of the eclipse (August 1, 477 BC) does not match exactly the conventional dates for the invasion accepted by historians.[51]
Chinese records of eclipses begin at around 720 BC.[52] The 4th century BC astronomer Shi Shen described the prediction of eclipses by using the relative positions of the Moon and Sun.[53] The "radiating influence" theory (i.e., the Moon's light was reflection from the Sun) was existent in Chinese thought from about the sixth century BC (in the Zhi Ran of Zhi Ni Zi),[54] though it was opposed by the 1st century AD philosopher Wang Chong, who made clear in his writing that this theory was nothing new.[53] Ancient Greeks, such as Parmenides and Aristotle, also supported the theory of the Moon shining because of reflected light.[54]
Attempts have been made to establish the exact date of Good Friday by assuming that the darkness described at Jesus's crucifixion was a solar eclipse. This research has not yielded conclusive results,[55][56] and Good Friday is recorded as being at Passover, which is held at the time of a full moon. Further, the darkness lasted from the sixth hour to the ninth, or three hours, which is much, much longer than the eight-minute upper limit for any solar eclipse's totality. In the Western hemisphere, there are few reliable records of eclipses before 800 AD, until the advent of Arab and monastic observations in the early medieval period.[52] The first recorded observation of the corona was made in Constantinople in 968 AD.[49][52]
The first known telescopic observation of a total solar eclipse was made in France in 1706.[52] Nine years later, English astronomer Edmund Halley observed the solar eclipse of May 3, 1715.[49][52] By the mid-19th century, scientific understanding of the Sun was improving through observations of the Sun's corona during solar eclipses. The corona was identified as part of the Sun's atmosphere in 1842, and the first photograph (or daguerreotype) of a total eclipse was taken of the solar eclipse of July 28, 1851.[49] Spectroscope observations were made of the solar eclipse of August 18, 1868, which helped to determine the chemical composition of the Sun.[49]
Viewing
Looking directly at the photosphere of the Sun (the bright disk of the Sun itself), even for just a few seconds, can cause permanent damage to the retina of the eye, because of the intense visible and invisible radiation that the photosphere emits. This damage can result in impairment of vision, up to and including blindness. The retina has no sensitivity to pain, and the effects of retinal damage may not appear for hours, so there is no warning that injury is occurring.[57][58]
Under normal conditions, the Sun is so bright that it is difficult to stare at it directly. However, during an eclipse, with so much of the Sun covered, it is easier and more tempting to stare at it. Looking at the Sun during an eclipse is as dangerous as looking at it outside an eclipse, except during the brief period of totality, when the Sun's disk is completely covered (totality occurs only during a total eclipse and only very briefly; it does not occur during a partial or annular eclipse). Viewing the Sun's disk through any kind of optical aid (binoculars, a telescope, or even an optical camera viewfinder) is extremely hazardous and can cause irreversible eye damage within a fraction of a second.[59][60]
Partial and annular eclipses

Viewing the Sun during partial and annular eclipses (and during total eclipses outside the brief period of totality) requires special eye protection, or indirect viewing methods, if eye damage is to be avoided. The Sun's disk can be viewed using appropriate filtration to block the harmful part of the Sun's radiation. Sunglasses do not make viewing the Sun safe. Only properly designed and certified solar filters should be used for direct viewing of the Sun's disk.[61] Especially, self-made filters using common objects such as a floppy disk removed from its case, a Compact Disc, a black colour slide film, smoked glass, etc. must be avoided.[62][63]
The safest way to view the Sun's disk is by indirect projection.[64] This can be done by projecting an image of the disk onto a white piece of paper or card using a pair of binoculars (with one of the lenses covered), a telescope, or another piece of cardboard with a small hole in it (about 1 mm diameter), often called a pinhole camera. The projected image of the Sun can then be safely viewed; this technique can be used to observe sunspots, as well as eclipses. Care must be taken, however, to ensure that no one looks through the projector (telescope, pinhole, etc.) directly.[65] Viewing the Sun's disk on a video display screen (provided by a video camera or digital camera) is safe, although the camera itself may be damaged by direct exposure to the Sun. The optical viewfinders provided with some video and digital cameras are not safe. Securely mounting #14 welder's glass in front of the lens and viewfinder protects the equipment and makes viewing possible.[63] Professional workmanship is essential because of the dire consequences any gaps or detaching mountings will have. In the partial eclipse path, one will not be able to see the corona or nearly complete darkening of the sky, however, depending on how much of the Sun's disk is obscured, some darkening may be noticeable. If three-quarters or more of the sun is obscured, then an effect can be observed by which the daylight appears to be dim, as if the sky were overcast, yet objects still cast sharp shadows.[66]
Totality
When the shrinking visible part of the photosphere becomes very small, Baily's beads will occur. These are caused by the sunlight still being able to reach the Earth through lunar valleys. Totality then begins with the diamond ring effect, the last bright flash of sunlight.[67]
It is safe to observe the total phase of a solar eclipse directly only when the Sun's photosphere is completely covered by the Moon, and not before or after totality.[64] During this period, the Sun is too dim to be seen through filters. The Sun's faint corona will be visible, and the chromosphere, solar prominences, and possibly even a solar flare may be seen. At the end of totality, the same effects will occur in reverse order, and on the opposite side of the Moon.[67]
Photography
Photographing an eclipse is possible with fairly common camera equipment. In order for the disk of the Sun/Moon to be easily visible, a fairly high magnification long focus lens is needed (at least 200 mm for a 35 mm camera), and for the disk to fill most of the frame, a longer lens is needed (over 500 mm). As with viewing the Sun directly, looking at it through the viewfinder of a camera can produce damage to the retina, so care is recommended.[68]
Other observations

A total solar eclipse provides a rare opportunity to observe the corona (the outer layer of the Sun's atmosphere). Normally this is not visible because the photosphere is much brighter than the corona. According to the point reached in the solar cycle, the corona may appear small and symmetric, or large and fuzzy. It is very hard to predict this in advance.[69]
Phenomena associated with eclipses include shadow bands (also known as flying shadows), which are similar to shadows on the bottom of a swimming pool. They only occur just prior to and after totality, when a narrow solar crescent acts as an anisotropic light source.[70]
1919 observations

The observation of a total solar eclipse of May 29, 1919 helped to confirm Einstein's theory of general relativity. By comparing the apparent distance between stars in the constellation Taurus, with and without the Sun between them, Arthur Eddington stated that the theoretical predictions about gravitational lenses were confirmed.[71] The observation with the Sun between the stars was only possible during totality, since the stars are then visible. Though Eddington's observations were near the experimental limits of accuracy at the time, work in the later half of the 20th century confirmed his results.[72][73]
Gravity anomalies
There is a long history of observations of gravity-related phenomena during solar eclipses, especially around totality. In 1954, and again in 1959, Maurice Allais reported observations of strange and unexplained movement during solar eclipses.[74] This phenomenon is now called the Allais effect. Similarly, in 1970, Saxl and Allen observed the sudden change in motion of a torsion pendulum; this phenomenon is called the Saxl effect.[75]
A recent published observation during the 1997 solar eclipse by Wang et al. suggested a possible gravitational shielding effect,[76] which generated debate. Later in 2002, Yang and Wang published detailed data analysis, which suggested that the phenomenon still remains unexplained.[77]
Eclipses and transits
In principle, the simultaneous occurrence of a Solar eclipse and a transit of a planet is possible. But these events are extremely rare because of their short durations. The next anticipated simultaneous occurrence of a Solar eclipse and a transit of Mercury will be on July 5, 6757, and a Solar eclipse and a transit of Venus is expected on April 5, 15232.[78]
More common, but still infrequent, is a conjunction of a planet (especially, but not only, Mercury or Venus) at the time of a total solar eclipse, in which event the planet will be visible very near the eclipsed Sun, when without the eclipse it would have been lost in the Sun's glare. At one time, some scientists hypothesized that there may be a planet (often given the name Vulcan) even closer to the Sun than Mercury; the only way to confirm its existence would have been to observe it in transit or during a total solar eclipse. No such planet was ever found, and general relativity has since explained the observations that led astronomers to suggest that Vulcan might exist.[79]
Earthshine
During a total solar eclipse, the Moon's shadow covers only a small fraction of the Earth. The Earth continues to receive at least 92 percent of the amount of sunlight it receives without an eclipse – more if the penumbra of the Moon's shadow partly misses the Earth. Seen from the Moon, the Earth during a total solar eclipse is mostly brilliantly illuminated, with only a small dark patch showing the Moon's shadow. The brilliantly-lit Earth reflects a lot of light to the Moon. If the corona of the eclipsed Sun were not present, the Moon, illuminated by earthlight, would be easily visible from Earth. This would be essentially the same as the earthshine which can frequently be seen when the Moon's phase is a narrow crescent. In reality, the corona, though much less brilliant than the Sun's photosphere, is much brighter than the Moon illuminated by earthlight. Therefore, by contrast, the Moon during a total solar eclipse appears to be black, with the corona surrounding it.
Artificial satellites


Artificial satellites can also pass in front of the Sun as seen from the Earth, but none is large enough to cause an eclipse. At the altitude of the International Space Station, for example, an object would need to be about 3.35 km (2.08 mi) across to blot the Sun out entirely. These transits are difficult to watch, because the zone of visibility is very small. The satellite passes over the face of the Sun in about a second, typically. As with a transit of a planet, it will not get dark.[80]
Observations of eclipses from spacecraft or artificial satellites orbiting above the Earth's atmosphere are not subject to weather conditions. The crew of Gemini 12 observed a total solar eclipse from space in 1966.[81] The partial phase of the 1999 total eclipse was visible from Mir.[82]
During the Apollo–Soyuz Test Project conducted in July 1975, the Apollo spacecraft was positioned to create an artificial solar eclipse giving the Soyuz crew an opportunity to photograph the solar corona.
Impact
The solar eclipse of March 20, 2015, was the first occurrence of an eclipse estimated to potentially have a significant impact on the power system, with the electricity sector taking measures to mitigate any impact. The continental Europe and Great Britain synchronous areas were estimated to have about 90 Gigawatts of solar power and it was estimated that production would temporarily decrease by up to 34 GW compared to a clear sky day.[83][84] The temperature may decrease by 3 °C, and wind power potentially decrease as winds are reduced by 0.7 m/s.[85]Template:Update-line
Recent and forthcoming solar eclipses

Eclipses only occur in the eclipse season, when the Sun is close to either the ascending or descending node of the Moon. Each eclipse is separated by one, five or six lunations (synodic months), and the midpoint of each season is separated by 173.3 days, which is the mean time for the Sun to travel from one node to the next. The period is a little less than half a calendar year because the lunar nodes slowly regress. Because 223 synodic months is roughly equal to 239 anomalistic months and 242 draconic months, eclipses with similar geometry recur 223 synodic months (about 6,585.3 days) apart. This period (18 years 11.3 days) is a saros. Because 223 synodic months is not identical to 239 anomalistic months or 242 draconic months, saros cycles do not endlessly repeat. Each cycle begins with the Moon's shadow crossing the earth near the north or south pole, and subsequent events progress toward the other pole until the Moon's shadow misses the earth and the series ends.[22] Saros cycles are numbered; currently, cycles 117 to 156 are active.
| Solar eclipses | ||||||||
| 1997–2000 | 2000–2003 | 2004–2007 | 2008–2011 | 2011–2014 | 2015–2018 | 2018–2021 | 2022–2025 | 2026-2029 |
See also
- Besselian elements
- Black Sun (mythology)
- Solar eclipses in fiction
- Solar eclipses on other planets
- Solar eclipses on the Moon
- Transit of Deimos from Mars
- Transit of Phobos from Mars
Notes
- 1 2 Littmann, Mark; Espenak, Fred; Willcox, Ken (2008). Totality: Eclipses of the Sun. Oxford University Press. pp. 18–19. ISBN 0-19-953209-5.
- ↑ Five solar eclipses occurred in 1935.NASA (September 6, 2009). "Five Millennium Catalog of Solar Eclipses". NASA Eclipse Web Site. Fred Espenak, Project and Website Manager. Retrieved January 26, 2010.
- ↑ Koukkos, Christina (May 14, 2009). "Eclipse Chasing, in Pursuit of Total Awe". New York Times. Retrieved January 15, 2012.
- ↑ Pasachoff, Jay M. (July 10, 2010). "Why I Never Miss a Solar Eclipse". New York Times. Retrieved January 15, 2012.
- ↑ Harrington, pp. 7–8
- 1 2 3 4 5 Harrington, pp. 9–11
- ↑ "Transit of Venus, Sun-Earth Day 2012". nasa.gov. Retrieved February 7, 2016.
- ↑ "Solar Eclipses". University of Tennessee. Retrieved January 15, 2012.
- ↑ Espenak, Fred (September 26, 2009). "Solar Eclipses for Beginners". Retrieved January 15, 2012.
- ↑ Steel, p. 351
- 1 2 Espenak, Fred (January 6, 2009). "Central Solar Eclipses: 1991–2050". Greenbelt, MD: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. Retrieved January 15, 2012.
- ↑ Verbelen, Felix (November 2003). "Solar Eclipses on Earth, 1001 BC to AD 2500". Retrieved January 15, 2012.
- ↑ Harrington, pp. 13–14; Steel, pp. 266–279
- ↑ Mobberley, pp. 30–38
- 1 2 3 Harrington, pp. 4–5
- ↑ Hipschman, Ron. "Why Eclipses Happen". Exploratorium. Retrieved January 14, 2012.
- ↑ Brewer, Bryan (January 14, 1998). "What Causes an Eclipse?". Earth View. Retrieved January 14, 2012.
- ↑ NASA - Eclipse 99 - Frequently Asked Questions — There is a mistake in the How long will we continue to be able to see total eclipses of the Sun? answer, "...the Sun's angular diameter varies from 32.7 minutes of arc when the Earth is at its farthest point in its orbit (aphelion), and 31.6 arc minutes when it is at its closest (perihelion)." It should appear smaller when farther, so the values should be swapped.
- ↑ Steel, pp. 319–321
- ↑ Steel, pp. 317–319
- ↑ Harrington, pp. 5–7
- 1 2 Espenak, Fred (August 28, 2009). "Periodicity of Solar Eclipses". Greenbelt, MD: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. Retrieved January 15, 2012.
- ↑ Espenak, Fred; Meeus, Jean (January 26, 2007). "Five Millennium Catalog of Solar Eclipses: -1999 to +3000". Greenbelt, MD: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. Retrieved January 15, 2012.
- ↑ Mobberley, pp. 33–37
- ↑ "How do eclipses such as the one on Wednesday 14 November 2012 occur?". Sydney Observatory. Retrieved 20 March 2015.
- ↑ Steel, pp. 52–53
- 1 2 3 Meeus, J. (December 2003). "The maximum possible duration of a total solar eclipse". Journal of the British Astronomical Association. 113 (6): 343–348. Bibcode:2003JBAA..113..343M. Retrieved 22 December 2013.
- ↑ M. Littman, et al.
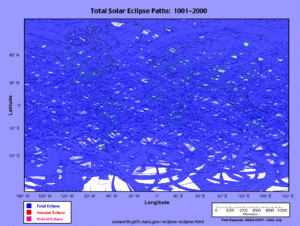
- ↑ Espenak, Fred (March 24, 2008). "World Atlas of Solar Eclipse Paths". NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. Retrieved January 15, 2012.
- ↑ Steel, p. 4
- ↑ For 360 years, see Harrington, p. 9; for 410 years, see Steel, p. 31
- ↑ Mobberley, pp. 33–36; Steel, p. 258
- ↑ "Eclipse Flight of Concorde 001". nature.com.
- ↑ Stephenson, F. Richard (1997). Historical Eclipses and Earth's Rotation. Cambridge University Press. p. 54. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511525186. ISBN 0-521-46194-4.
- ↑ Mobberley, p. 10
- ↑ Espenak, Fred (August 28, 2009). "Eclipses and the Saros". NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. Retrieved January 15, 2012.
- ↑ Pogo, Alexander (1935). "Calendar years with five solar eclipses". Popular Astronomy. 43: 412. Bibcode:1935PA.....43..412P.
- ↑ "What are solar eclipses and how often do they occur?". timeanddate.com. Retrieved 2014-11-23.
- 1 2 Walker, John (July 10, 2004). "Moon near Perigee, Earth near Aphelion". Fourmilab. Retrieved March 7, 2010.
- ↑ Ribas, Ignasi (February 2010). "The Sun and stars as the primary energy input in planetary atmospheres". Solar and Stellar Variability: Impact on Earth and Planets, IAU Symposium. Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union. 264. 3–18. arXiv:0911.4872
 . Bibcode:2010IAUS..264....3R. doi:10.1017/S1743921309992298.
. Bibcode:2010IAUS..264....3R. doi:10.1017/S1743921309992298. - ↑ van Gent, Robert Harry. "Astronomical Chronology". University of Utrecht. Retrieved January 15, 2012.
- ↑ Harrington, p. 2
- ↑ Blakeslee, Sandra (November 14, 2006). "Ancient Crash, Epic Wave". New York Times. Retrieved November 14, 2006.
- ↑ Steel, p. 1
- ↑ Steel, pp. 84–85
- ↑ Le Conte, David (December 6, 1998). "Eclipse Quotations". MrEclipse.com. Retrieved January 8, 2011.
- ↑ Herodotus. Book VII. p. 37.
- ↑ Chambers, G. F. (1889). A Handbook of Descriptive and Practical Astronomy. Oxford: Clarendon Press. p. 323.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Espenak, Fred. "Solar Eclipses of Historical Interest". NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. Retrieved December 28, 2011.
- ↑ Herodotus. Book IX. p. 10.
- ↑ Schaefer, Bradley E. (May 1994). "Solar Eclipses That Changed the World". Sky and Telescope. 87 (5): 36–39. Bibcode:1994S&T....87...36S.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Stephenson, F. Richard (1982). "Historical Eclipses". Scientific American. 247 (4): 154–163. Bibcode:1982SciAm.247..154S.
- 1 2 Needham, Joseph (1986). Science and Civilization in China: Volume 3. Taipei: Caves Books. pp. 411–413. OCLC 48999277.
- 1 2 Needham, p. 227.
- ↑ Humphreys, C. J.; Waddington, W. G. (1983). "Dating the Crucifixion". Nature. 306 (5945): 743–746. Bibcode:1983Natur.306..743H. doi:10.1038/306743a0.
- ↑ Kidger, Mark (1999). The Star of Bethlehem: An Astronomer's View. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. pp. 68–72. ISBN 0-691-05823-7.
- ↑ Espenak, Fred (July 11, 2005). "Eye Safety During Solar Eclipses". NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. Retrieved January 15, 2012.
- ↑ Dobson, Roger (August 21, 1999). "UK hospitals assess eye damage after solar eclipse". British Medical Journal. 319: 469. doi:10.1136/bmj.319.7208.469.
- ↑ MacRobert, Alan M. "How to Watch a Partial Solar Eclipse Safely". Sky & Telescope. Retrieved August 4, 2007.
- ↑ Chou, B. Ralph (July 11, 2005). "Eye safety during solar eclipses". NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. Retrieved January 15, 2012.
- ↑ Littmann, Mark; Willcox, Ken; Espenak, Fred (1999). "Observing Solar Eclipses Safely". MrEclipse.com. Retrieved January 15, 2012.
- ↑ Chou, B. Ralph (January 20, 2008). "Eclipse Filters". MrEclipse.com. Retrieved January 4, 2012.
- 1 2 "Eclipse Viewing Safety". Perkins Observatory. Retrieved January 15, 2012.
- 1 2 Harrington, p. 25
- ↑ Harrington, p. 26
- ↑ Harrington, p. 40
- 1 2 Littmann, Mark; Willcox, Ken; Espenak, Fred (1999). "The Experience of Totality". MrEclipse.com. Retrieved January 15, 2012.
- ↑ Kramer, Bill. "Photographing a Total Solar Eclipse". Eclipse-chasers.com. Archived from the original on January 29, 2009. Retrieved March 7, 2010.
- ↑ "The science of eclipses". ESA. September 28, 2004. Retrieved August 4, 2007.
- ↑ Dravins, Dainis. "Flying Shadows". Lund Observatory. Retrieved January 15, 2012.
- ↑ Dyson, F.W.; Eddington, A.S.; Davidson, C.R. (1920). "A Determination of the Deflection of Light by the Sun's Gravitational Field, from Observations Made at the Solar eclipse of May 29, 1919". Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. A. 220 (571-581): 291–333. Bibcode:1920RSPTA.220..291D. doi:10.1098/rsta.1920.0009.
- ↑ "Relativity and the 1919 eclipse". ESA. September 13, 2004. Retrieved January 11, 2011.
- ↑ Steel, pp. 114–120
- ↑ Allais, Maurice (1959). "Should the Laws of Gravitation be Reconsidered?". Aero/Space Engineering. 9: 46–55.
- ↑ Saxl, Erwin J.; Allen, Mildred (1971). "1970 solar eclipse as 'seen' by a torsion pendulum". Physical Review D. 3 (4): 823–825. Bibcode:1971PhRvD...3..823S. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.3.823.
- ↑ Wang, Qian-shen; Yang, Xin-she; Wu, Chuan-zhen; Guo, Hong-gang; Liu, Hong-chen; Hua, Chang-chai (2000). "Precise measurement of gravity variations during a total solar eclipse". Physical Review D. 62 (4): 041101(R). arXiv:1003.4947
 . Bibcode:2000PhRvD..62d1101W. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.62.041101.
. Bibcode:2000PhRvD..62d1101W. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.62.041101. - ↑ Yang, X. S.; Wang, Q. S. (2002). "Gravity anomaly during the Mohe total solar eclipse and new constraint on gravitational shielding parameter". Astrophysics and Space Science. 282 (1): 245–253. Bibcode:2002Ap&SS.282..245Y. doi:10.1023/A:1021119023985.
- ↑ Meeus, J.; Vitagliano, A. (2004). "Simultaneous transits" (PDF). J. Br. Astron. Assoc. 114 (3): 132–135. Bibcode:2004JBAA..114..132M. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 10, 2007.
- ↑ Grego, Peter (2008). Venus and Mercury, and How to Observe Them. Springer. p. 3. ISBN 978-0387742854.
- ↑ "ISS-Venustransit" (in German). astronomie.info.
- ↑ "JSC Digital Image Collection". NASA Johnson Space Center. January 11, 2006. Retrieved January 15, 2012.
- ↑ Nemiroff, R.; Bonnell, J., eds. (August 30, 1999). "Looking Back on an Eclipsed Earth". Astronomy Picture of the Day. NASA. Retrieved January 15, 2012.
- ↑ "Solar Eclipse 2015 - Impact Analysis" pp3+6+7+13 . European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity, 19 February 2015. Accessed: 4 March 2015.
- ↑ Curve of potential power loss
- ↑ S. L. Gray , R. G. Harrison. "Diagnosing eclipse-induced wind changes" Proceedings of the Royal Society. DOI: 10.1098/rspa.2012.0007 Published 25 May 2012. Archive
References
- Harrington, Philip S. (1997). Eclipse! The What, Where, When, Why and How Guide to Watching Solar and Lunar Eclipses. New York: John Wiley and Sons. ISBN 0-471-12795-7.
- Mobberley, Martin (2007). Total Solar Eclipses and How to Observe Them. Astronomers' Observing Guides. New York: Springer. ISBN 978-0-387-69827-4.
- Steel, Duncan (1999). Eclipse: The celestial phenomenon which has changed the course of history. London: Headline. ISBN 0-7472-7385-5.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Solar eclipses. |
- NASA Eclipse Web Site
- Eclipsewise, Fred Espenak's new eclipse site
- Detailed eclipse explanations and predictions, Hermit Eclipse
- Eclipse Photography, Prof. Miroslav Druckmüller
- Animated maps of August 21, 2017 solar eclipses, Larry Koehn
- Five Millennium (−1999 to +3000) Canon of Solar Eclipses Database, Xavier M. Jubier
- Animated explanation of the mechanics of a solar eclipse, University of South Wales
- Eclipse Image Gallery, The World at Night
- Ring of Fire Eclipse: 2012, Photos
-
 "Sun, Eclipses of the". Collier's New Encyclopedia. 1921.
"Sun, Eclipses of the". Collier's New Encyclopedia. 1921. - Centered and aligned video recording of Total Solar Eclipse 20th March 2015 on YouTube
- Solar eclipse photographs taken from the Lick Observatory from the Lick Observatory Records Digital Archive, UC Santa Cruz Library’s Digital Collections
- Video with Total Solar Eclipse March 09 2016 (From the Beginning to the Total Phase) on YouTube
- Total Solar Eclipse Shadow on Earth March 09 2016 CIMSSSatelite
![]() Wikiversity has a solar eclipse lab that students can do on any sunny day.
Wikiversity has a solar eclipse lab that students can do on any sunny day.