Fulham
| Fulham | |
 Fulham Palace, the former residence of the Bishop of London |
|
 Fulham |
|
| Population | 87,161 (2011) [1] |
|---|---|
| OS grid reference | TQ245765 |
| – Charing Cross | 3.7 mi (6.0 km) NE |
| London borough | |
| Ceremonial county | Greater London |
| Region | London |
| Country | England |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | LONDON |
| Postcode district | SW6, W14, W6 |
| Dialling code | 020 |
| Police | Metropolitan |
| Fire | London |
| Ambulance | London |
| EU Parliament | London |
| UK Parliament | Chelsea and Fulham and Hammersmith |
| London Assembly | |
Coordinates: 51°28′58″N 0°11′42″W / 51.4828°N 0.1950°W
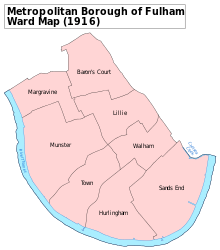
Fulham (/ˈfʊləm/) is part of the London Borough of Hammersmith and Fulham, in southwest London. It is an Inner London district located 3.7 miles (6.0 km) south-west of Charing Cross. It lies on the north bank of the River Thames, between Hammersmith and Kensington and Chelsea, facing Putney and Barnes and is bounded on the east by the West London Line, previously the course of a canal and creek.[2] It was formerly a parish in the County of Middlesex. The area is identified in the London Plan as one of 35 major centres in Greater London.[3] Until 1965 the former Metropolitan Borough of Fulham incorporated the areas of Sands End, Hurlingham, North End (Lillie), Baron's Court (Margravine), West Kensington, Fulham Broadway (Walham), 'Munstervillage' (Town) and along Fulham Palace Road. Fulham Palace, now a museum, served between 1900 and 1976 as the official residence of the Bishops of London.
Fulham has a history of industry and enterprise dating back to the 15th-century, in the shape of its Mill at Millshot, on the south-side of what is now Fulham Palace Road. This was followed by pottery, tapestry-weaving (the Gobelins Manufactory had established a branch in London in the 1700s), paper-making and brewing in the 17th and 18th-centuries all in the area of present-day Fulham High Street. The next two centuries saw involvement with energy production, transportation, the automotive industry, including early aviation and food production, (MacFarlane Lang Biscuits) and laundries.[4]
The Lillie Bridge Depot a railway engineering and stabling depot, opened 1872, heralded the arrival of the railway transport boom in London and was closely involved with the building and extensions of the London Underground network in the capital. It was associated with the electrification of the tube lines from the nearby Lots Road Power Station, just over the borough border in Chelsea and for well over a century, it has been the maintenance hub for the rolling stock and track. It is to be decommissioned by 2019.[5][6]
In contrast to its modest post-World War II reputation, Fulham is now considered among the "prime" London areas by estate agents.[7] Two football clubs, the eponymous Fulham F.C. and Premier League rivals, Chelsea F.C., are situated within Fulham.[8][9] There are two exclusive sporting clubs, The Hurlingham Club known for Polo and the Queen's tennis club known for its annual pre-Wimbledon Tennis tournament.[10][11] In the 1800s Lillie Bridge Grounds, (currently beneath the rising 'Lillie Square' residential development), hosted the first meetings of the Amateur Athletic Association of England, the second FA Cup Final and the first ever amateur boxing matches.[12] The Lillie Bridge area was also the former home-ground of the Middlesex County Cricket Club, before it moved to Marylebone.[13]
History
Fulham Palace - the Manor of Fulham


Fulham, or in its earliest form "Fulanhamme", is thought to have signified the place either "place of fowls" or "of mud" (which probably had to do with the fact that the River Thames would flood it periodically), or alternatively, "land in the crook of a river bend belonging to an Anglo Saxon chief named Fulla". The manor of Fulham is said to have been given to Bishop Erkenwald about the year 691 for himself and his successors in the See of London. In effect, Fulham Palace, for nine centuries the summer residence of the Bishops of London, is the manor of Fulham.[14] In 879 Danish invaders, sailed up the Thames and wintered at Fulham and Hammersmith. Raphael Holinshed relates that the Bishop of London was lodging in his manor place in 1141 when Geoffrey de Mandeville, riding out from the Tower of London, took him prisoner. During the Commonwealth the manor was temporarily out of the bishops' hands, having been sold to Colonel Edmund Harvey.
In recent years there has been a great revival of interest in Fulham's earliest history, due almost entirely to the efforts of the Fulham Archaeological Rescue Group. This has carried out a number of interesting digs, particularly in the vicinity of Fulham Palace, which show that approximately 5,000 years ago Neolithic people were living by the riverside and in other parts of the area. Excavations have also revealed Roman settlements during the third and fourth centuries AD.
Fulham parish
There is no record of the original erection of a Parish church in Fulham, but the first written record of a church dates from 1154 as a result of a tithe dispute. The first known parish priest of All Saints Church, Fulham was appointed in 1242. The medieval extant part of All Saints Church was demolished in 1881, during reconstruction by Sir Arthur Blomfield, in order to enlarge it, however, it did not date farther back than the 15th century.[15] Interestingly, there is a comparably old church on the opposite bank of the Thames, St Mary's Church, Putney, on the other side of the river crossing.
In 1642 the Earl of Essex threw a bridge of boats across the river in order to march his army in pursuit of Charles I, who thereupon fell back on Oxford. This is thought to have been near the subsequent wooden Fulham Bridge, built in 1729 and replaced in 1886 with Putney Bridge. Margravine Road recalls the existence of Brandenburg House, a riverside mansion built by Sir Nicholas Crispe in the time of Charles I, and used as the headquarters of General Fairfax in 1647 during the civil wars. In 1792 it was occupied by Charles Alexander, Margrave of Brandenburg-Ansbach and his wife, and in 1820 by Caroline, consort of George IV. His non-political 'wife' was Maria Fitzherbert who lived in East End House in Parson's Green. They are reputed to have had several children.[16]

During the 18th century Fulham had a reputation for debauchery, becoming a playground for the wealthy of London, where there was much gambling and prostitution and breweries. Until 1834, the neighbouring village of Hammersmith had been incorporated in the parish of Fulham.[17] However, due to population expansion, it was decided to create separate parishes for the purposes of administration. They did not come together again until 1965.
19th-century transport and power plays

The 19th-century roused Walham Green village, and the surrounding hamlets that made up the parish of Fulham, from their rural slumber and market gardens with the advent first of power production and then more hesitant transport development.[18] This was accompanied by accelerating urbanisation, as in other centres in the county of Middlesex, which encouraged trade skills among the growing population. In 1824 the Imperial Gas Light and Coke Company, the first public utility company in the world, bought the Sandford estate in Sands End to produce gas for lighting - and in the case of the Hurlingham Club, for ballooning.[19] Its ornately decorated number 2 gasholder is Georgian, completed in 1830 and reputed to be the oldest gasholder in the World.[20] In connection with gas property portfolios, in 1843 the newly formed Westminster Cemetery Company had trouble persuading the Equitable gas people (a future Imperial take-over) to sell them a small portion of land to gain southern access, onto the Fulham Road, from their recently laid out Brompton Cemetery, over the parish border in Chelsea. The sale was finally achieved through the intervention of cemetery shareholder and Fulham resident, John Gunter.[21][22]

Meanwhile, another group of local landowners, led by Lord Kensington with Sir John Scott Lillie and others had conceived, in 1822, the idea of exploiting the water course up-river from Chelsea Creek on their land by turning it into a two-mile canal. It was to have a basin, a lock and wharves, to be known as the Kensington Canal, and link the Grand Union Canal with the Thames. In practice the project was over budget and delayed by contractor bankruptcies and only opened in 1828, when railways were already gaining traction.[23] The short-lived canal concept did however leave a legacy: the creation on Lillie's land of a brewery and residential development, 'Rosa' - and 'Hermitage Cottages', and several roads, notably, the Lillie Road connecting the canal bridge, (Lillie Bridge) at West Brompton with North End Lane and the eventual creation of two railway lines, the West London Line and the District Line connecting South London with the rest of the capital. This was done with the input of two noted consulting engineers, Robert Stephenson in 1840 and from 1860, Sir John Fowler.[23]

It meant also that the area around Lillie Bridge was to make a lasting, if largely unsung, contribution for well over a century to the development and maintenance of public transport in London and beyond. Next to the Lillie Bridge engineering Depot, the Midland Railway established its own coal and goods yard. In !907 the engineering HQ of the Piccadilly Line in Richmond Place (16-18 Empress Place) oversaw the westward expansion of the line into the suburbs. At the turn of the century, the London Omnibus Co. in Seagrave Road oversaw the transition of horse-drawn to motor buses, which were eventually integrated into London Transport and London Buses. This attracted a host of other automotive enterprises to move into the area.
With the growth of 19th-century transport links into East Fulham and its sporting venues by 'Lillie Bridge', along with the immediately neighbouring 24-acre Earl's Court exhibition grounds, and the vast the Empress Hall (see entertainment section below). During the First World War it would become accommodation for Belgian refugees. Meanwhile, the historic hamlet of North End was massively redeveloped in the 1880s by Messrs Gibbs & Flew, who built 1,200 houses on the fields. They had trouble disposing of the properties, so for public relations purposes, they renamed the area 'West Kensington', to refer to the more prosperous neighbourhood over the parish boundary.[24]
The last farm to function in Fulham was Crabtree Farm, which closed at the beginning of the 20th-century. A principal recorder of all these changes was a local man, Charles James Féret (1854-1921), who conducted research over a period of decades before publishing his three volume history of Fulham in 1900.[25][26]
Art and Craft
Ceramics and weaving in Fulham go back to at least the 17th-century, most notably with the Fulham Pottery, followed by the establishment of tapestry and carpet production with a branch of the French 'Gobelins manufactory' and then the short-lived Parisot weaving school venture in the 1750s. William De Morgan, ceramicist and novelist, moved into Sands End with his painter wife, Evelyn De Morgan, where they lived and worked. Another artist couple, also members of the Arts and Crafts movement, lived at 'The Grange' in North End, Georgiana Burne-Jones and her husband, Edward Burne-Jones, both couples were friends of William Morris. Other artists who settled along the Lillie Road, were Francesco Bartolozzi, a florentine engraver, and Benjamin Rawlinson Faulkner, a society portrait painter. Henri Gaudier-Brzeska, the French expressionist painter and friend of Ezra Pound, lived in Walham Green till his early death in 1915. Glass production was, until recently, represented by the Stained glass studio of the purpose-built and Grade II listed Glass House in Lettice Street and latterly, by the Aaronson Noon Studio, with the 'Zest' Gallery in Rickett Street, that was obliged to shut down in 2012, after 20 years by the developers of 'Lillie Square' and Earl's Court. Both glass businesses have now moved out of London.[27][28][29] The Art Bronze Foundry, founded by Charles Gaskin in 1922 still operates in Michael Road, off the New King's Road, a short distance from Eel Brook Common. It has produced works by Henry Moore, Elisabeth Frink, Barbara Hepworth and Jacob Epstein among others. Its work may be seen in public spaces all over the world.[30]
20th-century


Fulham remained a predominantly working class area for the first half of the twentieth century, with genteel pockets at North End, along the top of Lillie Road and New King's Road, especially around Parsons Green, Eel Brook Common, South Park and the area surrounding the Hurlingham Club. Essentially, the area had attracted waves of immigrants from the countryside to service industrialisation and the more privileged parts of the capital. With rapid demographic changes there was poverty, as had been noted by Charles Dickens and Charles Booth and Fulham had its Poorhouses, and attracted several benefactors, including: the Samuel Lewis (financier) Housing Trust, the Peabody Trust and Sir Oswald Stoll Foundation to provide low-cost housing.[31] The Metropolitan Asylums Board acquired in 1876 a 13-acre site at the bottom of Seagrave Road, to build a fever hospital, 'The Western Hospital', that later became an NHS centre of excellence for treating polio until its final closure in 1979.[32][33] Bar one ward block remaining in private occupation, it was replaced by a gated flats development and a small public space, Brompton Park.[34]
Aside from the centuries-old brewing industry, e.g. The Swan Brewery on the Thames,[35] the main activities were motor and early aviation- Rolls Royce, Shell-Mex, Rover, the London Omnibus Co. - and rail engineering (Lillie Bridge Depot), laundries - the Palace Laundry is still extant - and the building trades.[36] Later there was distilling, Sir Robert Burnett's White Satin Gin,[37] food processing, e.g. Telfer's Pies, Encafood and Spaghetti House and Kodak's photographic processing. This encouraged the southern stretch of North End Road to become Fulham's unofficial 'High street', almost a mile from the actual Fulham High Street, with its own department store, F.H. Barbers, along with Woolworth's, Marks & Spencer and Sainsbury's outlets, all long gone. The second ever Tesco shop opened in the North End Road. The UK's reputedly oldest independent health food shop, opened in 1966 by the Aetherius Society, still trades in the Fulham Road.
Allied to these developments, the post-war period saw the extensive demolition of Fulham's early 19th-century architectural stock, replaced by some Brutalist architecture - the current Ibis hotel - and the Empress State Building in Lillie Road that in 1962 replaced the declining Empress Hall. The LCC and local council continued with much needed social housing development between the Second World War and up to the 1980s.
A piece of aviation history

Geoffrey de Havilland, aviation pioneer, built his first aeroplane at his workshop in Bothwell Street, Fulham in 1909.[38] Later, during World War I, Cannon's Brewery site at the corner of Lillie and North End Road was used for aircraft manufacture.[39] The Darracq Motor Engineering Company of Townmead Road, became aircraft manufacturers in Fulham for the Airco company, producing De Havilland designs and components for the duration of the war.
Musical heritage

William Crathern, the composer, was organist at St Mary's church, West Kensington, when it was still known as North End. Edward Elgar, the composer, lived at 51 Avonmore Road, W14, between 1890–1891.[40] Eugène Goossens and his wife Annie Cook, a Carl Rosa Opera Company singer settled in Fulham with their family. They were part of a musical dynasty of Belgian descent. Their eldest son was the conductor and composer Sir Eugene Aynsley Goossens next was Léon Jean Goossens (1897-1988), a British oboist, their daughters were the harpists, Marie and Sidonie Goossens. The family lived at 70, Edith Road, off the North End Road. Elvis Costello spent part of his youth in the area as he recalls in his Memoir.[41]
21st-century 'Gentrification'
In the 21st-century, Fulham is rated as one of the most expensive parts of London, and therefore the UK; average actual sale price of all property (both houses and flats) sold in the SW6 area in September 2007 was £639,973.[42] There are renewed plans to forcibly displace the residents of social housing, some of whom are immigrants and demolish large numbers of the small enterprises, some of them run by people of ethnic minorities, for which Fulham has been famous and replace them with dense high-rise luxury blocks and the ubiquitous high street chains.[43]
Redevelopment

With the accession of Boris Johnson to the mayoralty of London, a controversial 80 acre high-rise redevelopment has been under way on the eastern borough boundary with the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea, involving the dismantling of the two Earls Court Exhibition Centres in RBKC and in Hammersmith and Fulham and the emptying and demolition of hundreds of commercial properties, thousands of both private and social housing units and including the demolition of a rare example of mid-Victorian housing, designed by John Young (architect) in Fulham, in the proximity of Grade I and II listed structures and a number of conservation areas in both boroughs. It also involves the closure of the historic Lillie Bridge Depot,opened and the dispersal of its operations by TfL[44][45]
Namesake
The latest edition (2008) of the Chambers Dictionary defines a fulham as 'a die loaded at the corner to ensure that certain numbers are thrown (also full'am or full'an). Prob the place name 'Fulham' in London.' The OED distinguishes between a high fulham which was loaded so as to ensure a cast of 4, 5, or 6; and a low fulham, so as to ensure a cast of 1, 2, or 3). It also cites Arthur Conan Doyle's usage in 1889 in Micah Clarke xxx. 316 "There is no loading of the dice, or throwing of fulhams."
Politics

Fulham is part of two constituencies: one, Hammersmith bounded by the north side of the Lillie Road, is represented by Andy Slaughter for Labour, the other, Chelsea and Fulham parliamentary seat is currently held by Greg Hands for the Conservatives. Fulham was formerly a part of the Hammersmith and Fulham parliamentary constituency which was dissolved in 2010 to form the current seats. They are among the most affluent in the United Kingdom.. However, parts of Fulham continue to score highly on the Jarman Index, indicating poor health outcomes due to adverse socio-economic factors.
Fulham has in the past been solid Labour territory. Michael Stewart, one time Foreign Secretary in the Wilson government, was its long-standing MP. It became a politically significant part of the country, having been the scene of two major parliamentary by-elections in the 20th century. In 1933, the Fulham East by-election became known as the "peace by-election". The 1986 by-election following the death of Conservative MP, Martin Stevens, resulted in a Labour win for Nick Raynsford on a 10% swing. With 'Gentrification' Fulham voters have, however, been leaning towards the Conservatives since the 1980s as the area underwent huge demographic change: the tightly-packed terraces which had housed working-class families employed in trade, engineering and the industry that dominated Fulham's riverside being gradually replaced with young professionals. In the 2005 General Election, Greg Hands won the Hammersmith and Fulham Parliamentary seat for the Conservatives, polling 45.4% against Labour's 35.2%, a 7.3% swing. In the 2010 General Election, he was re-elected this time for the newly formed Chelsea and Fulham constituency. In the 2015 General Election he was returned with an increased share of the vote.
Hammersmith and Fulham is currently controlled by Labour. At the 2014 local elections, Labour won 11 seats from the Conservatives, giving them 26 councillors and control of the council (said to have been the then Prime Minister David Cameron's "favourite"[46]) for the first time since 2006. This was probably due to the Government's austerity programme and swingeing cuts to the NHS, threatening to close Charing Cross Hospital and allowing developers a free hand over a large swathe of the borough, to the detriment of ordinary families and traders.
Sport, entertainment and life-style
Sport

Before the area became home to the Fulham F.C. stadium Craven Cottage and the Chelsea F.C. stadium Stamford Bridge (and the various flats and entertainment centres built into it), the Lillie Bridge Grounds was the venue where British Amateur Athletics were born and the first codified Boxing under Marquess of Queensberry Rules took place. All this was accomplished through the catalyst that was John Graham Chambers from the mid-1860s.
Famously exclusive sports clubs, the The Queen's Club for tennis and the Hurlingham Club, are located within Fulham. In the case of the latter, members have included British monarchs and the waiting list for membership currently averages over fifteen years. Public tennis courts are located at the entrance to Fulham Palace. Tennis courts can also be found on Eel Brook Common. Hurlingham Park's tennis courts are used as netball courts and tennis nets are taken down and so restricting access to the courts for tennis. Hurlingham Park hosts the annual Polo in the Park tournament, which has become a recent feature of the area. The Hurlingham club is the historic home of polo in the United Kingdom and of the world governing body of polo.
[47] Rugby is played on Eel Brook Common and South Park. Normand Park in Lillie Road is the entry into the Virgin Active-operated Fulham Pools swimming facilities and neighbouring tennis courts.
Fulham can boast of two connections with the 'royal' game of Real tennis. There are the courts at the Queen's Club and then there was an unsurpassed designer of real tennis courts, one Joseph Bickley (1835-1923), who lived in Lillie Road and who took out a patent on his plaster mixture that withstood condensation and damp. To Bickley's skill are owed the survival, among others, of courts at Hampton Court Palace, Jesmond Dene, at Troon in Ayrshire as well as at the local Queen's.[48][49]
Entertainment

The most considerable entertainment (and sports) destinations in Fulham, after the Lillie Bridge Grounds closed in 1888, have been the 6,000-seater Empress Hall,[50] built in 1894 at the instigation of international impresario, Imre Kiralfy - the scene of his spectacular shows and later sporting events and famous ice shows - and latterly, Earls Court II, part of the Earls Court Exhibition Centre in the neighbouring, Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea.[51] The first closed in 1959, replaced by an office block, the Empress State Building. The second, opened by Diana, Princess of Wales, has lasted just over 20 years to 2014. Along with the architecturally pleasing Mid-Victorian Empress Place, formerly access to the exhibition centre, it is destined for High rise re-development, but with usage as yet to be confirmed.[52][53]
No trace is left today of either of Fulham's two theatres, both opened in 1897. The 'Grand Theatre' was on the approach to Putney Bridge and was designed by the prolific WGR Sprague, author of venues such as Wyndham's Theatre and the Aldwych Theatre in London's West End. It gave way to office blocks in the late 1950s. The 'Granville Theatre', founded by Dan Leno, to the design of Frank Matcham, once graced a triangle of land at Walham Green.[54] After the Music hall era had passed, It served as a film and television studio, but was finally demolished in 1971. It too has been replaced by an office block in Fulham Broadway.[55]
If traditional or heritage venues have been swept away - apparently during conservative administrations in the main - the performing arts continue in Fulham, like the notable Fulham Symphony Orchestra and the successful Fulham Opera.[56] St John's Parish Church, at the top of North End Road, stages choral and instrumental concerts as do other churches in the area.[57]
There is a cinema complex as part of the Fulham Broadway Centre. Fulham Town Hall, built in 1888 in the classical renaissance, is now used as a popular venue for concerts and dances, especially its Grand Hall. Behind Fulham Broadway, the heart of the original village of Walham Green has undergone pedestrianization, including the spot once occupied by the village green and its pond next to St.John's Parish Church and is bordered by a number of cafés, bars, and a dance studio in the old Fulham Public Baths. The largest supermarket in Fulham, is located on the site of a cinema later converted to the iconic 'Dicky Dirts' jean store with its sloping shop-floor, at the top of North End Road's Street market. It started a new trend in how retail was done.[58] Another, still extant, Fulham institution is the toy shop (named like the patron saint of Ireland) along Lillie Road going West, close to the junction with North End Road.
Gin, Breweries and Pubs
_1835.jpg)
The most illustrious brewery in Fulham was the Swan Brewery, Walham Green, dating back to the 17th-century. Among its patrons were kings and other royalty.[59] It was followed by the 'North End Brewery' in 1832, Cannons again in North End in 1867 and finally on account of temperance, the alcohol-free phenomenon that was Kops Brewery founded in 1890 at a site in Sands End. Gin distilling came to the remnants of the North End Brewery in Seagrave Road after a brief period of service as a timber works in the 1870s and lasted for almost a century. The premises were taken over by distillers, Vickers who at the outbreak of World War I sold out to Burnett's, producers of White Satin Gin, until a 1970s take-over by a Kentucky liquor business. None of the breweries remain.
With its long history of brewing, Fulham still has a number of pubs and gastropubs.[60] The oldest tavern is the 'Lillie Langtry' in Lillie Road, originally the 'Lillie Arms' named after its first freeholder, Sir John Scott Lillie, who built it in 1835 as part of the 'North End Brewery' complex, run from 1832-3 by a Miss Goslin.[61] It was intended originally to service the Kensington Canal workers and bargees. Later, it was the watering hole of the new railway builders, motor and omnibus company staff and latterly Earl's Court exhibition and Chelsea FC visitors. Of the three popular neighbouring pubs acquired by developers during 2014-15, 'The Imperial Arms' and 'The Prince of Wales' were forced to shut; only "The Atlas", reconstructed after bomb damage in World War II, has been reprieved. The White Horse in Parsons Green is colloquially known by many as the "Sloaney Pony",[62] a reference to the "Sloane Rangers" who frequent it. Pubs which are Grade II listed buildings include the Duke on the Green and Aragon House both facing Parsons Green, The Cock in North End Road, and the Temperance in Fulham High Street. Other pubs include the Durrell in Fulham Road, the locally and Michelin Guide listed, 1866 Harwood Arms in Walham Grove and the Mitre on Bishops Road.[63]
Open space
Fulham has several parks, cemeteries and open spaces, of which Bishop's Park, Fulham Palace Gardens, Hurlingham Park, South Park, Eel Brook Common and Parsons Green are the largest. Among the other spaces are Normand Park, the vestige of a convent garden with a bowling green, Lillie Road Recreation Ground with its gym facility and Brompton Park in Seagrave Road. The Thames riverside walk in Bishop's Park is interrupted by the Fulham football ground, but resumes after the neighbouring flats and continues to the Crabtree pub and beyond, past the Riverside Cafe on towards Hammersmith Bridge, affording views of the river and rural scenes on the opposite bank. It is part of the Thames Path.
Heritage
Architectural
Fulham parish's rural past meant that its grand houses and not so grand vernacular and industrial buildings were either clustered in the village of Walham Green, along the Thames or scattered among the fields of the hamlet of North End. Many historic structures fell prey to industrialisation, war-time bombing or a rush to demolition and redevelopment. Gone are Burne-Jones's 'Grange' in W14 and Foote's 'Hermitage' villa and park as is Lovibond's Cannon Brewery in SW6.[64] However, the ancient estate of Fulham Palace, the seat of the Bishops of London, remains the outstanding asset with its medieval and Tudor features, remnants of the grounds, now divided between public allotments and a park with a Kitchen garden and the part-excavated longest moat in England. Part of the buildings are Grade I listed, while others Grade II*. There are a number of other statutorily and locally listed structures strewn across Fulham. Worthy of note is the last remaining conical kiln of the Fulham Pottery. Broomhouse Lane has a number of structures of interest, ranging from the Broomhouse draw-dock of medieval origin to 18th-c. cottages (Sycamore and Ivy) and the Gothic revival Castle Club.[65] The Vineyard in Hurlingham Road is of 17th-c. origin with later 19th-c. additions such as the stable buildings. The Hurlingham Club and grounds are of 18th-c. origin and Grade II* listed. The winding North End Road has several buildings of note, especially, 'Crowthers' at no. 282, first built in 1712 with its extant 18th-c. gate-piers and the modernist (1938) Seven Stars public house, now converted into flats. Church Gate is the approach to All Saints Church, with its 14-15th-c. tower and 18th-c. tombs in the churchyard. The New King's Road contains several 18th-c. and early 19th-c. residences, namely, Northumberland House, Claybrook House, Jasmine House, Belgrave House and Aragon House, all Grade II listed.[66]
.jpg)
Much of the stock in Fulham attests its vigorous 19th-c. industrial and urban development, most of it, 'low-rise', and benefiting from the brick-fields that abounded locally at the time. An unlisted vestige of the early industrial era is the 1826 remnant of Gunter's canal bridge, still visible from platform 4 at West Brompton station.
Fulham in popular music and film

Fulham has several references in song lyrics. Willesden Green by The Kinks opens with the line: Well I tried to settle down Fulham Broadway.
The album, Passion Play, by progressive rock band, Jethro Tull, contains: There was a rush along the Fulham Road/There was a hush in the Passion Play. London's Brilliant Parade by Elvis Costello, has the lyrics, From the gates of St. Mary's/There were horses in Olympia/And a trolley bus in Fulham Broadway.
What A Waste by Ian Dury and the Blockheads, contains the lines: I could be a writer with a growing reputation/I could be a ticket man at Fulham Broadway Station.
Kiss Me Deadly by Billy Idol's 1970s punk rock band, Generation X, paints a gritty picture of casual street violence in 1970s Fulham. The song contains the refrain: Having fun, in South West Six, as well as the line, Hustling down the Fulham Road/Doing deals with Mr Cool. The song also makes reference to The Greyhound Pub, since closed, on Fulham Palace Road, and to the subway under Hammersmith Broadway.
West London Punk band, The Lurkers, titled their 1978 début LP, Fulham Fallout.
Maladjusted by Morrissey, former singer of The Smiths, contains the lines: As the Fulham Road lights/Stretch and invite into the night/From a Stevenage overspill/We'd kill to live around SW6. 'Stevenage overspill' is a reference to Fulham F.C. crowds as the club's ground, Craven Cottage is situated on Stevenage Road.
Ejector Seat Reservation by alternative rock band, Swervedriver, has the line: And just don't tell me the Fulham score.
Reformed boy band, Take That, sang the line: At Fulham Broadway Station, I see them every day in their song, Pretty Things, on their 2010 Progress, album.
West London hip-hop artist, Example, released a comedy song, You Can't Rap, with the chorus line: You can't rap, my friend/You're white and you're from Fulham/Please put down the mic./ There's no way you can fool them.
Fulham has appeared in a number of films, including The Omen and The L-Shaped Room. Fulham Broadway tube station was used in Sliding Doors. Esther Rantzen, presenter of the long-running BBC One TV magazine programme, That's Life!, often conducted vox pop interviews in North End market.[67]
Education
Fulham is home to several schools, including independent pre-preparatory and preparatory schools. Noted Fulham secondary establishments are the Grade II Listed Fulham Cross Girls School, The Oratory School, Lady Margaret School and Henry Compton School.[68] To cater for the large French-speaking population in the area, a French language primary school, 'Marie d'Orliac', has opened near Putney Bridge station. It is a feeder school for the Lycée Français Charles de Gaulle in South Kensington.
Interior design destinations
Fulham's artistic and craft heritage continues in the guise of groups of specialist retail outlets in several locations, such as the Wandsworth Bridge and Carnwarth Roads. The corner of Lillie Road and Munster Road hosts a number of antique shops.[69] New Kings Road has a number of interior shops and galleries, particularly near Lots Road and as it merges with Kings Road, Chelsea, and goes through Parsons Green. Chelsea Harbour is a favoured destination for interior designers.
Transport
An early account of Fulham, from a pedestrian's viewpoint, is provided by Thomas Crofton Croker in his journal published in 1860.[70]
Rail


Fulham nestles in a loop of the Thames across the river from Barnes and Putney. It straddles the Wimbledon and Richmond/Ealing Broadway branches of the District line of the tube — Fulham's tube stations are Putney Bridge, Parsons Green, Fulham Broadway (originally named Walham Green), West Kensington (originally Fulham - North End) and Baron's Court.[71]
The London Overground West London Line stops at West Brompton, just inside the Fulham borough boundary, and at Imperial Wharf in Fulham, Sands End. Until 1940 there was a Chelsea and Fulham railway station on this line, close to Stamford Bridge Stadium on Fulham Road, but this was closed following World War II bomb damage.[72]
Major roads
Major urban routes, or trunk roads, cross the area: The Talgarth Road - the A4, Fulham Palace Road - the A218 road, Fulham Road - the A219 road, the New King's Road - the A308 road, Wandsworth Bridge Road - the A217 road, Dawes Road - the A3219 road, Lillie Road - the A3218 road.
River crossings

By road:
- Wandsworth Bridge
- Putney Bridge
- Lillie Bridge, formerly a Thames tributary crossing, now over two railway routes.
- Counter's Bridge at Olympia, over the West London Line in the Counter's creek littoral.
By rail:
Places of interest

- Fulham Palace
- Fulham Pottery
- Margravine Cemetery
- Bishops Park
- Chelsea Harbour
- Stamford Bridge (stadium)
- All Saints Church, Fulham
- Craven Cottage
- New King's Road
- Riverside Studios, currently closed for refurbishment
- South Park, Fulham
John Roque's 1746 Map
The extract below of John Rocque's Map of London, 1746 shows the Parish of Fulham in the loop of the Thames, with Counter's Creek distinctly visible to the left, just below the 'elbow' in the river.
| B | ||
|---|---|---|
.jpg) |
2 | |
| This sheet extract is a clickable image for enlargement | ||
Notable people



16th-century
- Sir William Butts (1486-1545), physician to King Henry VIII of England[73]
- Sir Ralph Warren (c.1486-1553). twice Lord Mayor of London lived in Fulham House[74]
17th-century
- Joseph Addison (1672-1719), essayist, playwright lived at Sands End[75]
- Henry Compton (1632-1713), Bishop of London[73]
- Nell Gwyn (1650-1687), companion to Charles II of England, has a close named after her in Fulham[76]
- Humphrey Henchman (1592-1675), Bishop of London
- John Mordaunt, 1st Viscount Mordaunt (1626-1675), royalist conspirator prominent in the English Civil War
- John Robinson, Bishop of London
- John Saris (1580-1643), captain of the first English ship to reach Japan
- Sir William Withers (1657-1720), Lord Mayor of London
18th-century
- Francesco Bartolozzi (1725-1815), Italian engraver[77]
- Maria Fitzherbert (1756-1837), companion, and possibly wife, of King George IV[78]
- Samuel Foote (1721-1777), dramatist, actor and manager[73]
- Edmund Gibson (1669-1748), Bishop of London[73]
- Thomas Hayter (1702-1762), Bishop of London
- Nathaniel Kent (1737-1810), agriculturist
- Robert Lowth (1710-1787), Bishop of London
- Henry Holland (1745-1806), architect
- Samuel Richardson (1689-1761), writer and printer
- Granville Sharp (1735-1813), abolitionist and brother of William[79]
- William Sharp (1729-1810), surgeon
- Thomas Sherlock (1678-1761), Bishop of London
- Richard Terrick (1710-1777), Bishop of London
19th-century
- Joseph Bickley (1835-1923), Lillie Road-based Real tennis court designer and restorer[48][80]
- Sir Arthur Blomfield (1829-1899), architect[81]
- Charles James Blomfield (1786-1857), Bishop of London[81]
- William John Burchell (1781-1863), explorer, naturalist, artist, and author[82]
- Edward Burne-Jones (1833-1898), artist[83]
- Georgiana Burne-Jones (1840-1920), painter and writer, friend of George Eliot[84]
- Mandell Creighton (1843-1901), historian and Bishop of London. A popular social centre in Lillie Road is named after him
- Evelyn De Morgan (1855-1919), painter in the Pre-Raphaelite tradition[85]
- William De Morgan (1832-1917), potter, ceramicist, designer and novelist[86]
- Benjamin Rawlinson Faulkner (1787-1849), society portrait painter, lived in Richmond (Lillie) Road
- Charles James Féret (1854-1921), editor and historian of Fulham[87]
- Alfred Hackman (1811-1874), sub-librarian at the Bodleian Library[88]
- John Jackson (1811-1885), Bishop of London
- Sir John Scott Lillie (1790-1868), Peninsular War veteran, inventor and North End resident[89]
- Augustus Pugin (1812-1852), architect of St Thomas of Canterbury Church, Rylston Road
- Charles Rolls (1877–1910), co-founder of Rolls Royce Limited and pioneer aviator, had his car workshop in the former 'Lillie Hall'
- John Young (1797-1877) City architect and developer of Empress Place and Lillie Road (formerly Richmond Place and Richmond Road)
20th-century
- Henri Gaudier-Brzeska (1891-1915), expressionist sculptor and artist spent the last 5 years of his short life in Fulham[90]
- Linford Christie (born 1960), Olympian athlete
- Michael Cook (born 1933), Canadian playwright[91]
- Jill Craigie (1911-1999), documentary film maker and wife of Michael Foot
- Example (Elliot John Gleave) (born 1982), rapper, singer, and songwriter[92]
- Geoffrey de Havilland (1882-1965), aviation pioneer, had his first aircraft building workshop in Fulham
- Geoffrey Fisher (1887-1972), Bishop of London, then translated to the See of Canterbury
- Eugène Goossens, fils (1867-1958), musician and his 4 musical children, Sir Eugene Aynsley Goossens, Léon Jean Goossens, Marie and Sidonie Goossens
- Toni Halliday (born 1964), musician[93]
- Andy Hamilton (born 1954), Satirist, comic actor, writer and broadcaster
- Henry Montgomery Campbell (1887-1970), Bishop of London
- John Osborne (1929-1994), playwright[94]
- Baroness Phillips (1910-1992), Labour politician, radio personality and widow of Morgan Phillips and mother of Gwyneth Dunwoody, MP
- Daniel Radcliffe (born 1989), actor[95]
- Sir Oswald Stoll (1866-1942), theatre impressario and Fulham benefactor
- Robert Stopford (1901-1976), briefly Bishop of Fulham, before becoming Bishop of London, the last to reside at Fulham Palace
- Janet Street-Porter (born 1946), journalist, rambler, lived and went to school in Fulham
- William Wand (1885-1977), Bishop of London
- Bob White, (born 1936), First Class cricketer, then umpire
- Leslie Arthur Wilcox (1904-1982), marine artist
- Arthur Winnington-Ingram (1858-1946), Bishop of London (1901-1939), one of the longest serving
 Portrait of William Butts, physician to Henry VIII. He came from Fulham
Portrait of William Butts, physician to Henry VIII. He came from Fulham.jpg) Nell Gwyn by Simon Verelst. She lived in Fulham
Nell Gwyn by Simon Verelst. She lived in Fulham Kneller's portrait of Joseph Addison of Sands End
Kneller's portrait of Joseph Addison of Sands End Novelist, Samuel Richardson, who moved from North End to Parsons Green
Novelist, Samuel Richardson, who moved from North End to Parsons Green.jpg) Granville Sharp (Hoare memoire). He is buried in Fulham
Granville Sharp (Hoare memoire). He is buried in Fulham De Morgan and his wife, Evelyn. They lived and worked in Sands End
De Morgan and his wife, Evelyn. They lived and worked in Sands End Georgiana Burne-Jones and children by Edward Coley Burne-Jones. They lived in North End
Georgiana Burne-Jones and children by Edward Coley Burne-Jones. They lived in North End Henri Gaudier-Brzeska self-portrait
Henri Gaudier-Brzeska self-portrait Jill Craigie documentary maker was born in Fulham
Jill Craigie documentary maker was born in Fulham Janet Street-Porter grew up in Fulham
Janet Street-Porter grew up in Fulham Linford Christie in 2009. He attended Henry Compton School
Linford Christie in 2009. He attended Henry Compton School Daniel Radcliffe in 2009. He comes from Fulham
Daniel Radcliffe in 2009. He comes from Fulham
See also
- Metropolitan Borough of Fulham
- Counter's Creek
- Kensington Canal
- Lots Road Power Station
- West London Line
- West Brompton station
- Earls Court Exhibition Centre
- Sir John Scott Lillie
- Grade I and II* listed buildings in Hammersmith and Fulham
- Parks and open spaces in Hammersmith and Fulham
- Oxford and Cambridge Boat Race
Gallery
- Entrance to Fulham Broadway station
- Covered tankard made by Fulham Pottery, c. 1685-1690
- Cremorne Bridge, West London Extension Railway Bridge, towards Fulham
 Mulberries at Fulham Palace
Mulberries at Fulham Palace Tudor entrance to Fulham Palace kitchen garden
Tudor entrance to Fulham Palace kitchen garden vestige of 1826 canal bridge from Lillie Bridge, Fulham
vestige of 1826 canal bridge from Lillie Bridge, Fulham Corbett & McClymont's 1870 Carpentry workshop in Seagrave Road, Fulham
Corbett & McClymont's 1870 Carpentry workshop in Seagrave Road, Fulham Former Fulham County Court House in North End Road
Former Fulham County Court House in North End Road Parish Church of St John, Fulham
Parish Church of St John, Fulham- Fulham Town Hall entrance in Fulham Road
 Fulham Cemetery in Fulham Palace Road
Fulham Cemetery in Fulham Palace Road Pugin's St Thomas RC Church in Rylston Road, Fulham
Pugin's St Thomas RC Church in Rylston Road, Fulham London Overground at West Brompton in Fulham
London Overground at West Brompton in Fulham- Fulham House in Fulham High Street
 St Pauls' Studios, Talgarth Road
St Pauls' Studios, Talgarth Road- Imperial Wharf station western entrance 2
- Fulham Fire Station
 Market, North End Road, Fulham, London
Market, North End Road, Fulham, London- Kops Brewery, Sands End
 River Thames by Bishop's Park
River Thames by Bishop's Park
Bibliography
- The Fulham and Hammersmith Historical Society - [96] has a number of publications about the locality.
- Thomas Faulkner (1777-1855), An Historical and topographical account of Fulham; including the hamlet of Hammersmith . 1813. RCIN 1077212 See: retrieved 28 October 2016
References
- ↑ "Hammersmith and Fulham - UK Census Data 2011". Ukcensusdata.com. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- ↑ Kensington Canal: West Brompton to Olympia - http://londoncanals.uk/?p=7149 retrieved 6 October 2016
- ↑ Mayor of London (February 2008). "London Plan (Consolidated with Alterations since 2004)" (PDF). Greater London Authority.
- ↑ Denny, Barbara (1997). Fulham Past. London: Historical Publications. pp. 106–116. ISBN 0 948667 43 5.
- ↑ Route and Track diagrams for West Kensington and Lillie Bridge: http://www.trainweb.org/tubeprune/route%20and%20track%20diagrams.htm#West%20Kensington%20and%20Lillie%20Bridge retrieved 3 October 2016
- ↑ The Kensington Canal, railways and related developments Pages 322-338 Survey of London: Volume 42, Kensington Square To Earl's Court. Originally published by London County Council, London, 1986. http://www.british-history.ac.uk/survey-london/vol42/pp322-338#fnn61
- ↑ City A.M., Hot Property, 7 October 2016, 'Earl's Court on track for 7,500 new homes by 2030', p.26 CITYAM.COM
- ↑ http://www.fulhamfc.com/ retrieved 28 October 2016
- ↑ https://www.chelseafc.com/ retrieved 28 October 2016
- ↑ https://www.hurlinghamclub.org.uk/ retrieved 28 October 2016
- ↑ https://www.queensclub.co.uk/ retrieved 28 October 2016
- ↑ 'Sport, ancient and modern: Athletics', in A History of the County of Middlesex: Volume 2, General; Ashford, East Bedfont With Hatton, Feltham, Hampton With Hampton Wick, Hanworth, Laleham, Littleton, ed. William Page (London, 1911), pp. 301-302. British History Online http://www.british-history.ac.uk/vch/middx/vol2/pp301-302 [accessed 15 October 2016].
- ↑ 'Sport, ancient and modern: Cricket, Middlesex County', in A History of the County of Middlesex: Volume 2, General; Ashford, East Bedfont With Hatton, Feltham, Hampton With Hampton Wick, Hanworth, Laleham, Littleton, ed. William Page (London, 1911), pp. 270-273. British History Online http://www.british-history.ac.uk/vch/middx/vol2/pp270-273 [accessed 15 October 2016]
- ↑ Walford, Edward. Fulham: Introduction, in Old and New London: Volume 6 (London, 1878), pp. 504-521. British History Online http://www.british-history.ac.uk/old-new-london/vol6/pp504-521 [accessed 23 October 2016].
- ↑ Denny, Barbara (1997). Fulham Past. London: Historical Publications. pp. 35–39. ISBN 0 948667 43 5.
- ↑ Wilkins, F.H. (1905) Mrs Fitzherbert and George IV, London: Longman and Green. p.23 https://archive.org/stream/mrsfitzherbertge02wilkiala/mrsfitzherbertge02wilkiala_djvu.txt
- ↑ Faulkner, Thomas. (1813) ‘Historical and Topographical Account of the parish of Fulham, including the hamlet of Hammersmith’
- ↑ Old Ordnance Survey Maps Hammersmith & Fulham 1871, The Godfrey Edition, Consett: Alan Godfrey Maps
- ↑ "North Thames Gas". Sands End Revisited. Retrieved 27 June 2011.
- ↑ "Name: Number 2 Gasholder, Fulham Gas Works". The National Heritage List for England. English Heritage. Retrieved 28 June 2011.
- ↑ https://www.rbkc.gov.uk/wamdocs/BromptonCemeterypp_10_15.pdf
- ↑ "Tregunter - Capture Burnham".
- 1 2 "The Kensington Canal, railways and related developments - British History Online".
- ↑ Denny, Barbara (1997). Fulham Past. London: Historical Publications. p. 69. ISBN 0 948667 43 5.
- ↑ Denny, Barbara (1997). Fulham Past. London: Historical Publications. pp. 128–9. ISBN 0 948667 43 5.
- ↑ Féret, Charles (1900). Fulham Old and New, vol.I-III (PDF). III. Leadenhall Press.
- ↑ Cherry, Bridget and Nikolaus Pevsner "The Buildings of England. London 3: North West." Yale University Press. p. 249. ISBN 0-14-071048-5.
- ↑ Lowndes & Drury, stained glass workers: records. Archives hub. Retrieved 12 September 2012.
- ↑ http://adamaaronson.com/about-adam-aaronson/ retrieved 22 October 2016
- ↑ Art Bronze Foundry London Ltd. http://www.artbronze.co.uk/3.html accessed 22 October 2016.
- ↑ Charles Booth Poverty Map of London: London School of Economics Archives http://booth.lse.ac.uk/cgi-bin/do.pl?sub=list_parishes_by_deanery&arg0=Fulham
- ↑ Western Fever Hospital, Fulham, http://www.workhouses.org.uk/MAB-WFever/ retrieved 6 October 2016
- ↑ Western Hospital, Fulham, http://www.nationalarchives.gov.uk/hospitalrecords/details.asp?id=134 retrieved 6 October 2016
- ↑ 'Lost Hospitals of London' - Western: http://ezitis.myzen.co.uk/western.html, retrieved 6 October 2016
- ↑ A photograph of the maltings at Swan Wharf, https://historicengland.org.uk/services-skills/education/educational-images/swan-wharf-fulham-london-r7-13
- ↑ Photograph of Rolls' Lillie Hall car showroom http://www.scienceandsociety.co.uk/results.asp?image=10316386&cs=tJ~GpjmmK~WDyrs&pb=Cars&themex=51
- ↑ The Gentleman's Magazine: and Historical Chronicle. For the YEAR MDCCXCV. Volume LXV, Part the first. London. p. 344
- ↑ "Aviation Pioneer". rafmuseum.org.uk.
- ↑ Pearson, Lynn. (1990) British Breweries: An Architectural History, London: Bloomsbury Publishing. p. 60
- ↑ "ELGAR - The Elgar Trail".
- ↑ Costello, Elvis. (2015) Unfaithful Music & Disappearing Ink- a memoir
- ↑ "House Prices Report for SW6 – February 2013 to February 2014". home.co.uk. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ↑ Hill, Dave. (2016) Earls Court - Uncertain times for landmark London regeneration, Guardian newspaper: https://www.theguardian.com/uk-news/davehillblog/2016/jul/05/earls-court-uncertain-times-for-landmark-london-regeneration-scheme
- ↑ Carmichael, Sri (22 January 2010). "On the Bill: Earls Court Demolished To Make Way for 8,000 Flats". London Evening Standard. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
- ↑ Hatcher, David (19 June 2009). "Olympian Effort". Property Week. Retrieved 5 August 2012.
- ↑ Watts, Joseph (23 May 2014). "Labour take control of Hammersmith and Fulham council amid gains across London". The Evening Standard. Retrieved 13 September 2015.
- ↑ http://www.hurlinghamclub.org.uk/ Official website
- 1 2 Millar, William (2016). Plastering: Plain and Decorative. London: Routledge. p. 83. ISBN 978-1-873394-30-4.
- ↑ Hammersmith and Fulham entry in https://content.historicengland.org.uk/images-books/publications/played-in-london-directory-sporting-assets-london/DirectoryofHistoricSportingAssetsinLondon.pdf/ 4.19, p. 66.[accessed 24 October 2016]
- ↑ Empress Hall , Fulham: http://www.arthurlloyd.co.uk/EmpressHall.htm Retrieved 28 October 2016
- ↑ Aerial view of Empress Hall in 1937 http://www.britainfromabove.org.uk/image/epw055910 Retrieved 28 October 2016
- ↑ https://www.lbhf.gov.uk/planning/planning-applications/major-planning-applications/earls-court-planning-application Retrieved 15 January 2014
- ↑ "Save Earl's Court! – Home". Saveearlscourt.com. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ↑ http://www.arthurlloyd.co.uk/FulhamTheatres.htm Retrieved 28 October 2016
- ↑ Denny, Barbara (1997). Fulham Past. London: Historical Publications. p. 117. ISBN 0 948667 43 5.
- ↑ "Fulham Opera".
- ↑ "MUSIC".
- ↑ "The Advertising Archives - Magazine Advert - Dickie Dirts - 1980s".
- ↑ 'Industries: Brewing', in A History of the County of Middlesex: Volume 2, General; Ashford, East Bedfont With Hatton, Feltham, Hampton With Hampton Wick, Hanworth, Laleham, Littleton, ed. William Page (London, 1911), pp. 168-178. British History Online http://www.british-history.ac.uk/vch/middx/vol2/pp168-178 [accessed 8 November 2016].
- ↑ Amies, Chris. (2004) Images of London: Hammersmith and Fulham Pubs www.pubhistorysociety.co.uk/Hammersmith.html Published by Tempus Publications, ISBN 978-0752432533
- ↑ Féret, Charles. (1900) Fulham Old and New, volume II, p. 271-3.
- ↑ "London (part two) | Special reports | The Observer". Observer.guardian.co.uk. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ↑ UK Pub history and historical street directory of London and the UK, http://pubshistory.com/LondonPubs/Fulham/
- ↑ Lovibond's Cannon Brewery, North End, Fulham, http://www.heritage-explorer.co.uk/web/he/searchdetail.aspx?id=11712
- ↑ "Broom House Dock - Guide to London's Georgian Thames".
- ↑ Hammersmith and Fulham Historic Buildings Group, 2004, Local List. Ed. Angela Dixon, Fourth Edition revised September 2004
- ↑ That's Life! at the Internet Movie Database
- ↑ Historic England listing for Fulham Cross School: https://historicengland.org.uk/listing/the-list/list-entry/1393344
- ↑ James Tiplady, Ibis Design. "The Lillie Road Association › Representing the antiques shops of the Lillie Road, London". Lillieroad.co.uk. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- ↑ Thomas Crofton Croker (1860). A walk from London to Fulham. W. Tegg. pp. 187–188. Retrieved 1 December 2015.
- ↑ Denny, Barbara (1997). Fulham Past. London: Historical Publications. p. 72. ISBN 0 948667 43 5.
- ↑ "Chelsea & Fulham". Disused Stations. Subterranea Britannica. Retrieved 31 July 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 "Fulham | British History Online". British-history.ac.uk. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- ↑
- Archer, Ian (2004). "Warren, Sir Ralph (c.1483–1553)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (online ed.). Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/28787. (Subscription or UK public library membership required.)
- ↑ Denny, Barbara. (1997) Fulham Past, London: Historical Publications, p.77-78, ISBN 0 948667 43 5
- ↑ "Sandford Manor | British History Online". British-history.ac.uk. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- ↑ "Full text of "Francesco Bartolozzi, R. A"". Archive.org. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- ↑ "Parsons Green". Hidden London. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- ↑ "Granville Sharp: biography and bibliography". Brycchancarey.com. 3 March 2014. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- ↑ "Court Register". 12 October 2013.
- 1 2 David Goold. "Dictionary of Scottish Architects - DSA Architect Biography Report (October 2, 2016, 2:43 pm)". Scottisharchitects.org.uk. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- ↑ "TOMB OF BURCHELL FAMILY INCLUDING WILLIAM BURCHELL, LOCATED APPROXIMATELY 2M FROM THE SOUTH ELEVATION OF ALL SAINTS CHURCH - 1393343". Historic England. 1 July 2009. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- ↑ "The Flower Book by Edward Burne-Jones | LBHF Libraries". Lbhflibraries.wordpress.com. 22 June 2016. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- ↑ Bennett, David. "A brief history of the Macdonald sisters". Retrieved 20 November 2012.
- ↑ "Evelyn De Morgan". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (online ed.). Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/45491. (Subscription or UK public library membership required.)
- ↑ "William De Morgan and the Arts & Crafts Movement". Antique Marks. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- ↑ Dewe, Michael. (1972) Fulham's Historian - Charles Féret, published by Fulham and Hammersmith Historical Society, 42 pages.
- ↑ "Hackman: St Sepulchre's Cemetery, Oxford". Stsepulchres.org.uk. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- ↑ Féret, Charles (1900) Fulham Old and New vol. II, p. 179.
- ↑ Pound. Ezra (1916). "Gaudier-Brzeska, a memoire". Retrieved 11 October 2016.
- ↑ Denyse Lynde. "Playwright Michael Cook". Heritage.nf.ca. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- ↑ "Example: Sing When You're Winning". FourFourTwo. 27 May 2010. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- ↑ "The complete guide to living in Fulham". Snellandsnell.co.uk. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- ↑ "John Osborne". Telegraph. 27 December 1994. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- ↑ Isabelle Fraser (6 June 2016). "Daniel Radcliffe's childhood home up for sale... complete with a cupboard under the stairs". Telegraph.co.uk. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- ↑ "Publications". 3 January 2008.
External links
![]() London/Hammersmith and Fulham travel guide from Wikivoyage
London/Hammersmith and Fulham travel guide from Wikivoyage
- https://lbhflibraries.wordpress.com/2015/04/09/the-panorama-of-the-thames/
- https://www.historicengland.org.uk/services-skills/education/educational-images/?place=Fulham 'Educational images'
- FulhamSW6.com Local news and information for the Fulham area
- BBC Guide to Hammersmith, Fulham and Chiswick
- Fulham & Hammersmith Historical Society
- London Borough of Hammersmith & Fulham
- The Borough Guide from the Borough Council
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Fulham. |
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "article name needed". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "article name needed". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.

